Quenching agent
A technology of quenching agent and defoaming agent, applied in the direction of quenching agent, heat treatment equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of low flash point of mineral oil, easy environmental pollution, unsafe use, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
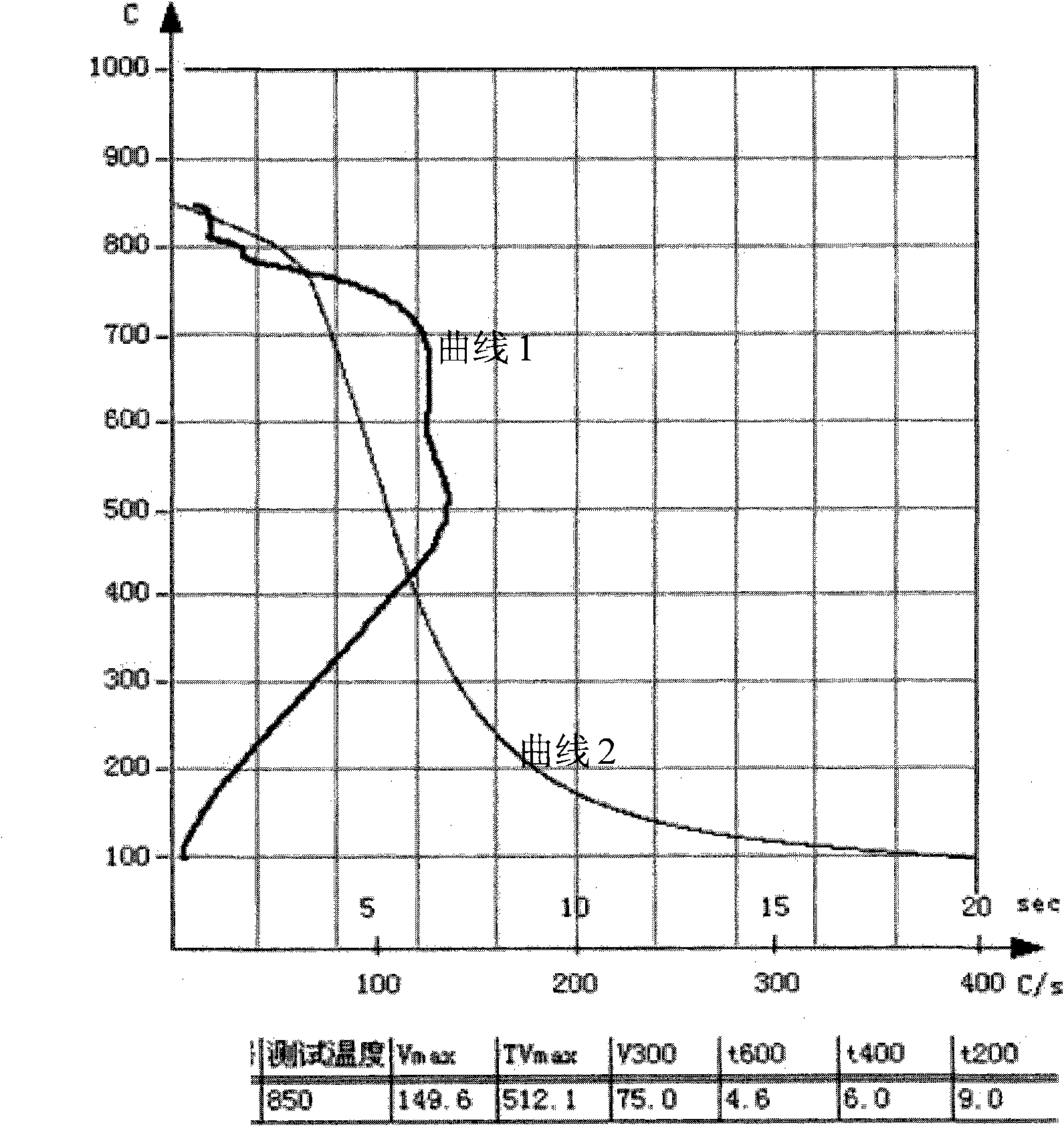
[0041] The quenching agent provided in this embodiment includes, by weight percentage, 40 parts by weight of PB-140 polyether, 1 part by weight of triethanolamine, 1 part by weight of sodium benzoate, 0.05 parts by weight of 5674 defoamer, 57.95 parts by weight of deionized water. Dilute the quenching agent provided by this embodiment 1 with 1900 parts by weight of water to a concentration of 5wt%, the flash point is non-flammable, and the cooling curve test results are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0042] figure 1 Among them, curve 1 is the cooling rate curve, curve 2 is the cooling time curve, and the test temperature starts from 850°C. From figure 1 It can be seen that, as shown in curve 1, the quenching agent provided by the present invention is in the high temperature region above 400°C, the maximum cooling rate Vmax is 149.6°C / S, and the corresponding cooling temperature TVmax is 512.1°C at this time, that is to say, the quenching agent The agent medium has a high c...
