Amphipathic chitosan with chemical crosslinking characteristic and preparation method thereof
A technology of chemical cross-linking and chitosan, applied in the field of polymer chemistry, can solve problems such as insufficient consideration, achieve good biocompatibility, improve research and application value, and achieve the effect of pure product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: the preparation of N-octyl chitosan
[0025] Set the molecular weight to 5 x 10 4 Unmodified chitosan (5.0g, 31mmol) was mixed with 50ml methanol, mechanically stirred to disperse and 5.0ml octanal (32mmol) was added dropwise, and reacted at room temperature for 24h. Weigh 1.8g solid KBH 4 And after dissolving with 15ml of distilled water, slowly drop into the reaction solution, octanal and KBH 4 The molar ratio is 1:1, and the reaction is continued at room temperature for 24h; then neutralized with dilute hydrochloric acid solution, washed with methanol several times after standing and suction filtration, and vacuum-dried at 50°C to obtain 7.0g N-octyl chitosan . The degree of substitution (DS) of the octyl group on the 2-amino group was 54.3% by elemental analysis (see Table 1).
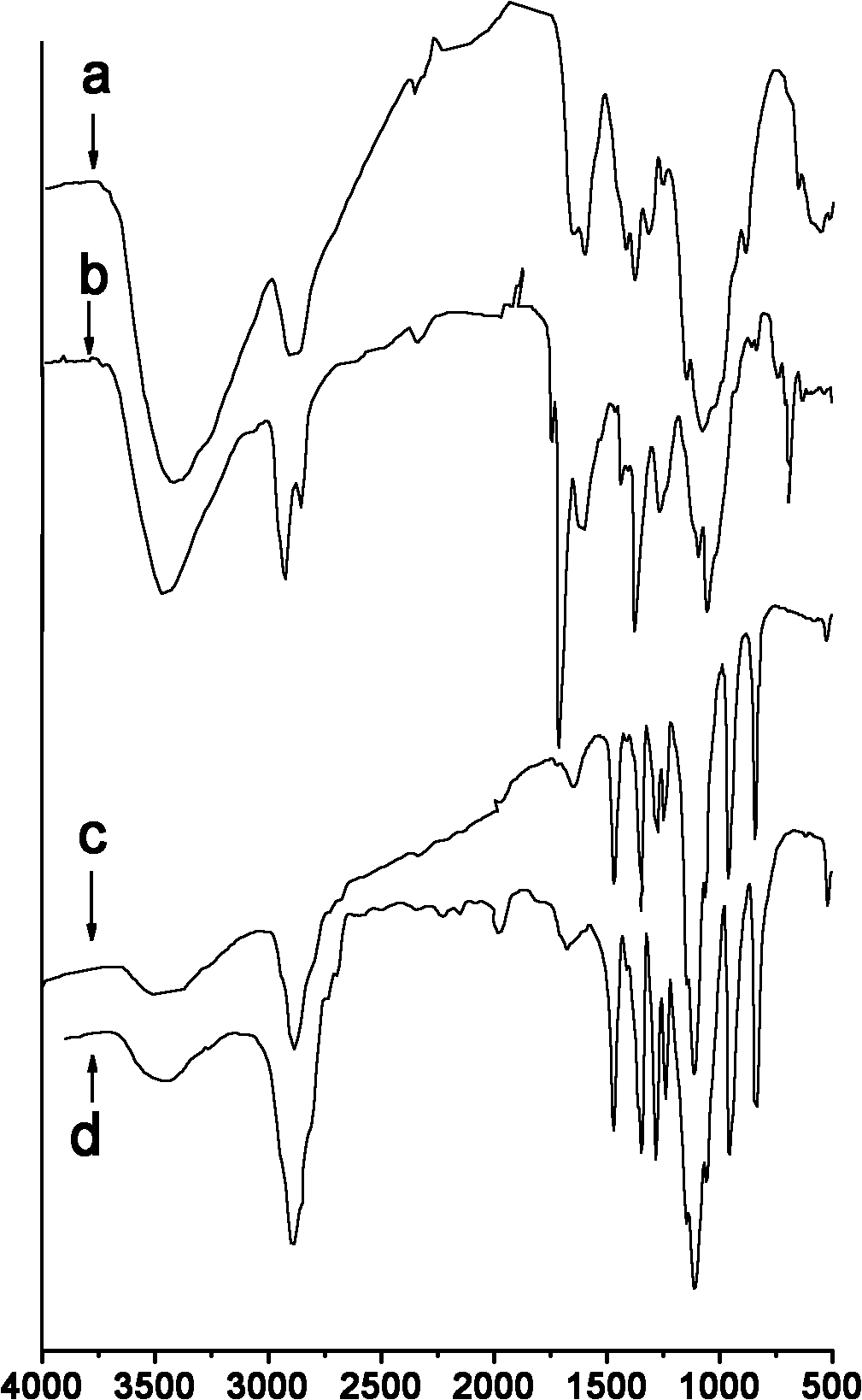
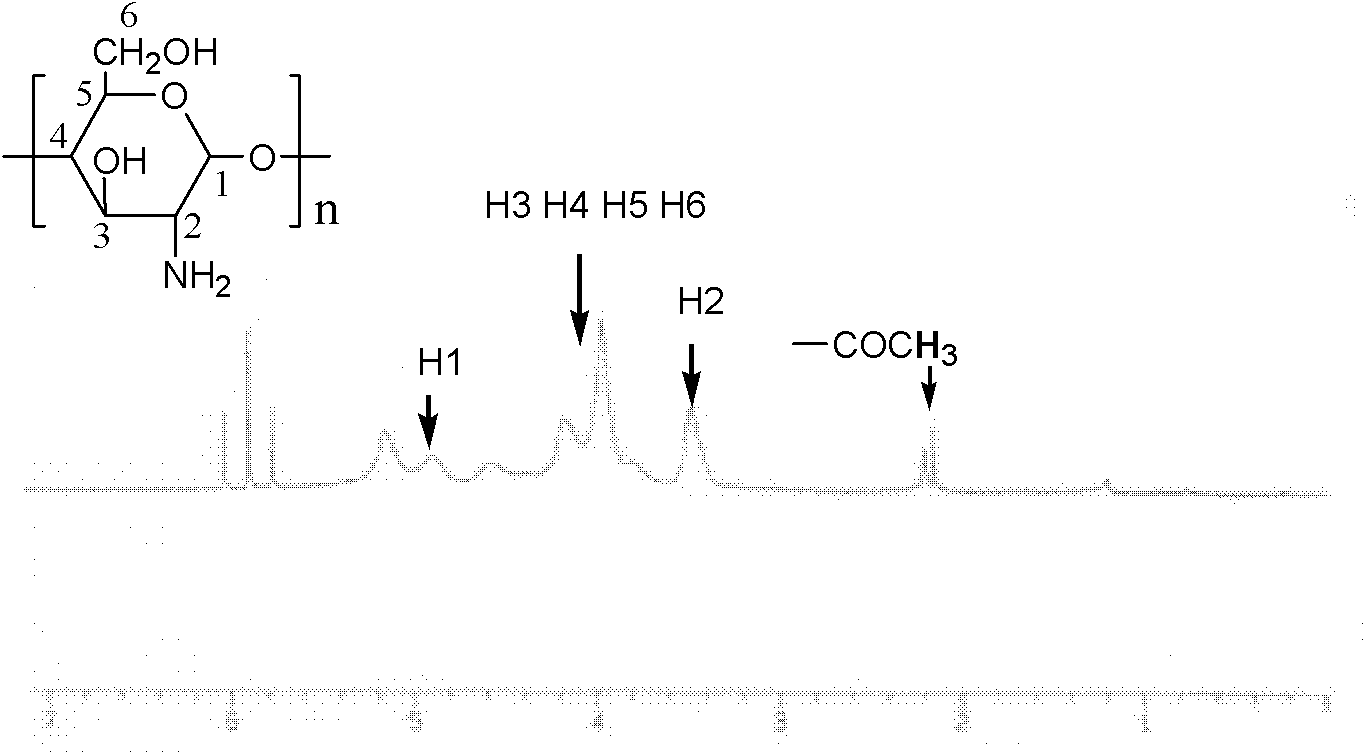
[0026] figure 1 -a is the infrared spectrum of unmodified chitosan; figure 2 It is the 1H NMR spectrum of unmodified chitosan.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: the preparation of N-phthaloyl-N-octyl chitosan (NOOPC)
[0028] Take N-octyl chitosan (3.0g, containing 6.2mmol of amino groups) and phthalic anhydride (2.8g, 18.6mmol) respectively and mix them in 40ml of anhydrous DMF. 2 Reaction under protection for 6h. Then the reaction solution was poured into ice water, and a precipitate was precipitated. The precipitate was extracted with ethanol Soxhlet for 48 hours, and the purified precipitate was vacuum-dried at 50°C to obtain 3.6 g of N-phthaloyl-N-octyl shell polysaccharides.
[0029] figure 1 Middle b is the infrared spectrum of N-phthaloyl-N-octyl chitosan, obtained by figure 1 -b Visible, the position of the peak and its attribution are as follows: IR: 3556cm -1 (-OH,-NH 2 ); 2927, 2958, 1464cm -1 (octyl groups); 721, 1776, 1716cm -1 (phthalimide groups)).
