Biomass degradable material preparation method and straw
A technology of biomass degradation and straws, applied in the field of biodegradable materials and their products, can solve the problems of incompleteness and inability to degrade, and achieve the effects of reducing consumption, saving energy and resource consumption, and saving direct costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
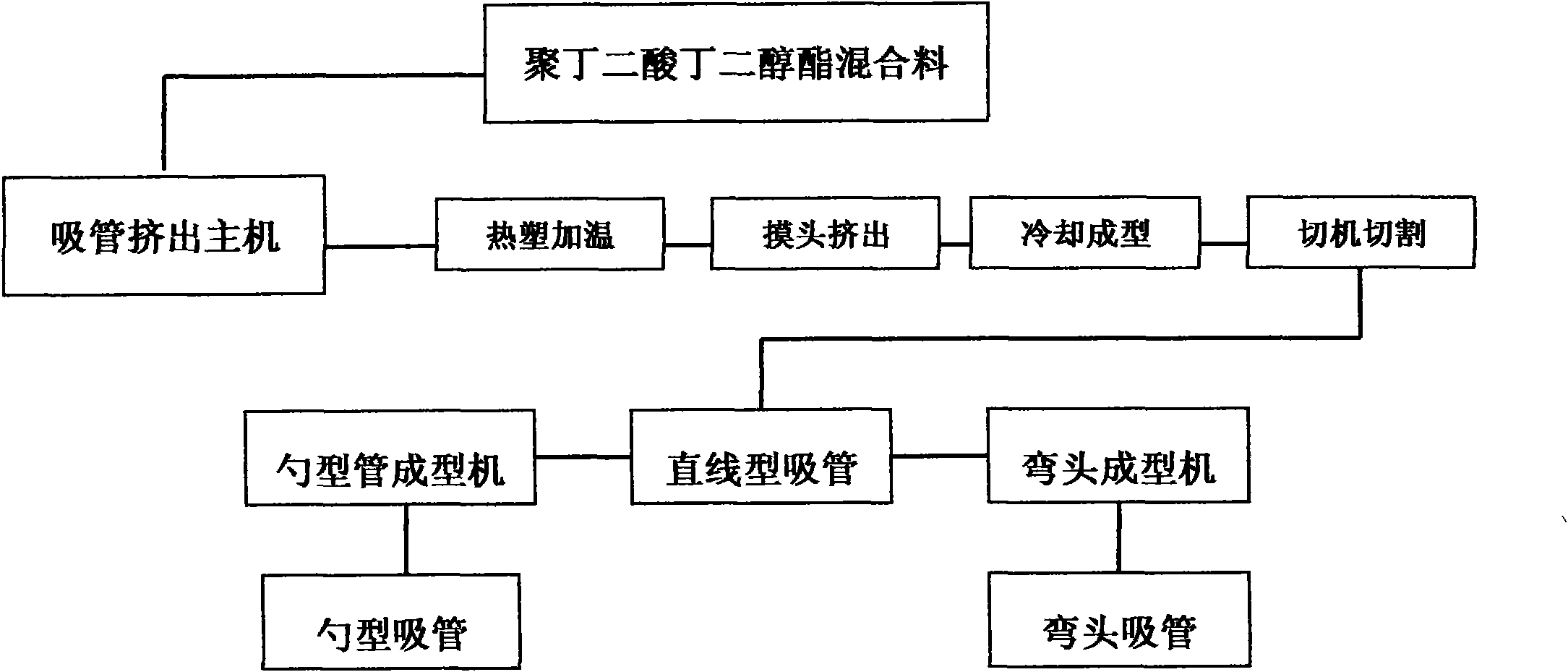
[0052] see figure 1 , a kind of preparation method of biomass degradable material provided by the embodiment of the present invention, it comprises the following steps:
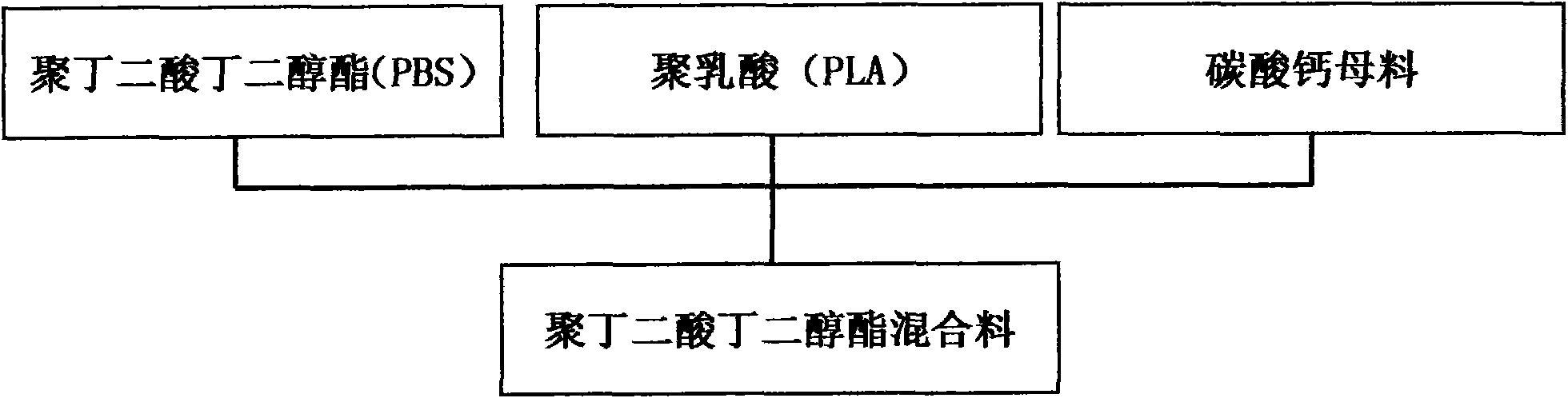
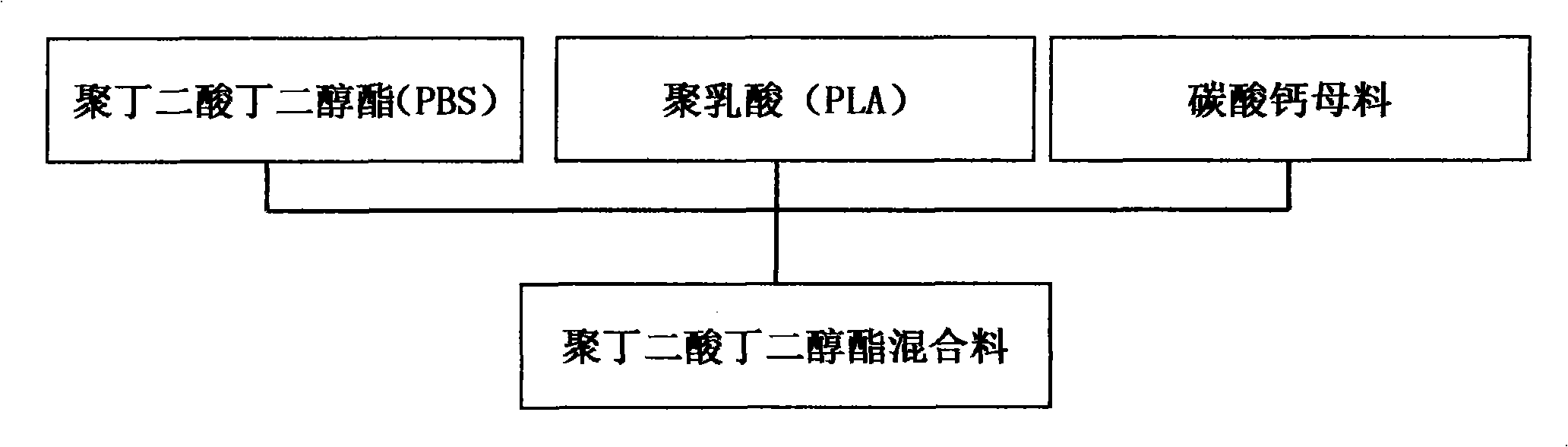
[0053] 1) Preparation of raw materials: According to weight percentage, take the following raw material components:
[0054] Main material polybutylene succinate 40-60, modified polylactic acid 40-60, filler calcium carbonate masterbatch 0.1-20;
[0055] 2) Component mixing:
[0056] Firstly, the above components are prepared into 100-300 mesh powder, and dried;
[0057] Weigh the polybutylene succinate of 1 / 3 of the total amount, add all the polylactic acid, stir and mix;
[0058] Then add the remaining polybutylene succinate and all the calcium carbonate masterbatch gradually and stir and mix until it is completely added, so that the powder components are evenly mixed to form a modified polybutylene succinate mixed material;
[0059] 3) Vacuumize the modified polybutylene succinate mixture under low te...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The preparation method of the biomass degradable material provided by this embodiment is basically the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that:
