Semiconductor light-emitting element and method of manufacturing the same
A light-emitting element and manufacturing method technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor lasers, electrical components, laser components, etc., can solve the problem of high contact resistance, increase in operating voltage of semiconductor light-emitting elements, reduction of contact area between p-type contact layer and p-side electrode, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of increasing the contact area and lowering the operating voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
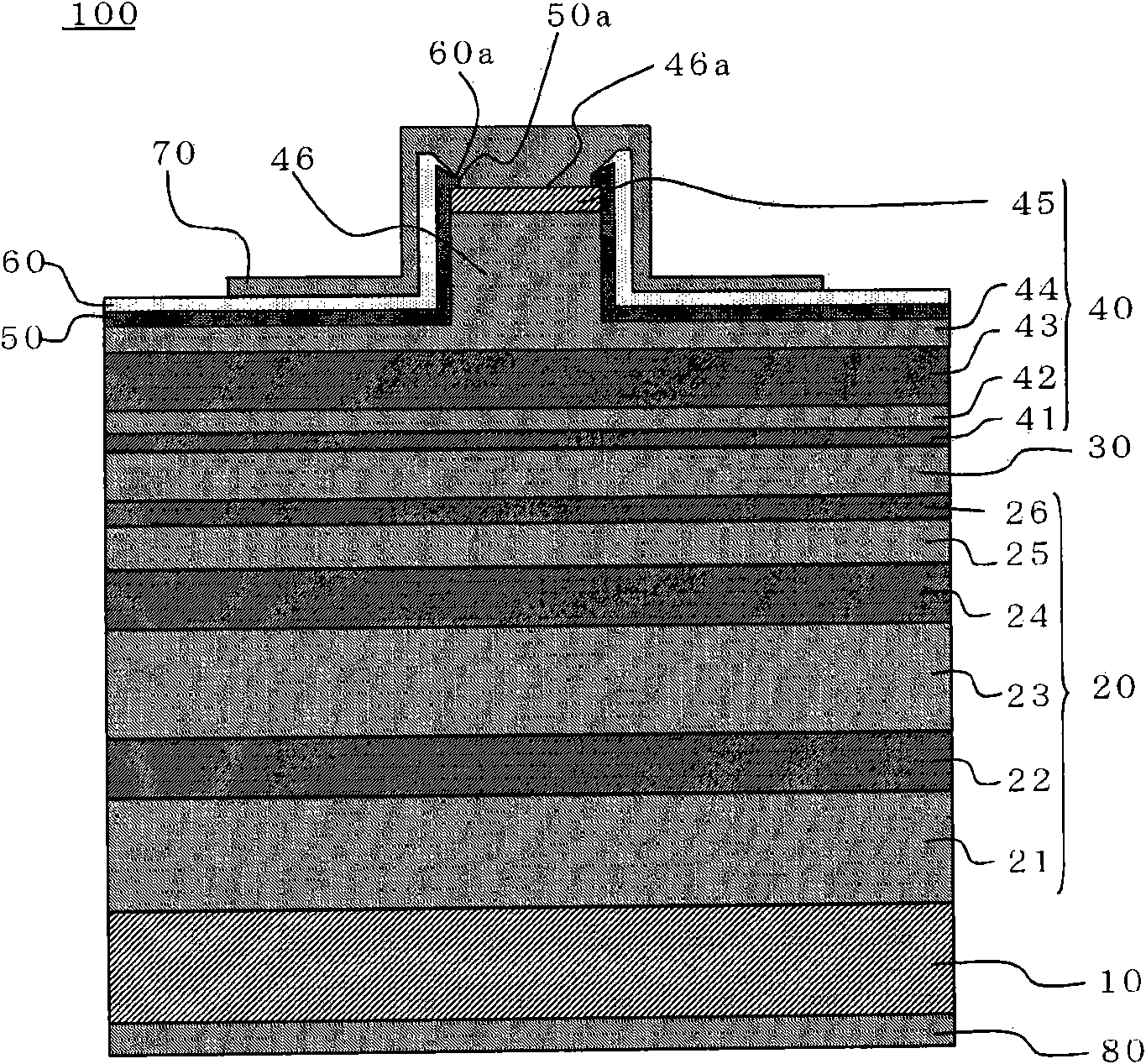
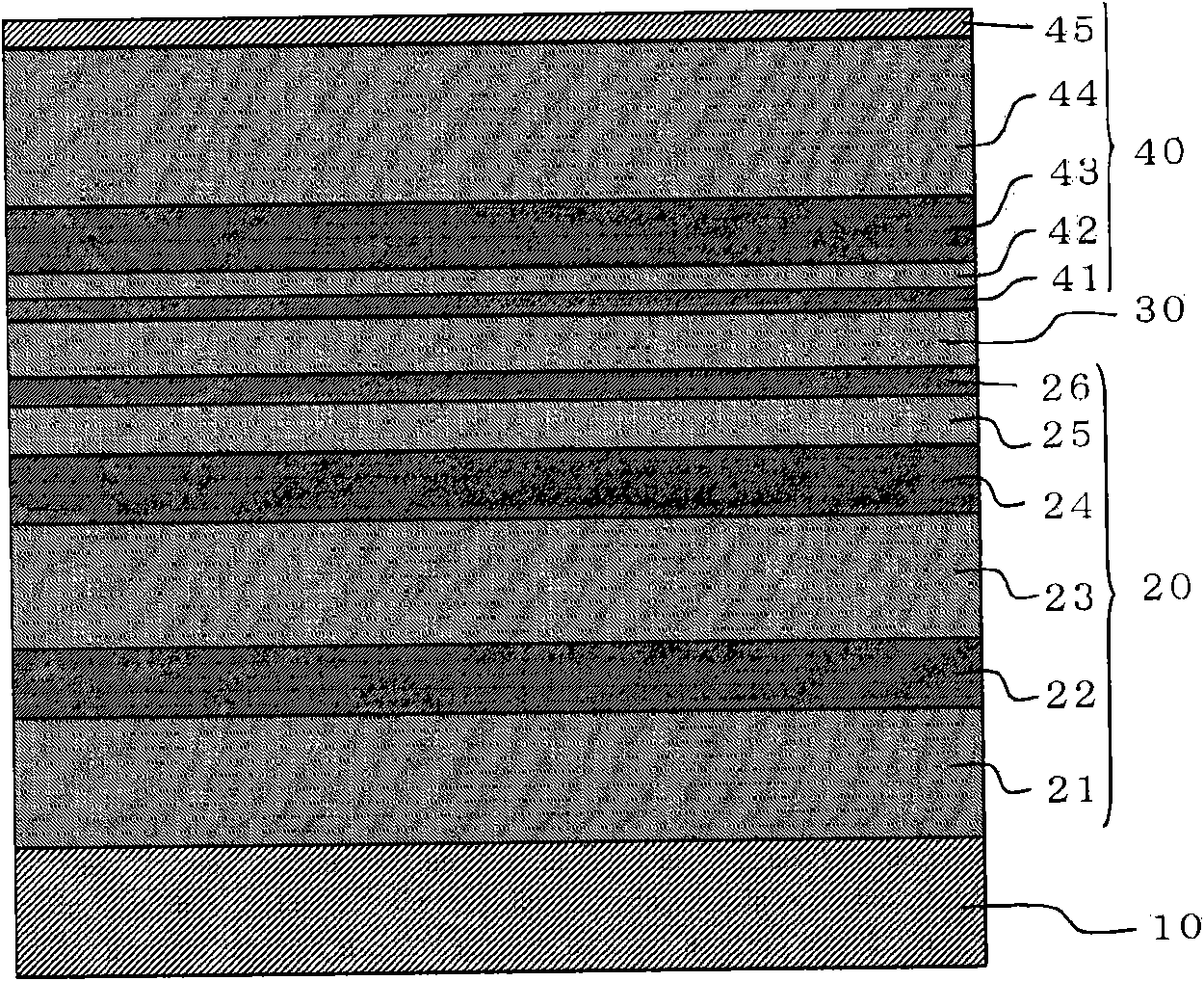
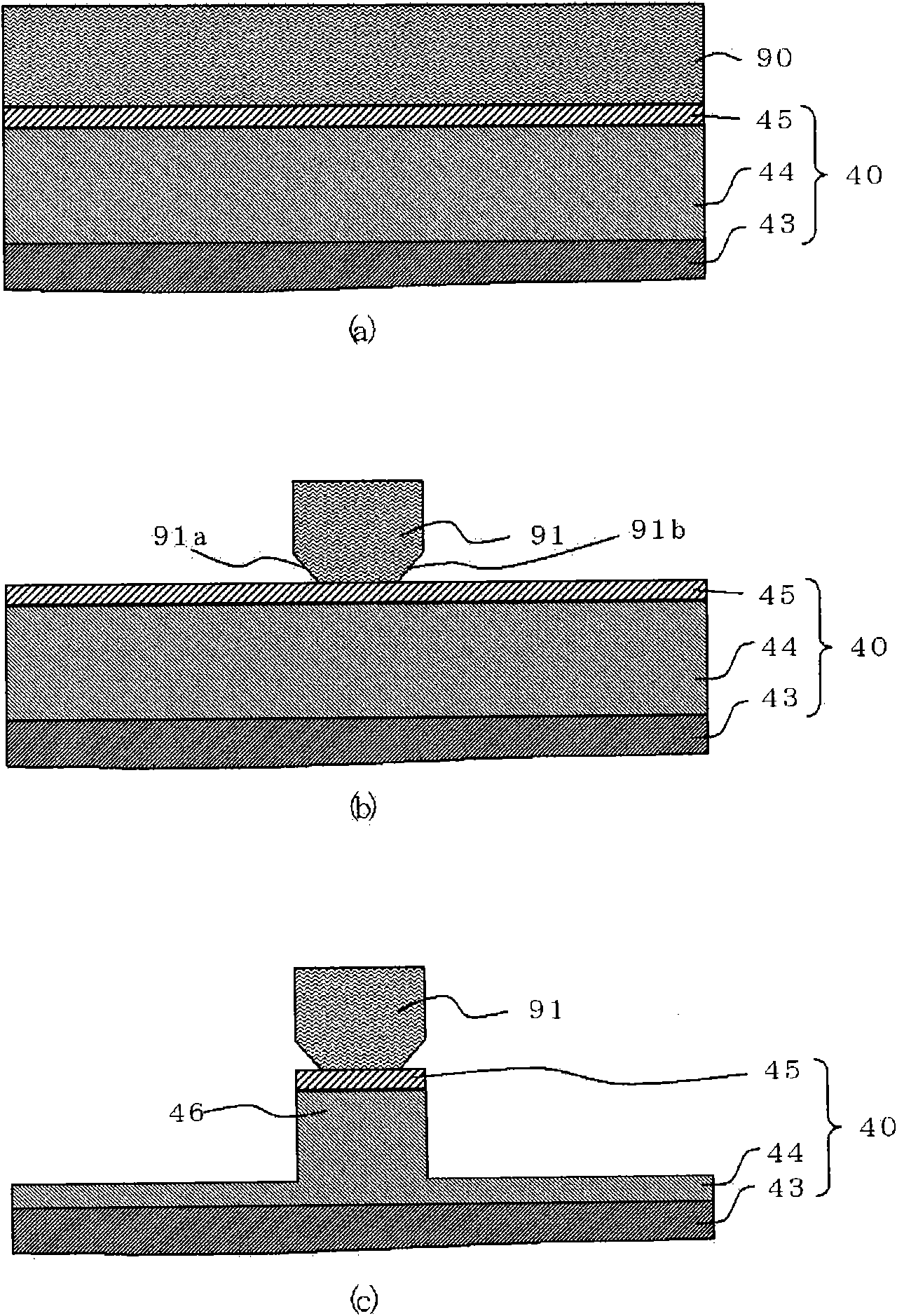
[0033] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view illustrating the structure of the semiconductor light emitting element in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, Figure 2 ~ Figure 6 It is a cross-sectional view illustrating a method of manufacturing a semiconductor light emitting element in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0034] First, refer to figure 1 The structure of the semiconductor light emitting element in Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0035] figure 1 In the semiconductor laser element 