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: the preparation of N-octyl-O-polyethylene glycol chitosan (NOOMC (I))
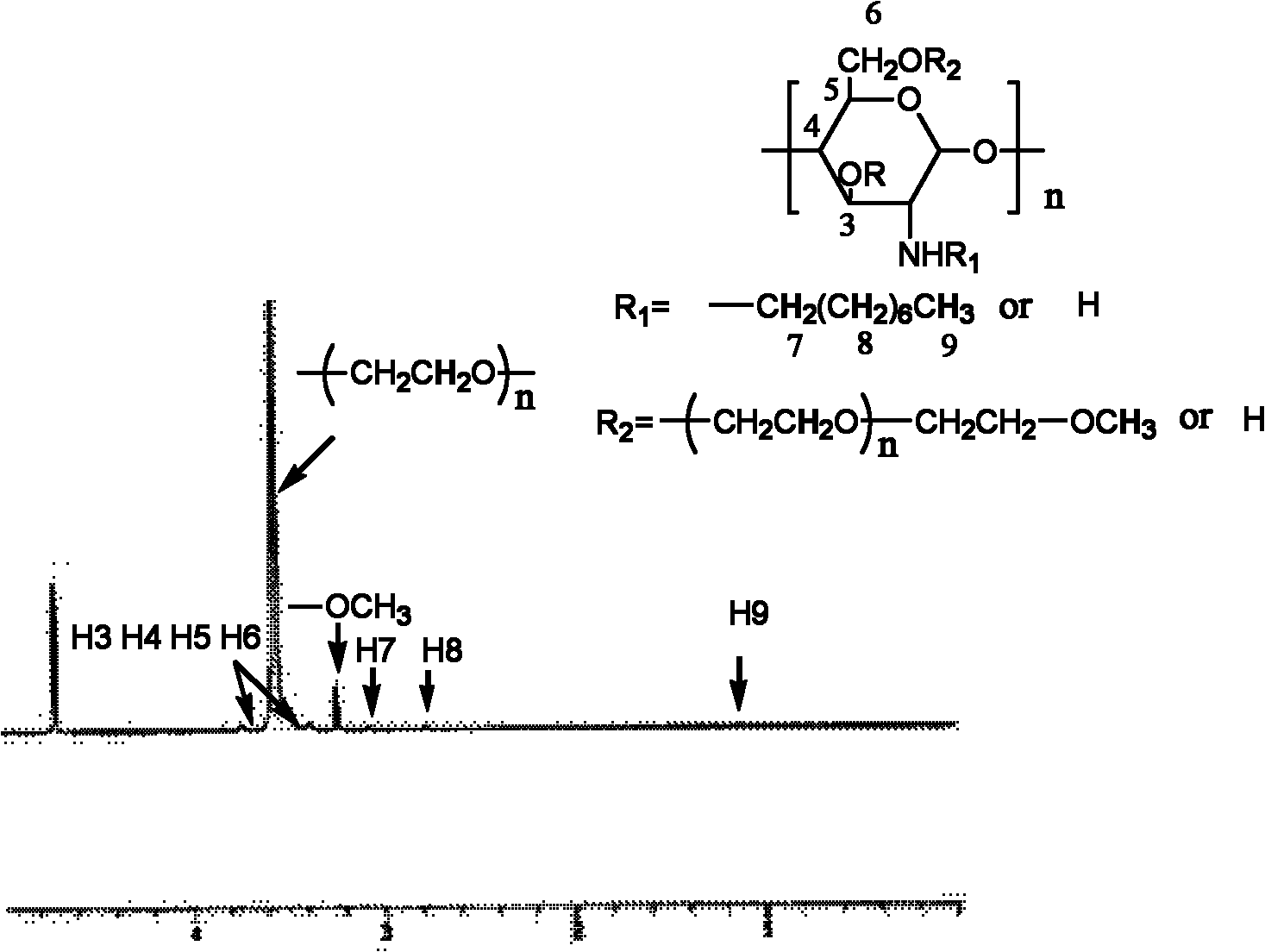
[0031] Take 1.5 g of N-phthaloyl-N-octyl chitosan (NOOPC), 10.2 g of iodopolyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (MPEGI) prepared in advance, freshly prepared Ag 2 O 1.2g, the molar ratio of the three is n(POCTS):n(MPEGI):n(Ag 2 (0)=1:1:1, the reactants were mixed in 60ml DMF, and stirred with magnetic force at 60°C for 16h, then added 80ml water and 50ml hydrazine hydrate (80%), and the temperature was raised to 90°C to continue the reaction for 15h; filter to remove Insoluble matter in the solution, the obtained filtrate was evaporated to a viscous state, then added an appropriate amount of deionized water to dissolve, and then dialyzed with deionized water for 72 hours to remove DMF and excess iodopolyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, and the dialyzed solution It is an aqueous solution of N-octyl-O-polyethylene glycol chitosan, and the aqueous solution is distilled and concentrated to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com