Method for purification of natural cobalamins by adsorption on insoluble materials containing carboxylic groups
A cobalamin, natural technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, materials of anion exchangers, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of high material prices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Example 1 Testing the combination with CM-Sepharose
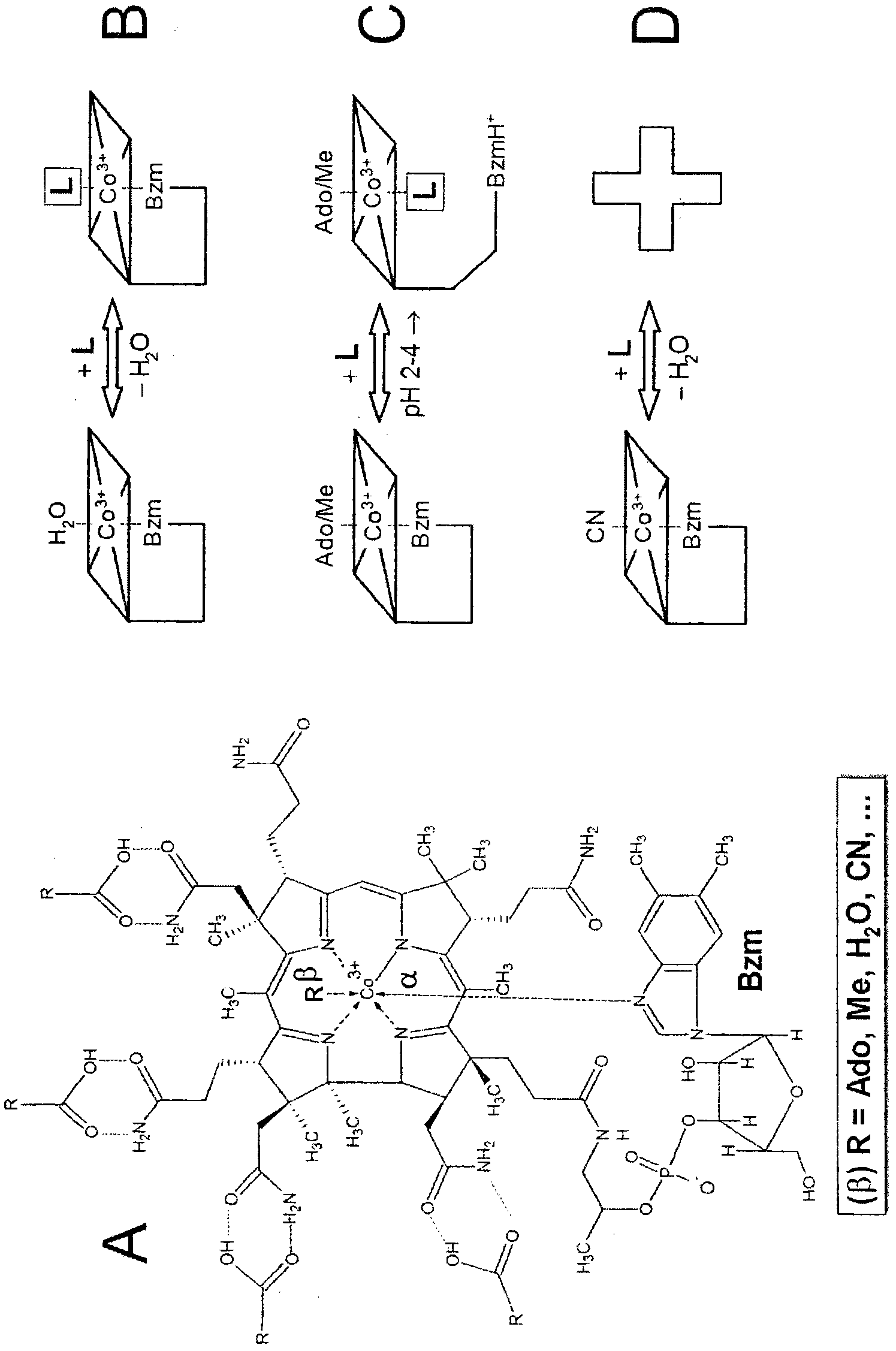
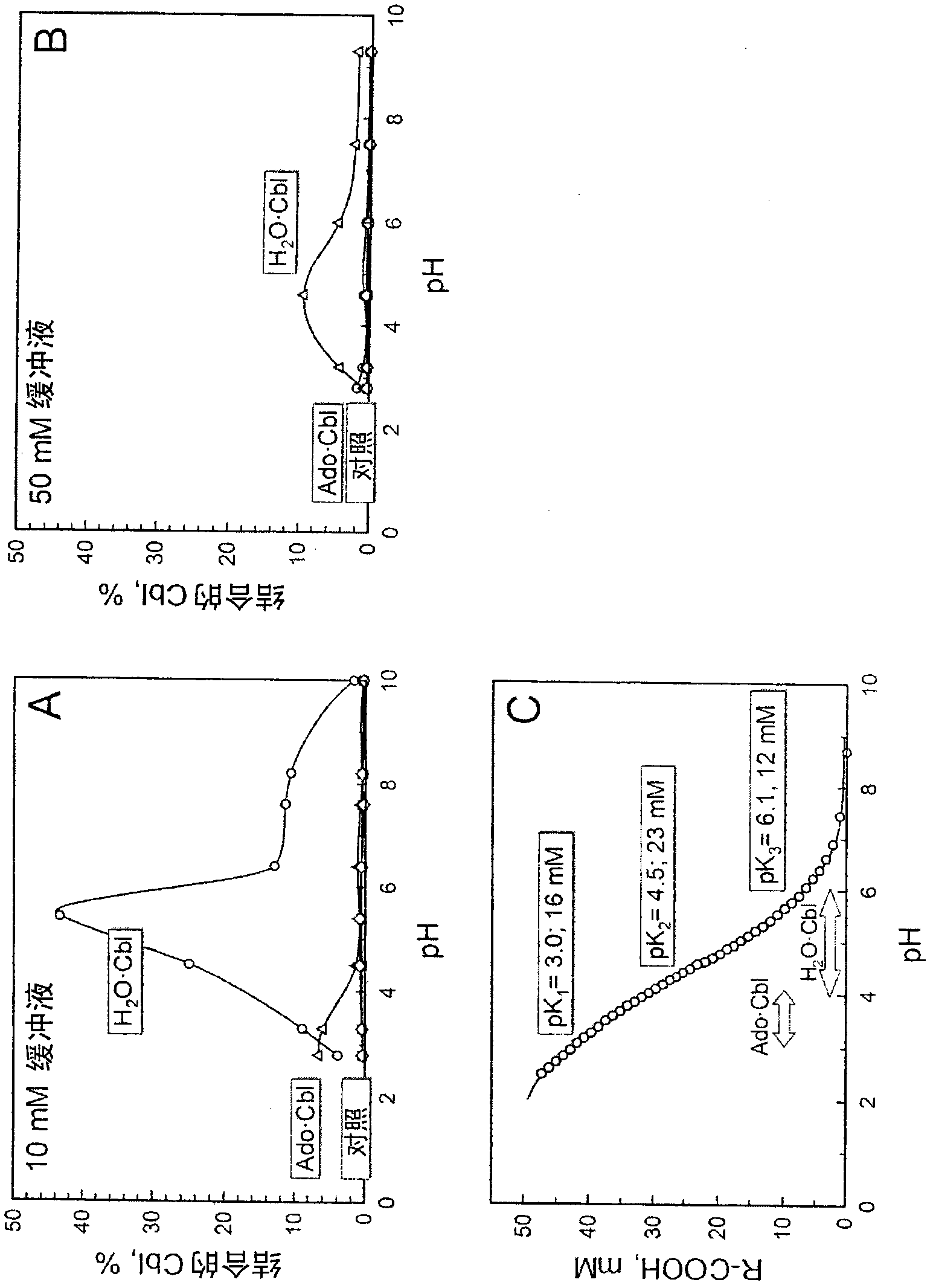
[0098] Initial experiments showed that Amberlite resins containing carboxyl groups (R-COOH) could interact with cobalamins (e.g. CN·Cbl) in a non-specific manner through the side chains of the corrin rings, as stated in the Introduction. Therefore, the matrix CM-Sepharose containing R-COOH was used to test the specific axial binding of the COOH group to the α / β-position of Cbl, in which no side effects of the interaction were observed. Thus, control experiments revealed that CM-Sepharose did not bind to CN·Cbl at all ( figure 2 Bottom curves of A and B). Similarly, the basic material Sepharose 4B (substrate without carboxyl groups) does not react with H 2 O·Cbl interaction. This means that the binding of natural cobalamins to Sepharose, if any, may be entirely due to their specific interaction with the COOH groups of the matrix.
[0099] CM-Sepharose adsorbed a significant amount of H from solution at pH 3-8 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2 Combination of Cbl with different Amberlite resins containing COOH groups
[0102] Amberlite is a strong adsorbent made of beads, able to withstand high pressure and aggressive media. The volume of the sorbent was measured in the experiment according to the space occupied by the acidic wet beads in the measuring cup. The volume between the beads is also included in this value. The active element in the test material was the carboxyl group R-COOH, and a pH of 3-4 was obtained after equilibrating the beads with water. The concentration of the active groups corresponds to 2-3 mol per 1 L of wet resin.
