Method for preparing targeted lidamycin production strain by utilizing gene disruption strain and application of lidamycin production strain
A technology for production of lidamycin and strains, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of complexity, low rate of gene homologous double exchange, difficulty in producing strains of daxamycin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
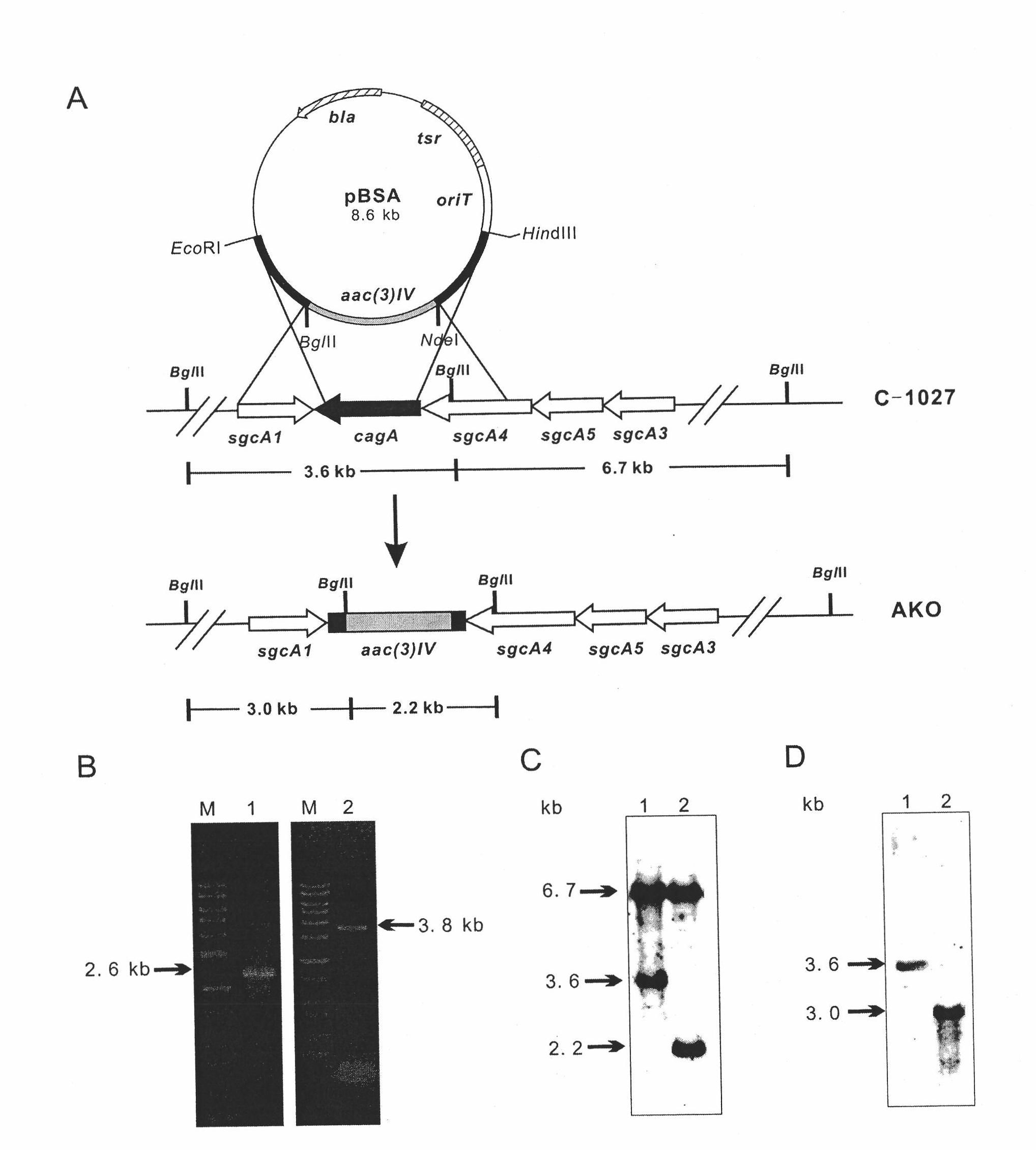
[0086] Example 1 Construction of lidamycin prosthetic protein gene blocking strain S.globisporus AKO
[0087] 1. Construction of cagA gene blocking plasmid
[0088] According to the known sequence of cagA gene, design PCR primers, use Pfu DNA polymerase, carry out PCR reaction with the total DNA of S. globisporus C-1027 as the template, and amplify the forearm Aup and hind arm Adown of the target fragment. The primers of the amplified forearm are AupF and AupR (see Table 3 for the primer sequence, SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2), and the primers for the back arm are AdownF and AdownR (see Table 3 for the primer sequence, SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No. 4).
