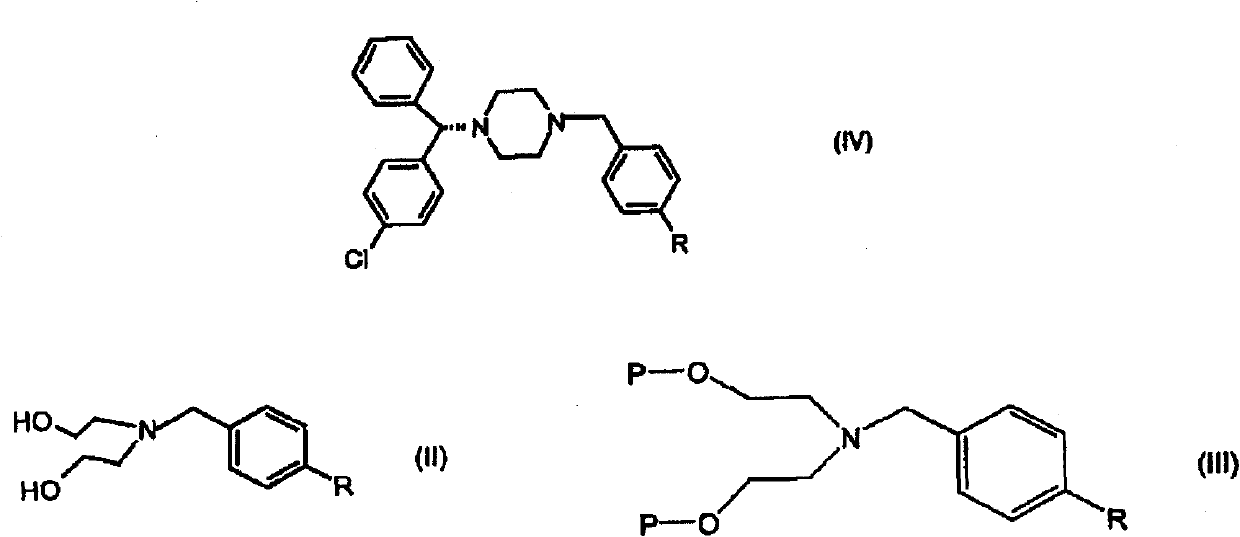
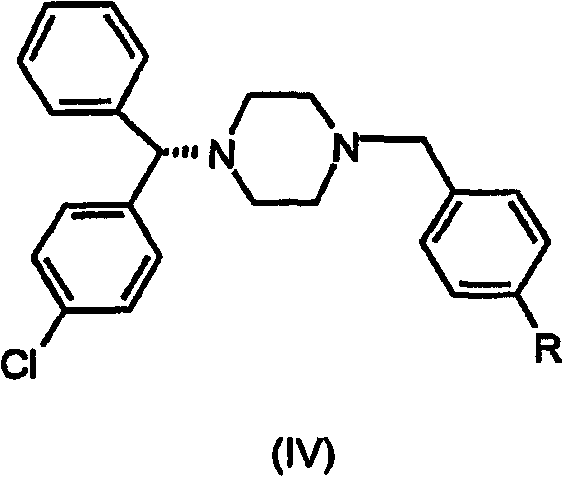
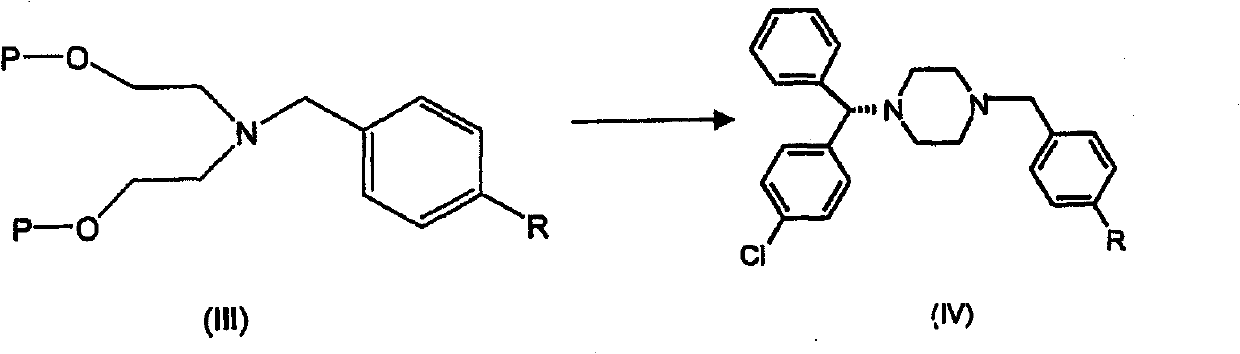
Processes for the synthesis of levocetirizine and intermediates for use therein
A technology of levocetirizine and compounds, which is applied in the field of new intermediates and can solve problems such as carcinogenesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0134] Preparation of 2-[(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-(4-methoxybenzyl)-amino]-ethanol
[0135] 25 gms (0.2380 moles) of diethanolamine and 60 ml (0.4312 moles) of triethylamine in 75 ml of dichloromethane were placed in a reaction vessel and cooled to 0-5°C with stirring. Then 40 gms (0.2554 mole) p-methoxybenzyl chloride in 50 ml dichloromethane was added slowly. Further, the reaction mass was stirred with dichloromethane and kept at a temperature of 25-30° C. for about 16 hours. The resulting solution was concentrated to obtain a residue. 200 ml of acetone were added to the residue, cooled to 0-5°C for about 1 hour and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated to give the title compound as an oil (50.8 gms).
Embodiment 2
[0137] Preparation of 2-[(2-methanesulfonyloxy-ethyl)-(4-methoxy-benzyl)-amino]-ethyl methanesulfonate
[0138] 25 gms (0.1111 moles) of the product obtained in Example 1 and 45 gms (0.4455 moles) of triethylamine and 125 ml of dichloromethane were placed in a reaction vessel and cooled to -5 to -10°C. A solution of methanesulfonyl chloride (45 gms, 0.3888 mol) in dichloromethane (50 ml) was slowly added at -5 to 10°C and stirred at 25-30°C for about 16 hours. The resulting mixture was washed with water (25ml). The collected organic layers were concentrated to give the title compound (36 gms).
Embodiment 3
[0140] Preparation of (-)-1-[(4-chloro-phenyl)-phenyl-methyl]4-(4-methoxy-benzyl)piperazine
[0141] i) 7 gms (0.03218 moles) of (-)-(4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethylamine and 10 gms (0.02624 moles) of the compound prepared in Example 2 were mixed with 14 ml of dimethylsulfoxide and 14 gms (0.1083 moles) of N -Ethyldiisopropylamine mixed. Next, the mixture was heated at 90° C. for about 4 hours and then cooled. The reaction mass was quenched in water and extracted with dichloromethane. The collected organic layers were concentrated to give a residue (13 gms).
[0142] ii) To the residue obtained in step i) were added 130 ml of ethyl acetate and 14 gms (0.1111 mol) of oxalic acid dihydrate. The mixture was heated to give a clear solution and cooled to give (-)-1-[(4-chloro-phenyl)-phenyl-methyl]-4-(4-methoxy-benzyl)piperazine. salt. The salt was filtered and dried under vacuum (15 gms) at 55°C.
[0143] iii) The oxalate was further treated with sodium hydroxide solution until...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com