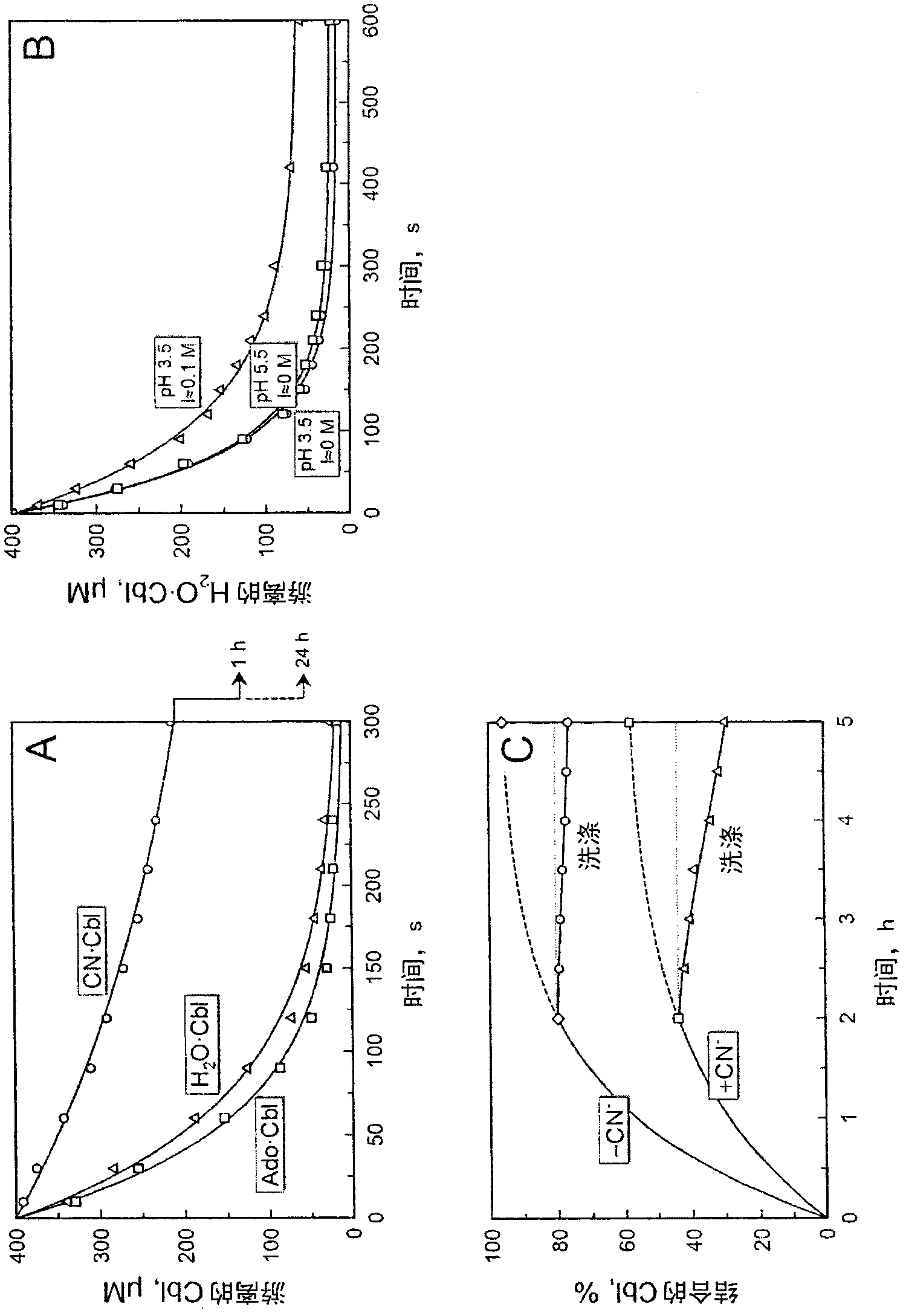
[0103] Three modified COOH-Amberlite (Cobalamion, IRC-76 and IRC-50) were used in the preliminary test, from which the most suitable adsorbent was selected. When batch conjugation was performed in water at a ratio of liquid:resin = 4:1, pH 3.5, 22°C, the beads interacted with H at the following rate coefficients: 2 O·Cbl binding: 1.2min -1 (Cobalamion), 0.3mi...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3 Binding of Cbl from fermentation broth to Amberlite Cobalamion
[0107] After preliminary experiments on the adsorption of pure cobalamin, a comparative binding analysis was performed on the fermentation broth provided by the B12 manufacturer. The solution contains natural cobalamin or CN·Cbl prepared by treatment with cyanide. In both cases, adsorption was performed batchwise at a ratio of liquid:resin = 10:1 (pH 3.7, 22°C). Incubation for 5 hours was sufficient to ensure about 95% and 60% binding of unused or cyanide-treated Cbl, respectively, image 3 c. The relatively slow process of combining the two can be explained by the apparent contamination of the resin combined with other components of the cell extract. The presence of contaminants on the surface of Cobalamion beads slows the permeation of Cbl through the bead pores and makes the process rate limiting. However, the binding of natural cobalamin in the fermentation broth to Cobalamion was 10-15 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com