Fusion proteins of mannose binding lectins for treatment of disease
A fusion protein and lectin technology, which is applied in the field of mannose-binding lectin fusion proteins for the treatment of diseases, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory induction of immune response and antibody generation, and harmful vaccine effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0108] Preparation of fusion protein
[0109] The fusion protein of the present invention can be expressed in any suitable standard protein expression system by culturing a host transformed with a vector encoding the fusion protein under conditions capable of expressing the fusion protein. Preferably, the expression system is one in which the desired protein can be easily isolated and refolded in vitro. In general, prokaryotic expression systems are preferred because of higher protein yields and efficient purification and refolding strategies. Accordingly, selection of appropriate expression systems, including vectors and cell types, is within the purview of those skilled in the art. Likewise, once the original amino acid sequence for a fusion protein of the present invention is selected, one skilled in the art can take into account factors such as codon bias in the selected host, the need for a secretory signal sequence in the host, and protease cleavage sites within the sig...
Embodiment 1
[0124] Example 1: Construction and expression of labeled and unlabeled MBP-CD 209 CTLD fusion protein expression plasmid clones in HEK293 cells
[0125] DC-SIGN (dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 binding non-integrin) is a type II transmembrane protein belonging to the C-type lectin family. This protein is expressed peripherally on the surface of dendritic cells (DCs) and is involved in the initial contact between antigen presenting cells and resting T cells in the lymphatic system through ICAM-3 on T cells. DC-SIGN also interacts with ICAM-2 on epithelial cells during DC migration to lymphoid tissues. DC-SIGN also strongly binds to the HIV envelope protein gp120 and promotes viral infection in trans CD4+ T cells. The DC-Sign protein consists of a short amino-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a transmembrane domain, a stalk of up to 71 / 2 repeats, followed by a C-terminal C-type carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). The stem promotes the formation of tetramers (coiled coils). DC-SIGN...
Embodiment 2
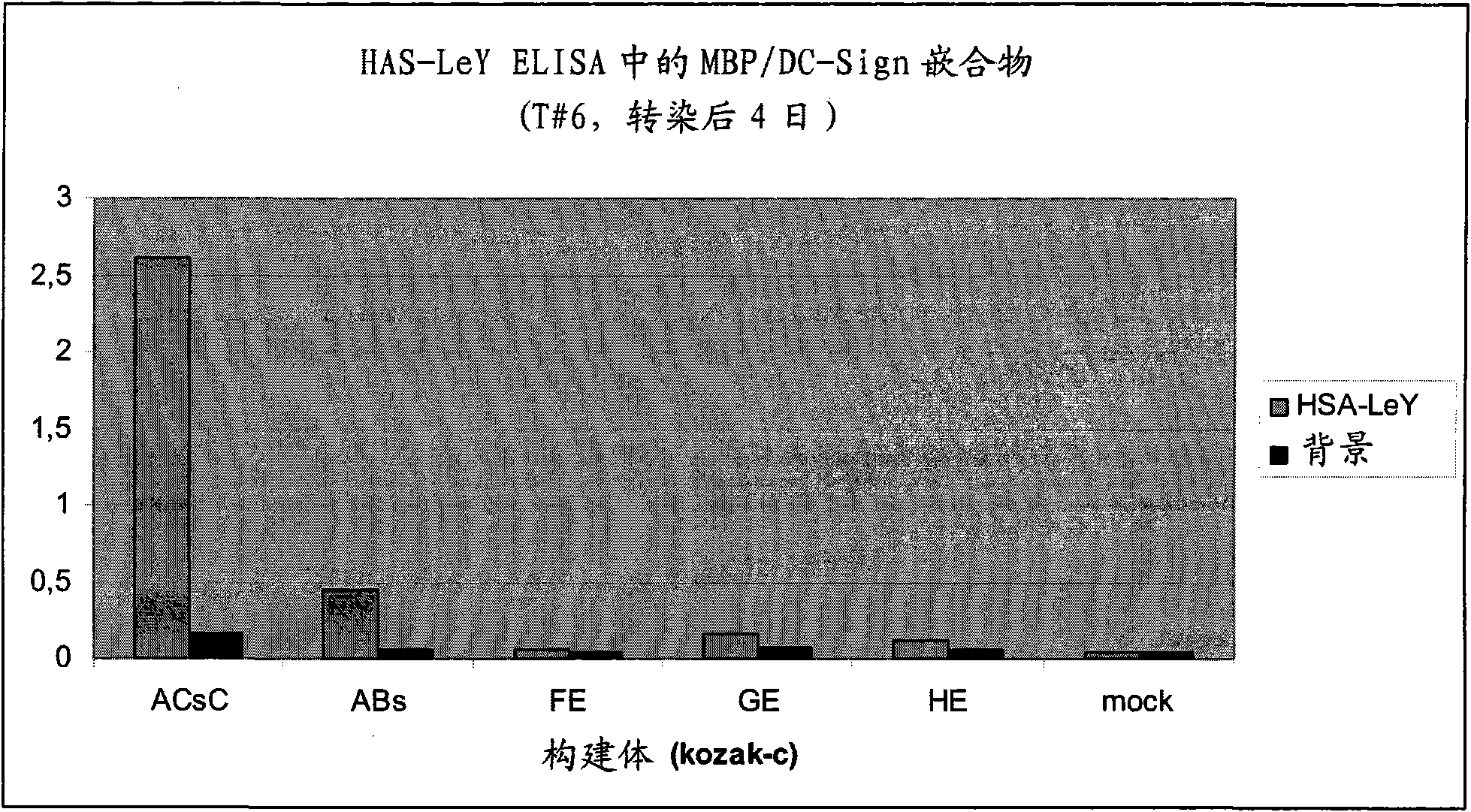
[0131] Example 2: with immobilized HSA-Le y or Le of cells expressing the human breast cancer cell line SKBR-3 y Analysis of Bound Various Tagged MBP-CD209CTLD Fusion Proteins
[0132] After 4 days of transient expression, expression plasmids from MBP / DC-SIGN CTLD with markers (pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-Abs, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-ACs, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-ADs, pMBP / DC -SIGN CTLD-ABsC, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-ACsC, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-ADsC, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-FE, pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-GE, and pMBP / DC-SIGN CTLD-HE ) transfected HEK293 cell culture supernatants were analyzed for their binding to immobilized Le y or expressing Le of the human breast cancer cell line SKBR-3 y Ability. The MBP / DC-SIGN CTLD Abs and MBP / DC-SIGN CTLD AbsC fusion proteins were also tested for their binding to MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, LNCap prostate cancer cells, and A431 skin epithelial squamous cell carcinoma cells ability.
[0133] In the first test, 0.5 μg Le in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl) y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com