Method for inoculating lactobacillus to rapidly reduce nitrite content in pickles
A technology for inoculating lactic acid bacteria and lactic acid bacteria, which is applied in the fields of application, food preparation, food science, etc., can solve the problems of high production conditions, high product costs, and vegetable nutrition damage, and achieve easy control of the fermentation process, low production costs, and inhibition The effect of growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
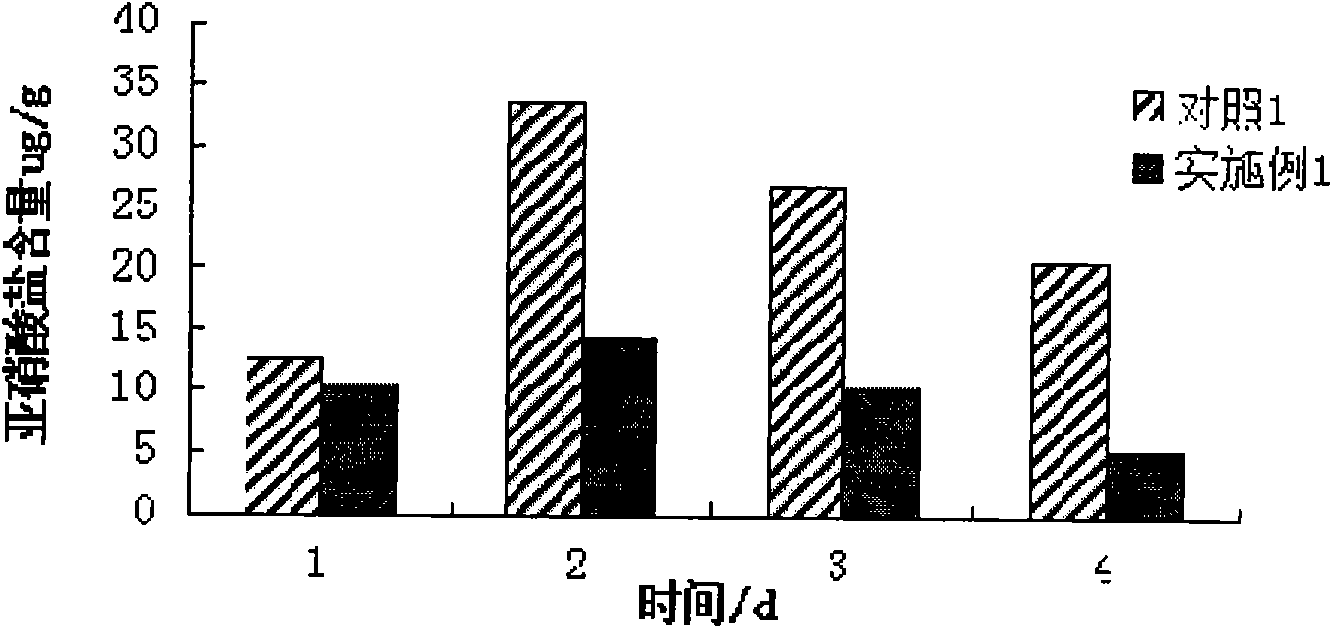
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0025] Strain activation medium: MRS medium
[0026] Liquid seed medium: liquid MRS medium (MRS medium without agar is liquid MRS medium)
[0027] (2) Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei were respectively activated according to the strain instructions provided by the Microbial Culture Collection Center of Guangdong Institute of Microbiology.
[0028] (3) Inoculate the activated Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei in 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1) respectively in (2), culture at 37°C for 48h, and then inoculate 2.5mL Insert the lactic acid bacteria solution into 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1), carry out step-by-step expansion culture, and prepare the first-level seed solution and the second-level seed solution successively, so that the number of viable bacteria in the second-level seed solution reaches 10 7 -10 8 CFU / ml.
[0029] (4) Put ...
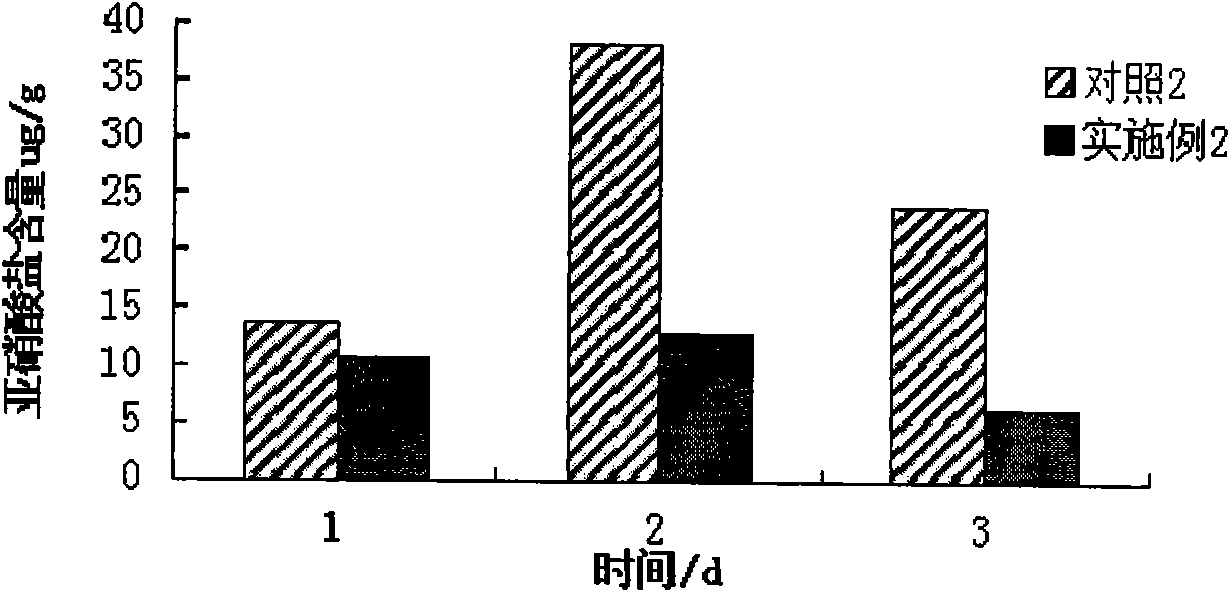
Embodiment 2
[0036] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0037] Strain activation medium: MRS medium
[0038] Liquid seed medium: liquid MRS medium (MRS medium without agar is liquid MRS medium)
[0039] (2) Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei were respectively activated according to the strain instructions provided by the Microbial Culture Collection Center of Guangdong Institute of Microbiology.
