Cooling structure of chip
A heat dissipation structure and chip technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve problems such as hidden dangers and leakage reliability of water-cooled heat dissipation liquid, and achieve the effects of not occupying chip area, reducing process difficulty and complexity, and saving process steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described below by example. It should be noted that the purpose of the disclosed embodiments is to help further understand the present invention, but those skilled in the art can understand that various replacements and modifications are possible without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention and the appended claims of. Therefore, the present invention should not be limited to the content disclosed in the embodiments, and the protection scope of the present invention is subject to the scope defined in the claims.
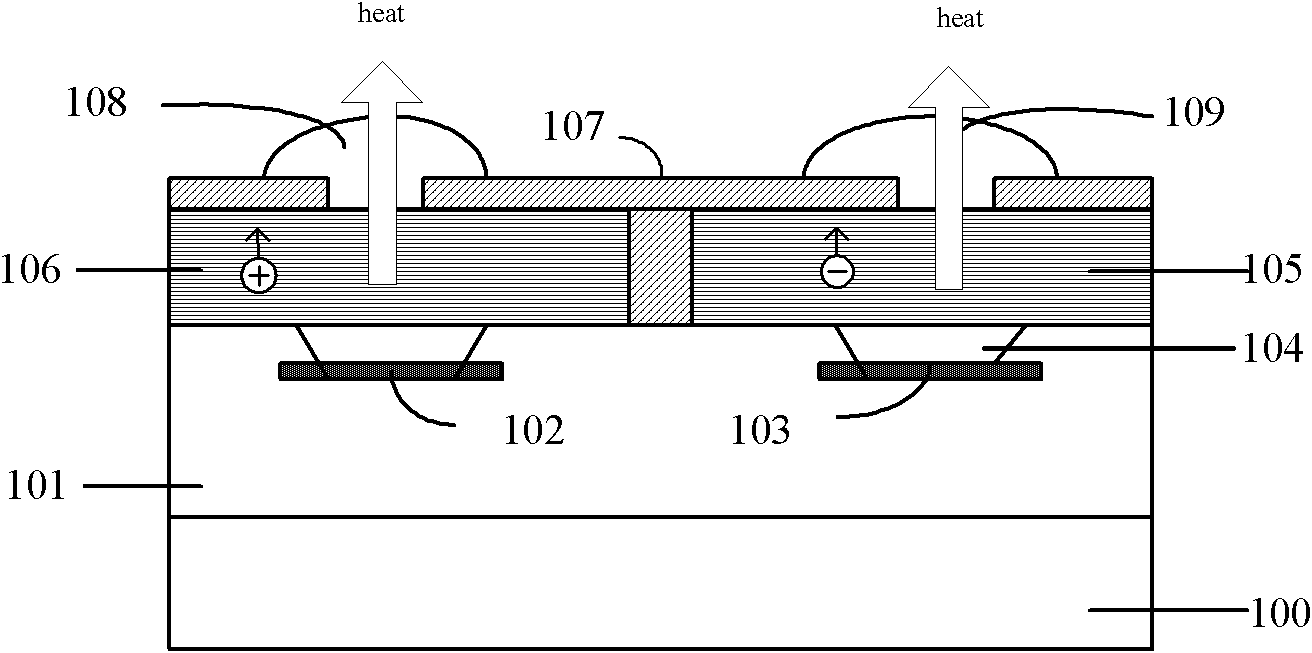
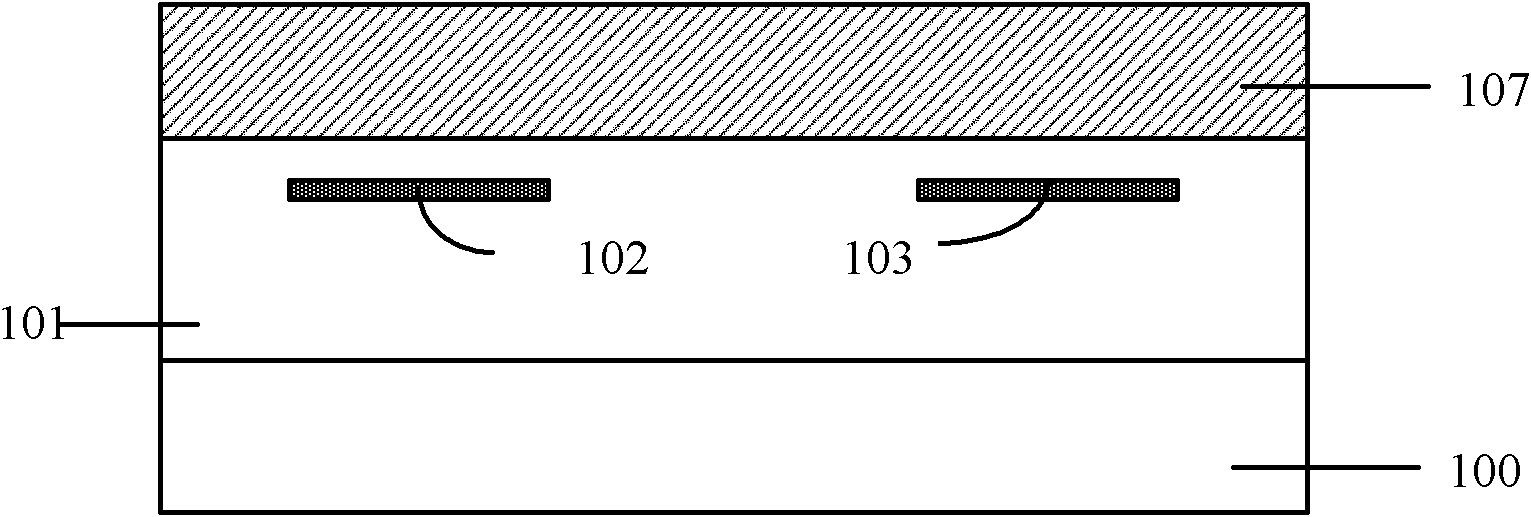
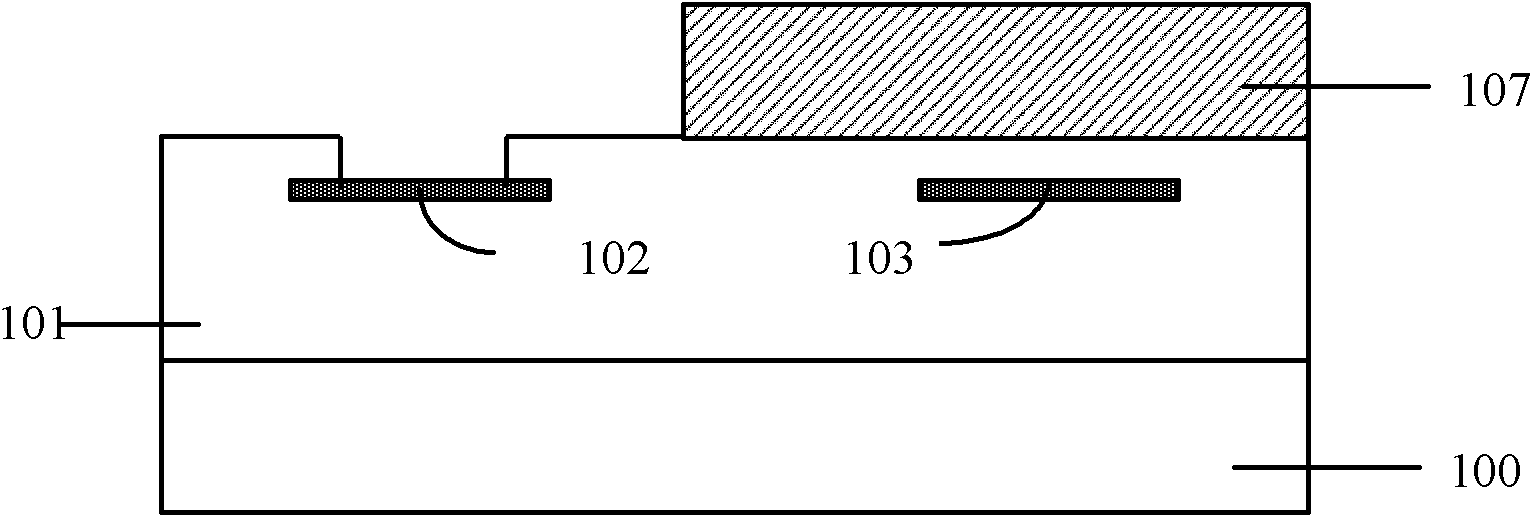
[0022] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of the chip thermoelectric heat dissipation structure. The chip includes a substrate 100 and a working area 101, wherein the working layer 101 of the chip includes polysilicon and metal interconnection lines. A P-type superlattice and an N-type superlattice are respectively formed above the chip, and the superlattices are separated by silicon dioxide. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com