A novel cationic lipid, a preparation method of the same and a delivery system comprising the same
A cationic lipid and delivery system technology, which can be used in other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, endocrine system diseases, cardiovascular system diseases, etc., can solve the problems of reduced inherent physiological activity of proteins, and achieve increased intracellular delivery and enhanced Efficiency, cytotoxicity reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
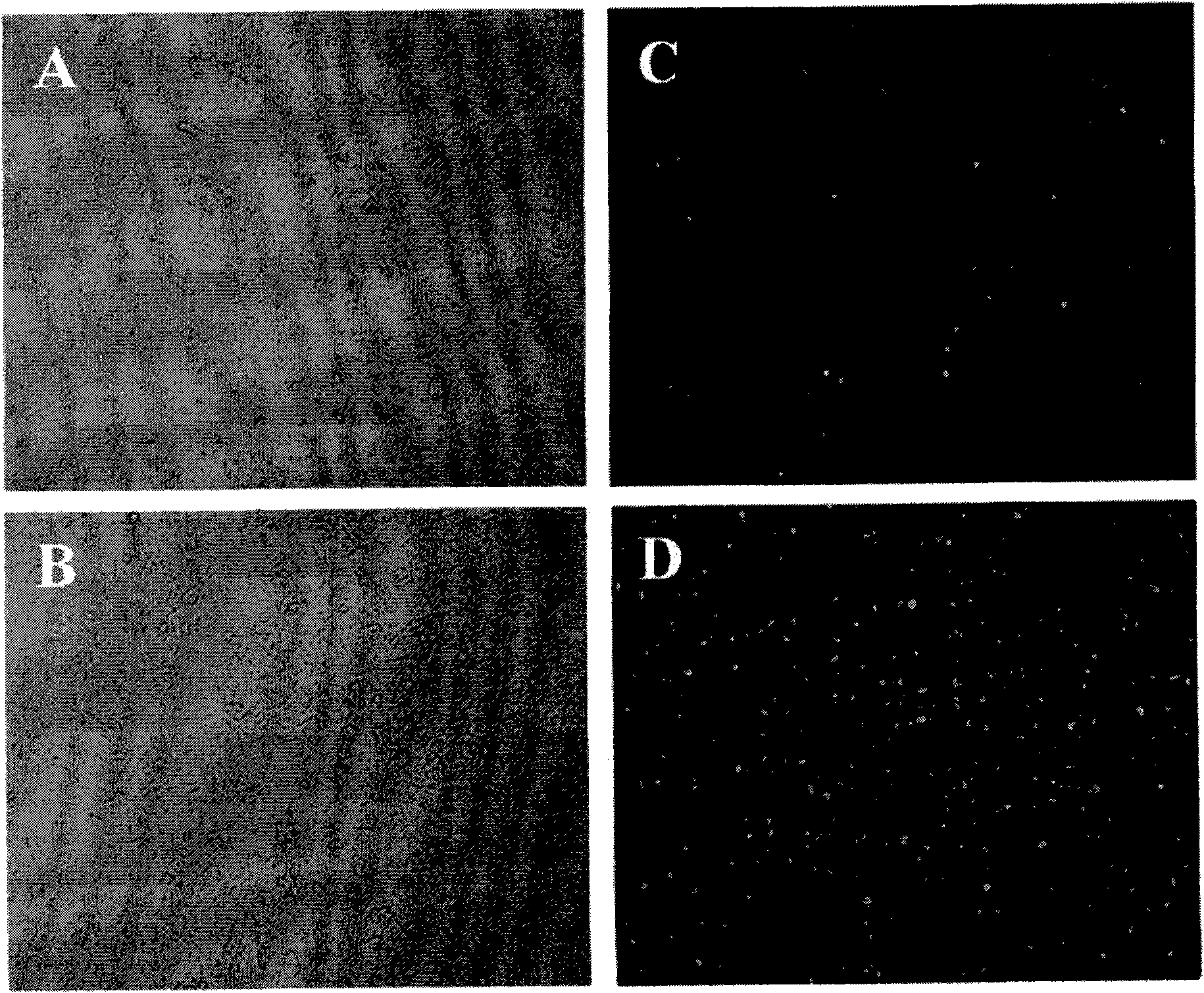
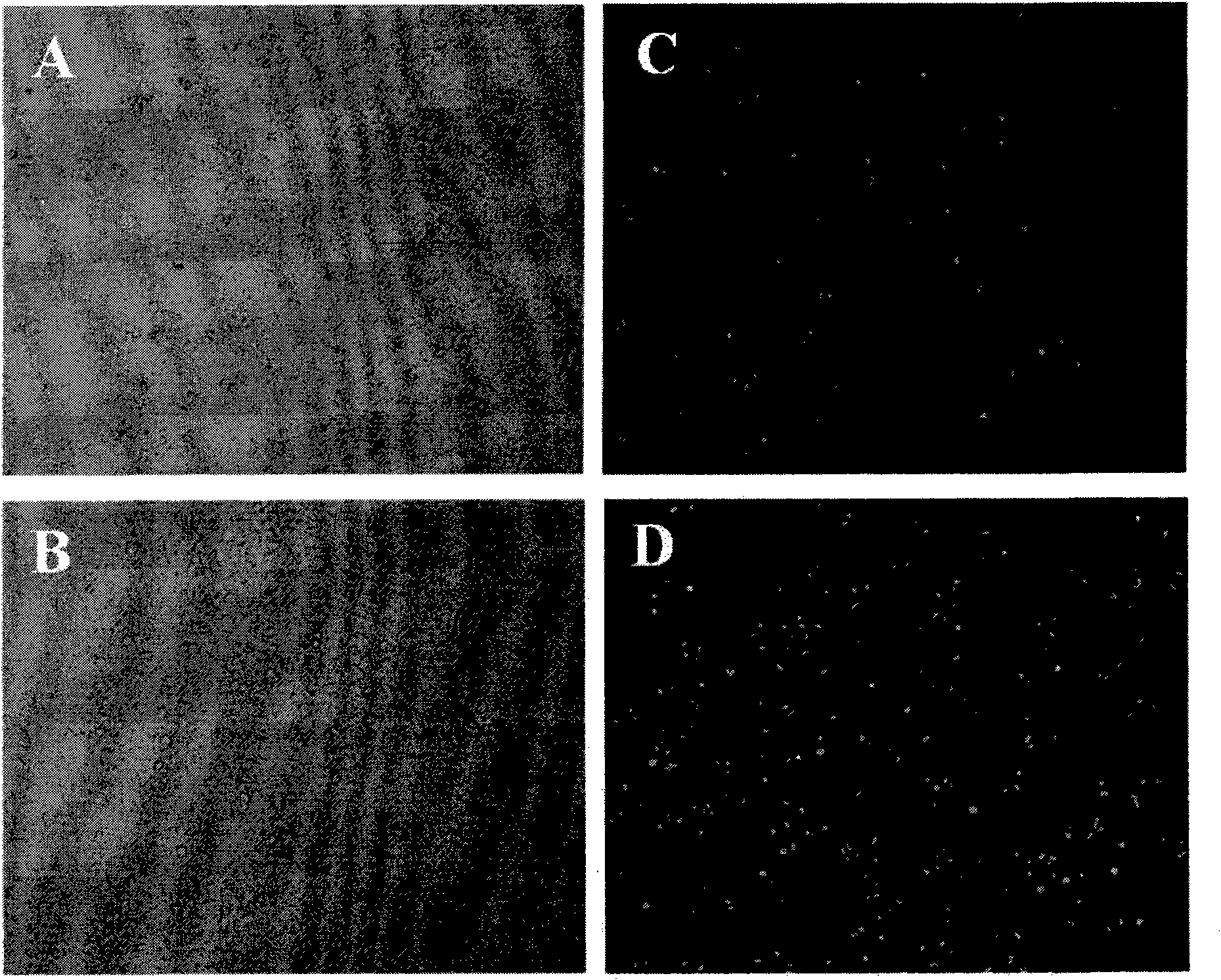
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
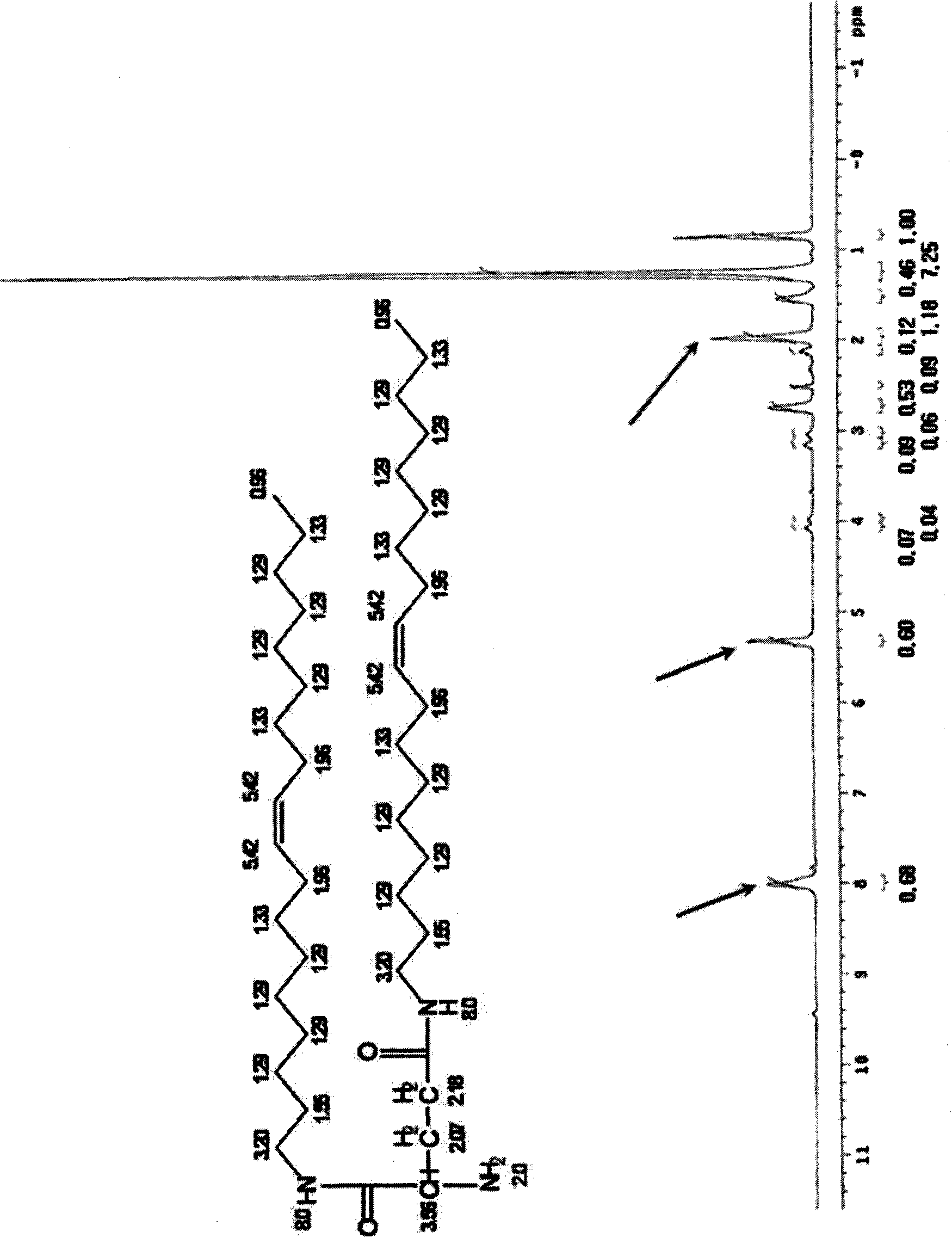
[0071] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of dioleoyl glutamine (dioleoyl glutamide)
[0072] 1-1) 1 equivalent (1.47 g, 10 mmol) of glutamic acid was added to 5 mL of trifluoroacetic acid and 5 mL of dichloromethane, and the resulting mixture was stirred at 40° C. for 1 hour. Then, 3 equivalents (2.18mL, 30mmol) of SOCl 2 Slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution in an ice bath, followed by reaction at 0-40°C for 6 hours. After the reaction was completed, trifluoroacetic acid and dichloromethane were removed by concentration under reduced pressure, and the reaction was confirmed by thin layer chromatography (TLC).