[0040] (3) Inoculate the activated Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei in 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1) respectively in (2), culture at 37°C for 48h, and then inoculate 2.5mL Insert the lactic acid bacteria solution into 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1), carry out step-by-step expansion culture, and prepare the first-level seed solution and the second-level seed solution successively, so that the number of viable bacteria in the second-level seed solution reaches 10 7 -10 8 CFU / m1.
[0041] (4) Put ...
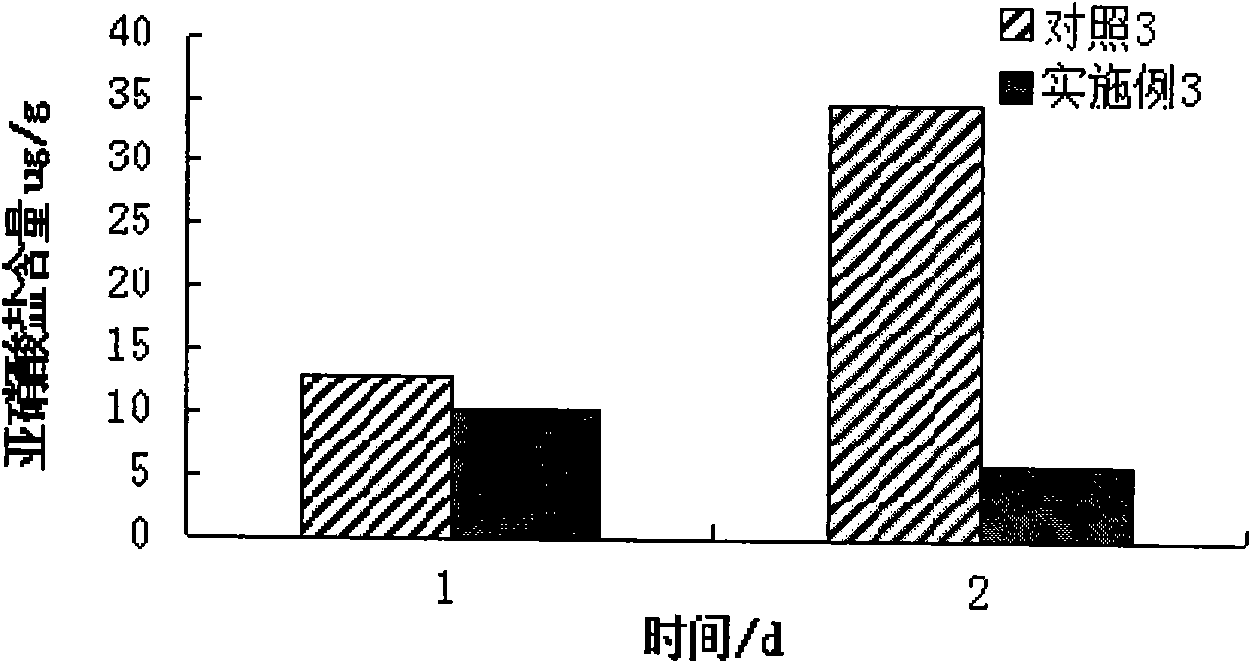
Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0049] Strain activation medium: MRS medium
[0050] Liquid seed medium: liquid MRS medium (MRS medium without agar is liquid MRS medium)
[0051] (2) Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei were respectively activated according to the strain instructions provided by the Microbial Culture Collection Center of Guangdong Institute of Microbiology.
[0052] (3) Inoculate the activated Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei in 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1) respectively in (2), culture at 37°C for 48h, and then inoculate 2.5mL Insert the lactic acid bacteria solution into 50mL of the liquid MRS medium prepared in (1), carry out step-by-step expansion culture, and prepare the first-level seed solution and the second-level seed solution successively, so that the number of viable bacteria in the second-level seed solution reaches 10 7 -10 8 CFU / ml.
[0053] (4) Put ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com