Embodiment 2
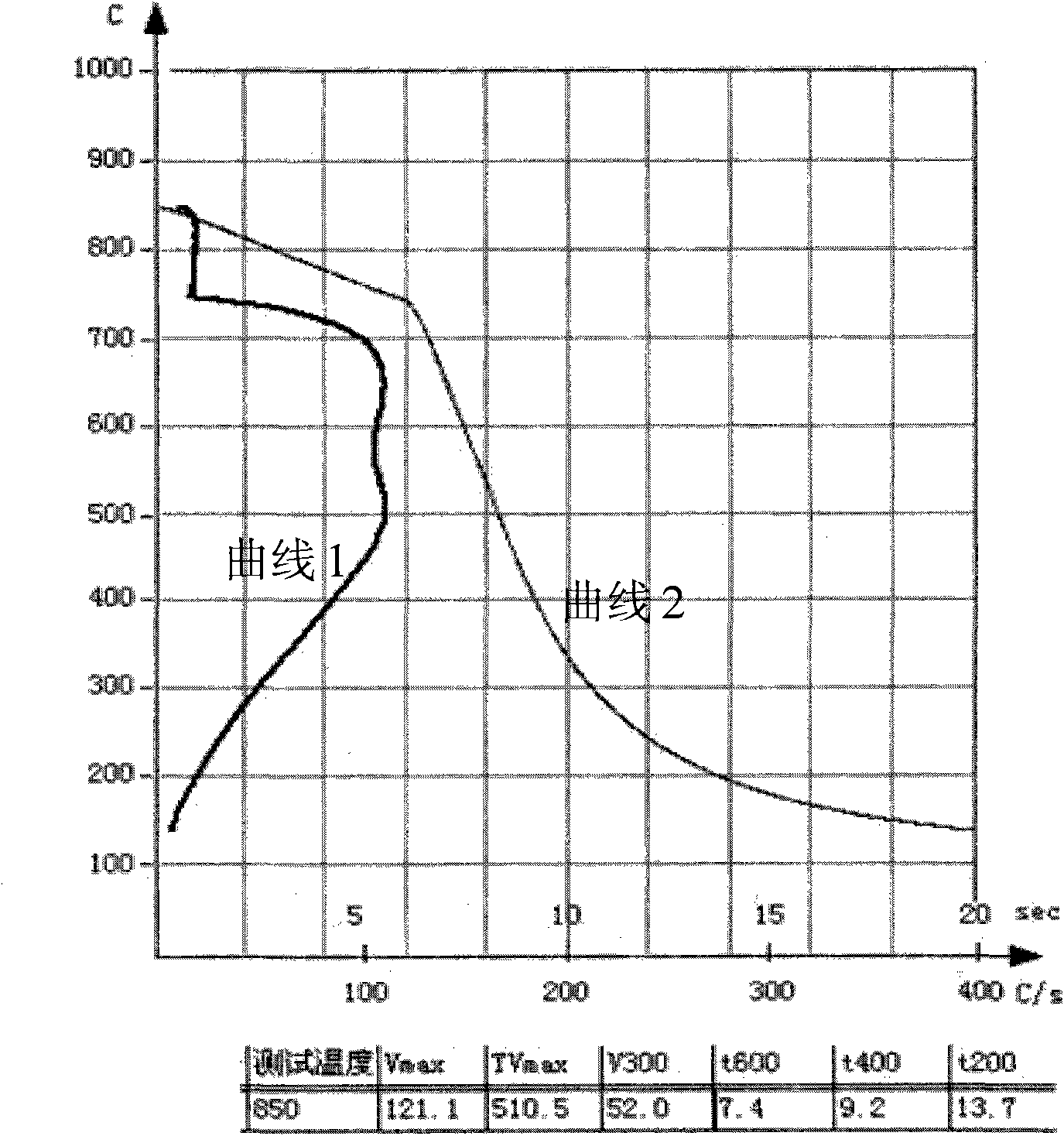
[0045]The quenching agent provided in this embodiment includes, by weight percentage, 30 parts by weight of PB-560 polyether, 5 parts by weight of triethanolamine, 0.2 parts by weight of sodium benzoate, 0.3 parts by weight of 5674 defoamer, 64.5 parts by weight of deionized water. Dilute the quenching agent provided by this embodiment with 900 parts by weight of water to a concentration of 10wt%, the flash point is non-flammable, and the cooling curve test results are as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0046] figure 2 Among them, curve 1 is the cooling rate curve, curve 2 is the cooling time curve, and the test temperature starts from 850°C. From figure 2 It can be seen that, as shown in curve 1, the quenching agent provided by the present invention is in the high temperature region above 400°C, the maximum cooling rate Vmax is 121.1°C / S, and the corresponding cooling temperature TVmax is 510.5°C at this time, that is to say, the quenching agent The agent medium has a high...
