Process for recovering zinc from hot-dip coating zinc ash
A hot-dip galvanizing and process technology, which is applied in the field of zinc secondary resource recovery, can solve the problems of low production energy consumption, low reaction reduction rate, low labor intensity, etc., and achieve the effects of friendly production environment, low labor intensity, and high purity of zinc products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
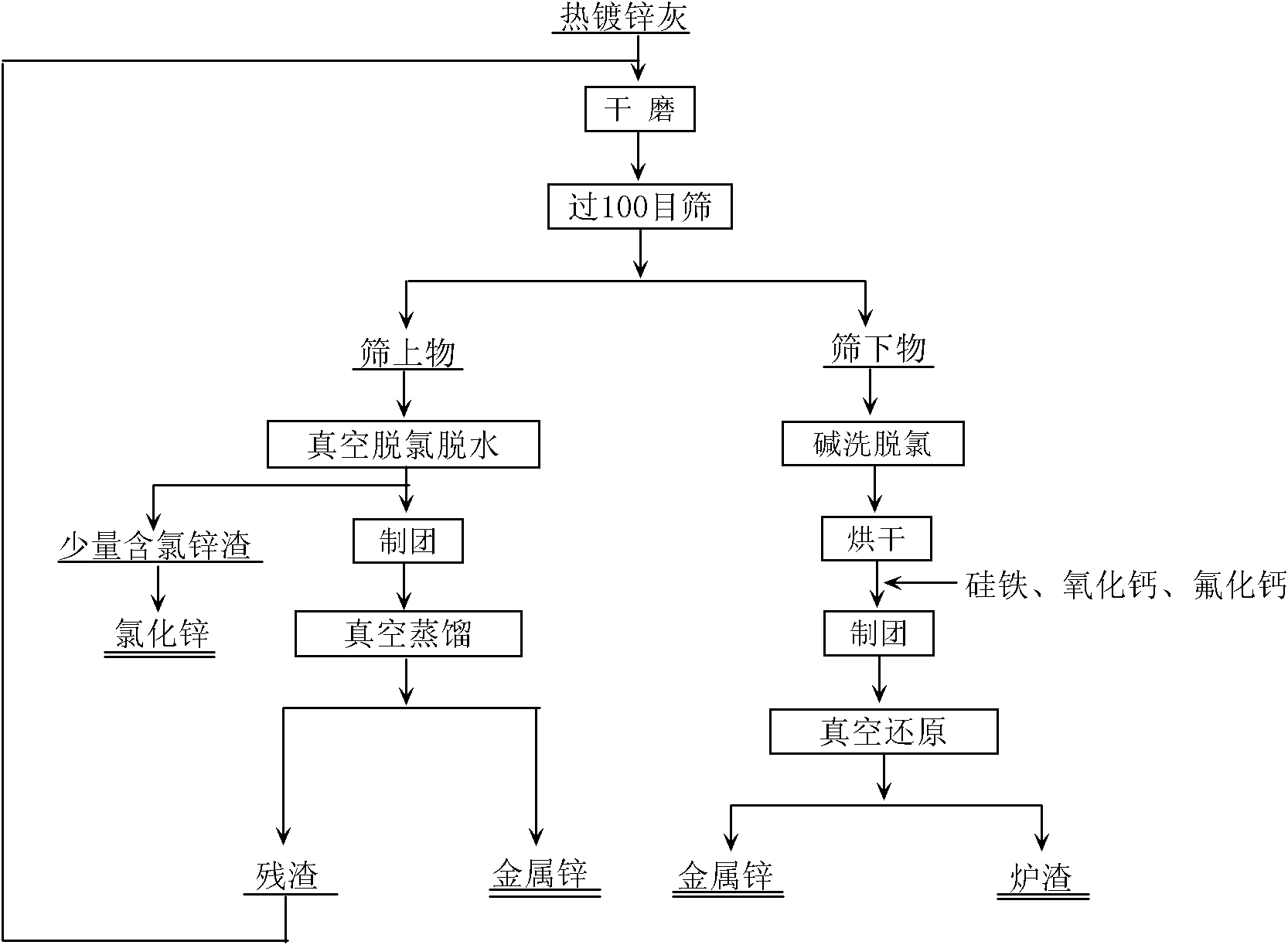
[0028] Zinc ash is passed through a 100-mesh sieve after dry grinding, and screened to obtain the oversize and undersize. Weigh 10.00 g of the sieved material, put it into a vacuum furnace, and keep the temperature at 450° C. for 30 minutes at a vacuum degree of 35 Pa, then take out the residual material in the vacuum furnace to form agglomerates. The bulk raw material was put into a vacuum furnace, and the vacuum degree in the furnace was 10 Pa, and the temperature was 750°C and distilled for 30 minutes, and 5.60 g of metal zinc could be recovered, and the quality of the residue was 3.30 g. The main component of the residue is zinc oxide according to XRD analysis. Take 10.00 g of the undersieve, wash with alkali and filter to obtain the filter residue. The main component of the filter residue is zinc oxide. Weigh 4.05g of the filter residue. The filter residue is mixed with 2.80g of calcium oxide, 1.16g of No. 75 ferrosilicon powder and 0.25g of calcium fluoride. In the fur...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Zinc ash is passed through a 100-mesh sieve after dry grinding, and screened to obtain the oversize and undersize. Weigh 10.00 g of the sieve, put it into a vacuum furnace, and distill for 30 minutes at a vacuum degree of 35 Pa and a temperature of 450° C., then take out the residual material in the vacuum furnace to form agglomerates. Put the bulk raw material into a vacuum furnace with a vacuum degree of 10 Pa, raise the temperature to 800°C, and distill for 50 minutes to obtain 5.75 g of metal (purity: 99.84%), and the quality of the residue is 3.26 g. The main component of the residue is zinc oxide according to XRD analysis. Take 10.00 g of the undersieve, wash with alkali and filter to obtain the filter residue. The main component of the filter residue is zinc oxide. Weigh 4.05g of the filter residue, 2.80g of calcium oxide, 1.16g of No. 75 ferrosilicon powder and 0.25g of calcium fluoride, and mix them uniformly to make agglomerates. Put the bulk raw material in...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Zinc ash is passed through a 100-mesh sieve after dry grinding, and screened to obtain the oversize and undersize. Weigh 10.00 g of the sieved material, put it into a vacuum furnace, and keep the temperature at 450° C. for 30 minutes at a vacuum degree of 35 Pa, then take out the residual material in the vacuum furnace to form agglomerates. Put the bulk raw material into a vacuum furnace with a vacuum degree of 10 Pa, raise the temperature to 800°C, and distill for 40 minutes. 5.71 g of metal (purity: 99.84%) can be recovered, and the mass of the residue is 3.21 g. The main component of the residue is zinc oxide according to XRD analysis. Take 10.00 g of the undersieve, wash with alkali and filter to obtain the filter residue. The main component of the filter residue is zinc oxide. Weigh 4.05g of the filter residue, 2.80g of calcium oxide, 1.16g of No. 75 ferrosilicon powder and 0.25g of calcium fluoride, and mix them evenly to form a lump, and put the lump raw materia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com