[0073] 1-2) The reaction product obtained in Example 1-1 was dissolved in dichloromethane, and 1.5 equivalents (4.01 g, 15 mmol) of oleylamine dissolved in dichloromethane was slowly added dropwise thereto. The mixture was stirred in an ice bath for 1 hour, 3 mL of triethylamine was added dropwise thereto, followed by reaction at a temperature of 0-50° C. for 4 ...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of dimyristoyl glutamine (dimyristoyl glutamide)
[0083] 2-1) Similar to Example 1-1, 2 equivalents of glutamic acid were used for reaction to obtain glutamic acid derivatives.
[0084] 2-2) The reaction product obtained in Example 2-1 was dissolved in dichloromethane. Similar to Example 1-2, 1.5 equivalents (3.20 g, 15 mmol) of myristylamine were subsequently used for the reaction. The product (3.22 g, yield: 85.7%) was obtained as a beige solid, which was subjected to structural analysis using a 1H NMR spectrophotometer.
[0085] 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6 , ppm): 8.0 (1H, -NH-CO of glutamic acid and tetradecylamine)
[0086] 2.0 (2H, -NH of glutamic acid 2 )
[0087] 1.29 (2H, -CH of tetradecylamine 2 -)
[0088] The reaction process of Example 2 is shown in Reaction Formula 2 below.
[0089] [Reaction 2]
[0090]
[0091] In Reaction 2, R 1 and R 2 independently is C 14 - saturated hydrocarbons.
Embodiment 3
[0092] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of dipalmitoyl glutamine (dipalmitoyl glutamide)
[0093] 3-1) Similar to Example 1-1, 2 equivalents of glutamic acid were used for reaction to obtain glutamic acid derivatives.
[0094] 3-2) The reaction product obtained in Example 3-1 was dissolved in dichloromethane. Similar to Example 1-2, 1.5 equivalents (3.62 g, 15 mmol) of palmitylamine were subsequently used for the reaction. The product (3.74 g, yield: 90.1%) was obtained as a beige solid, which was subjected to structural analysis using a 1H NMR spectrophotometer.
[0095] 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6 , ppm): 8.0 (1H, palmitamine / CH 2 Cl 2 Amine -NH-CO)
[0096] 2.0 (2H, -NH of glutamic acid 2 )
[0097] 1.29 (2H, -CH of palmitamine 2 -)
[0098] The reaction process of Example 3 is shown in Reaction Formula 3 below.
[0099] [reaction formula 3]
[0100]
[0101] In Equation 3, R 1 and R 2 independently is C 16 - saturated hydrocarbons.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com