[0072] The weight percentage of each component in the step 1) is: 40-50% polybutylene succinate as main material, 40-50% polylactic acid as modified material, and 1-10% calcium carbonate masterbatch as filler.
[0073] A method for preparing a straw using the biomass-degradable material provided in this embodiment is basically the same as in Example 1, except that it also includes the following steps:
[0074] 6) An elbow forming machine is prepared, and the pipe body of the continuous straw is subjected to an elbow indentation process to obtain a bendable straw in the middle;
[0075] The straw prepared by the above-mentioned method provided in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Example 1, the difference lies in that the middle part of the straw is provided with creases for bending the straw.
Embodiment 3
[0077] The preparation method of the biomass degradable material provided by this embodiment is basically the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that:
[0078] The weight percent of each component in the step 1) is:
[0079] The main material is polybutylene succinate 40, the modified polylactic acid, and the filler calcium carbonate masterbatch 20.
[0080] A method for preparing a straw using the biomass-degradable material provided in this embodiment is basically the same as in Example 1, except that it also includes the following steps:
[0081] 9) A scoop forming machine is prepared, and the cutting part of the tube body of the continuous straw is subjected to a scoop-shaped indentation process to obtain a scoop-shaped straw at one or both ends.
[0082] The straw prepared by the above method provided in this example is basically the same as that in Example 1, the difference is that the section of the straw at one or both ends is spoon-shaped.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com