[0089] After gel recovery and purification, the PCR products of the forearm and hind arm were ligated with pGEM-T (Promage, USA) using Taq DNA polymerase to add dATP to the tail of the product, and the ligated products were respectively transformed into E.coli DH5α competent cells (Dalian Bao Biological Company). Restriction si...
Embodiment 2
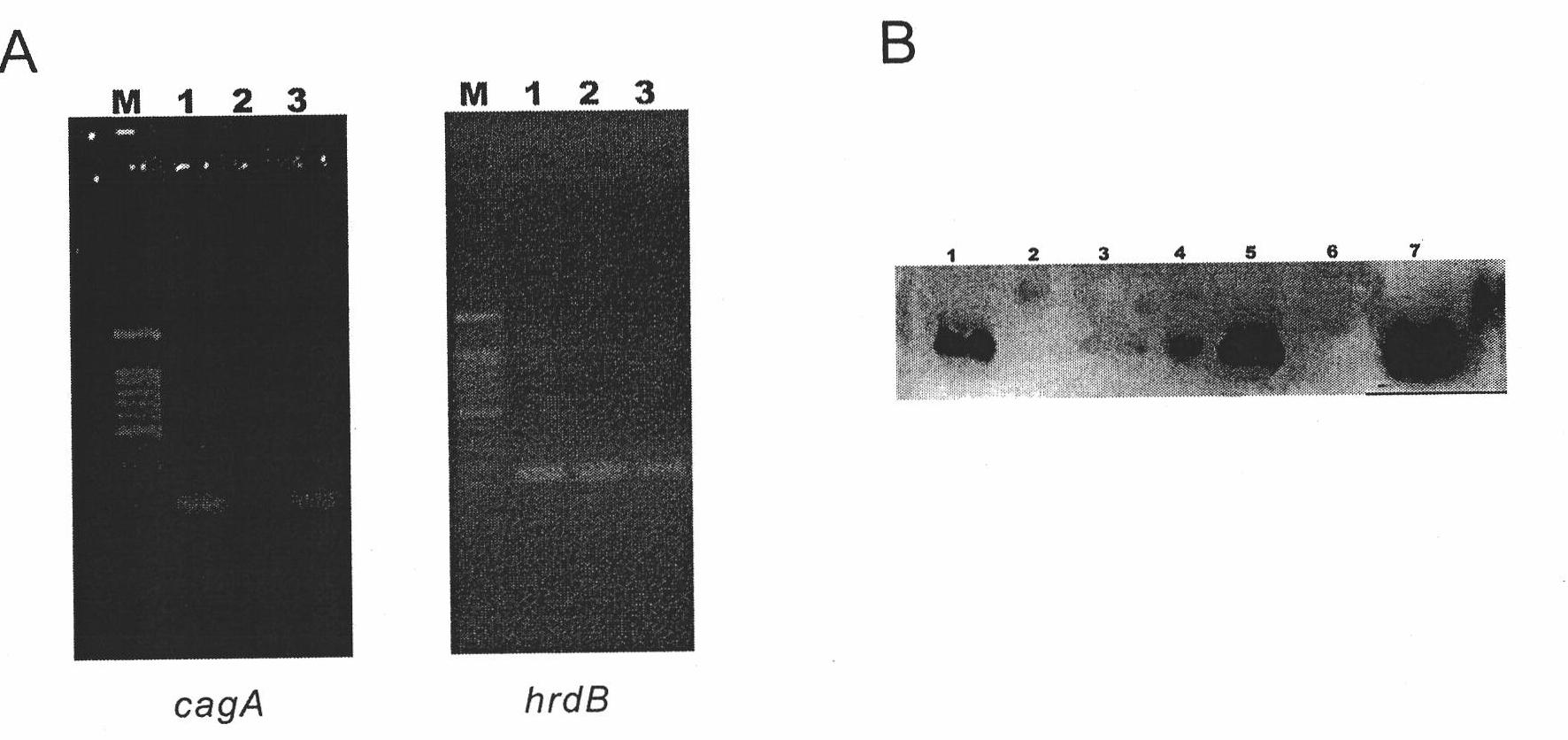
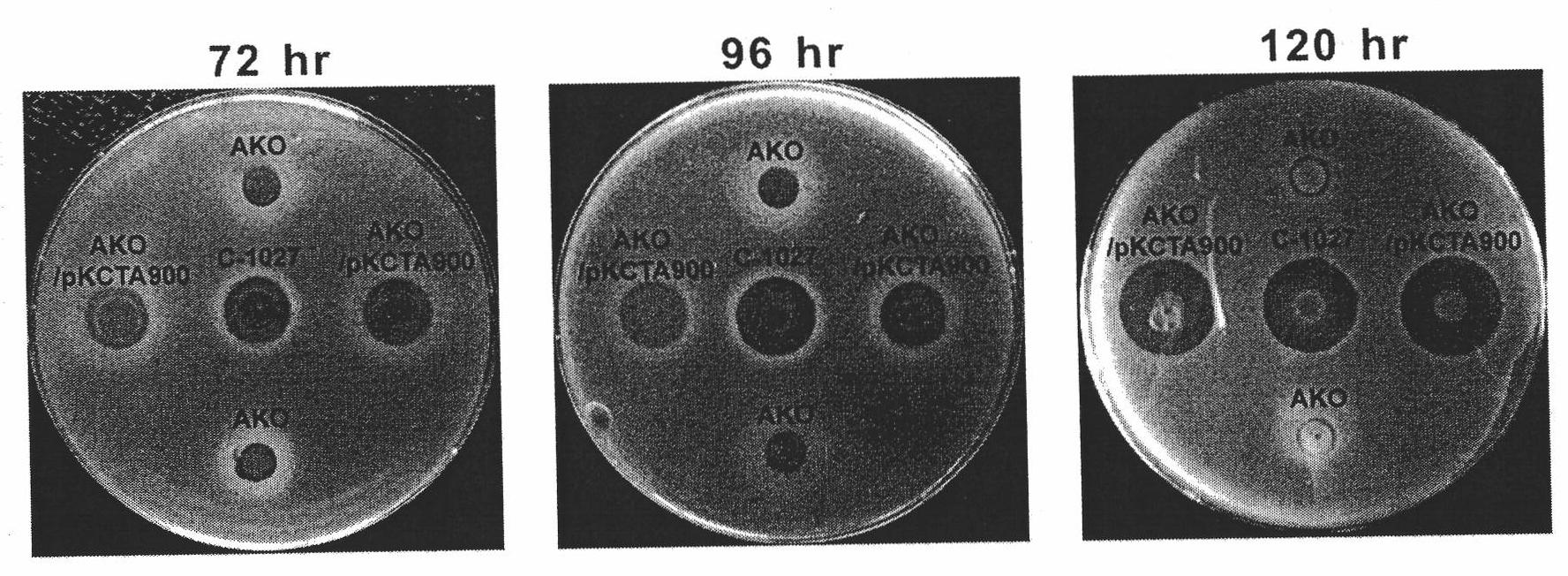
[0114] Example 2 Reply of lidamycin prosthetic protein gene blocking strain S.globisporus AKO
[0115] 1. Construction of cagA gene reversion plasmid
[0116] The inventors used a variety of different plasmids to perform recovery experiments on S. globisporus AKO. Plasmid pKC1139 is a multi-copy plasmid. Plasmid pSET152 is an integrative plasmid that does not contain Streptomyces replicons and contains ΦC31 attP site, which can be integrated into Streptomyces attB site. Plasmid pL646 was derived from pSET152 into which the strong promoter ermE*p and the SD sequence of the tuf1 gene were introduced upstream of the multiple cloning site.
[0117] Amplify the cagA gene coding region and its upstream promoter region and a fragment of about 900bp in the downstream terminator region by PCR (see Table 3 for the sequence, SEQ ID No.7 and SEQ ID No.8), and add enzymes to the two ends of the fragment respectively Fragment A9001 was amplified by cutting site EcoRI+BamHI; fragment A900...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Embodiment 3 is targeted at the construction of the lidamycin production bacterial strain of IV collagenase
[0136] 1. Construction of fusion protein expression plasmid
[0137] single domain antibody V H The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence are referenced [Tang Yong, Zhen Yongsu, Expression of Anti-IV Type Collagenase Single-Chain Antibody and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tumor Cell Invasion, Cancer, 2001, 20: 801-805], without change Under the principle of amino acid sequence, the codons of the original gene were replaced with codons preferred by Streptomyces.
[0138] In order to facilitate the cloning of fragments, XhoI and BglII restriction sites were introduced at both ends of the DNA sequence encoding the single-domain antibody gene; and when designing the upstream primer, the base sequence of the GGGGS flexible pentapeptide was added for connection Lidamycin prosthetic protein gene and anti-IV collagenase single domain antibody gene, so that lidamycin ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com