Embodiment 3
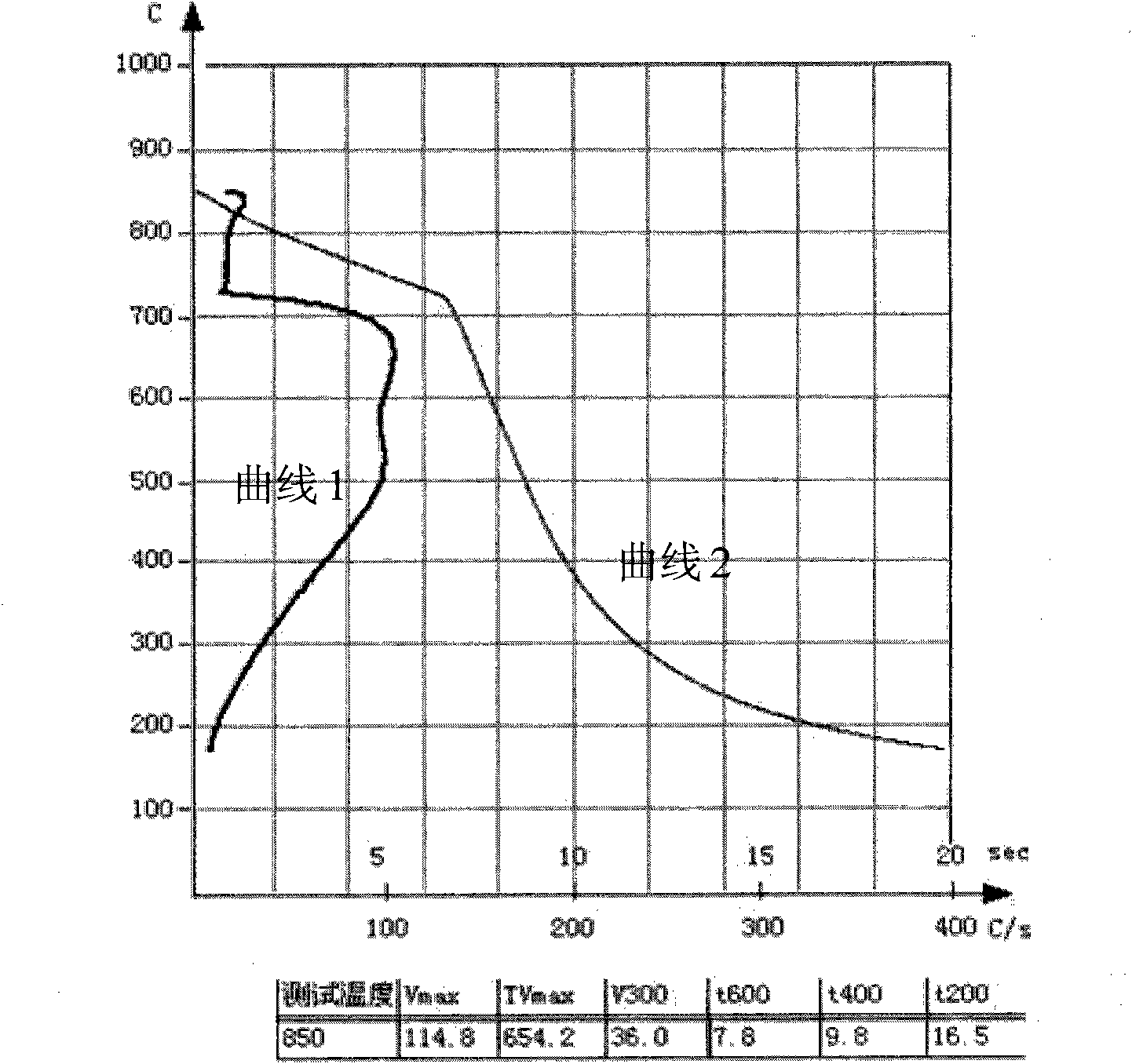
[0049] The quenching agent provided in this embodiment includes, by weight percentage, 43.5 parts by weight of PB-560 polyether, 6 parts by weight of triethanolamine, 1.2 parts by weight of sodium benzoate, 0.2 parts by weight of 5674 defoamer, 99.1 parts by weight of deionized water. Dilute the quenching agent provided by this embodiment with 850 parts by weight of water to a concentration of 15wt%, the flash point is non-flammable, and the cooling curve test results are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0050] image 3 Among them, curve 1 is the cooling rate curve, curve 3 is the cooling time curve, and the test temperature starts from 850°C. From image 3 It can be seen that, as shown in curve 1, the quenching agent provided by the present invention is in the high temperature region above 400°C, the maximum cooling rate Vmax is 114.8°C / S, and the corresponding cooling temperature TVmax is 654.2°C at this time, that is to say, the quenching agent The agent medium has a high...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com