Method and special engineering bacteria for producing N-terminal acetyl protein or polypeptide
An acetylase, recombinant engineering bacteria technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as inability to acetylate Tβ4, and achieve the effect of broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1, Escherichia coli host construction expressing the acetylase of halophilic archaea
[0048] 1. Design and synthesis of the acetylase ssArd1 gene of halophilic archaea
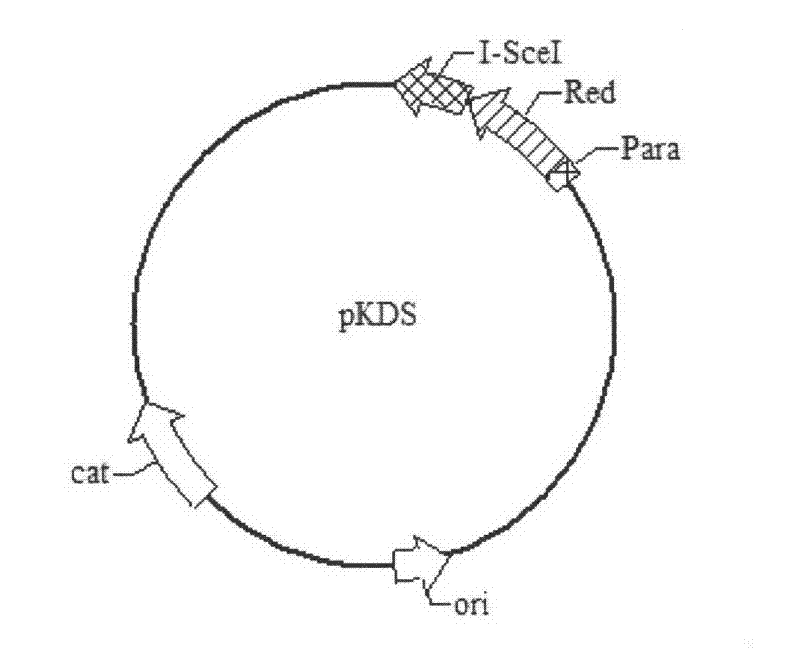
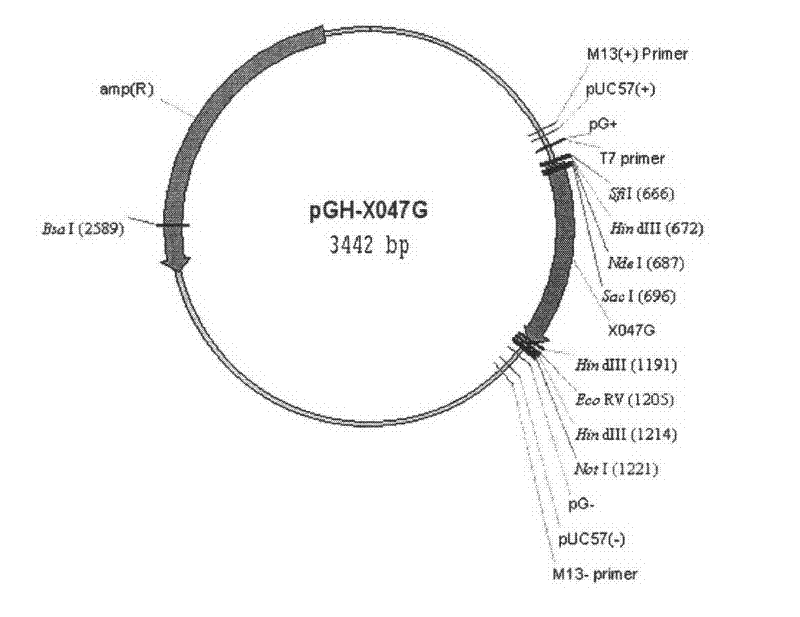
[0049] According to the amino acid sequence reported in the literature (Dale T.Mackay, Catherine H.Botting, Garry L.Taylor and Malcolm F.White. An acetylase with relaxed specificity catalysesprotein N-terminal acetylation in Sulfolobus solfataricus. Molecular Microbiology, 2007, 64: 1540-1548 ) and the partial tropism of Escherichia coli gene codons, the following gene sequence was designed and sent to Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. for synthesis. The synthetic ssArd1 gene sequence has NdeI and HindIII restriction sites added on both sides respectively, and the specific sequence is shown in sequence 1 (the 4th-501st nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of sequence 1 in the sequence listing is the coding sequence) , the encoded amino acid sequence is shown in Sequence ...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Example 2, Preparation of recombinant N-terminal acetylated Tα1
[0122] Tα1 has a small molecular weight and is difficult to express directly in cells, and needs to be fused with other protein genes. In order to obtain the complete structure of Tα1, the fusion protein needs to be cleaved. The cleavage method can adopt enzymatic cleavage method, chemical cleavage method, and intein-mediated cleavage method. This example describes the use of intein cleavage to obtain N-terminal acetylated thymosin Tα1.
[0123] 1. Construction of engineering bacteria I expressing fusion protein of Tα1 and intein
[0124] The gene sequence encoding the Spl DnaX intein is shown as sequence 3 in the sequence listing, and was synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd.
[0125]Use restriction endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I to double-digest the gene encoding the Spl DnaX intein, then use restriction endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I to double-digest the pET22b v...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Example 3, Preparation of recombinant N-terminal acetylated Tβ4
[0168] Tβ4 has a small molecular weight and is difficult to express directly in cells, and needs to be fused with other protein genes. To obtain the complete structure of Tβ4, the fusion protein needs to be cleaved. The cleavage method can adopt enzymatic cleavage method, chemical cleavage method, and intein-mediated cleavage method. This example describes the use of intein cleavage to obtain N-terminal acetylated thymosin Tβ4.
[0169] 1. Construction of engineering bacteria II expressing fusion protein of Tβ4 and intein
[0170] Preparation of human thymosin β4 with plasmid pET-B2 containing Tβ4 gene (Si Xinxi, Dai Hongmei, Fang Hongqing, Chen Huipeng. Chemical cleavage of recombinant fusion protein. Biotechnology Communications, 2009, 20(5), 677-679) (Military Medicine of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Institute of Bioengineering, Academy of Sciences) as a template, PCR amplified Tβ with prime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com