100 as a semiconductor light emitting element, on an n-type GaN substrate 10, as an n-type (first conductivity type) semiconductor layer 20, an n-type GaN buffer layer 21 with a layer thickness of 1000 nm, a layer thickness 400nm n-type Al 0.07 Ga 0.93 N-clad 22, n-type Al with a layer thickness of 1000nm 0.045 Ga 0.955 N-clad layer 23, n-type Al with a layer thickness of 300nm 0.015 Ga 0.985 N-clad layer 24, n-type GaN light guide layer 25 with a layer thickness of ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0081] Figure 7 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the semiconductor light emitting element in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In the semiconductor light-emitting element in Embodiment 1, the metal film 60 is formed of a single-layer metal film, but in the semiconductor light-emitting element in Embodiment 2, the metal film 60 is formed of multiple metal films.
[0082] Figure 7 In the second embodiment, the metal film 60 provided on the semiconductor laser device 200 which is a semiconductor light-emitting device in the second embodiment is formed by the first metal film 61 provided in contact with the p-side electrode 70 made of Pd and the first metal film 61 made of SiO. 2 The second metal film 62 formed in contact with the insulating film 50 is formed in two layers. Here, the first metal film 61 is formed of Au, and the second metal film 62 is formed of Cr or Ti. Except for these points, the semiconductor laser element 200 in the second embod...
Embodiment approach 3
[0089] Figure 8 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the semiconductor light emitting element in Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0090] Figure 8 In the semiconductor laser element 300 which is a semiconductor light-emitting element in the third embodiment, the opening width of the first opening 50 a provided in the insulating film 50 is set to be wider than the opening width of the second opening 60 a provided in the metal film 60 . Wide. Except for this point, the semiconductor laser element 300 has the same structure as the semiconductor laser element 100 of the first embodiment.
[0091] In addition, in the semiconductor structural element 300 , the steps other than the insulating film etching step described later are the same steps as those shown in Embodiment 1, and therefore description thereof will be omitted.
[0092] In the insulating film etching process, using the metal film 60 as a mask, dry etching or wet etching is performed by SiO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com