Optical fiber laser and collimator thereof
A fiber laser and collimator technology, which is applied in the field of optical collimators, can solve the problems of large reduction in beam quality and high cost, and achieve the effects of reduced processing cost, low cost and simple manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
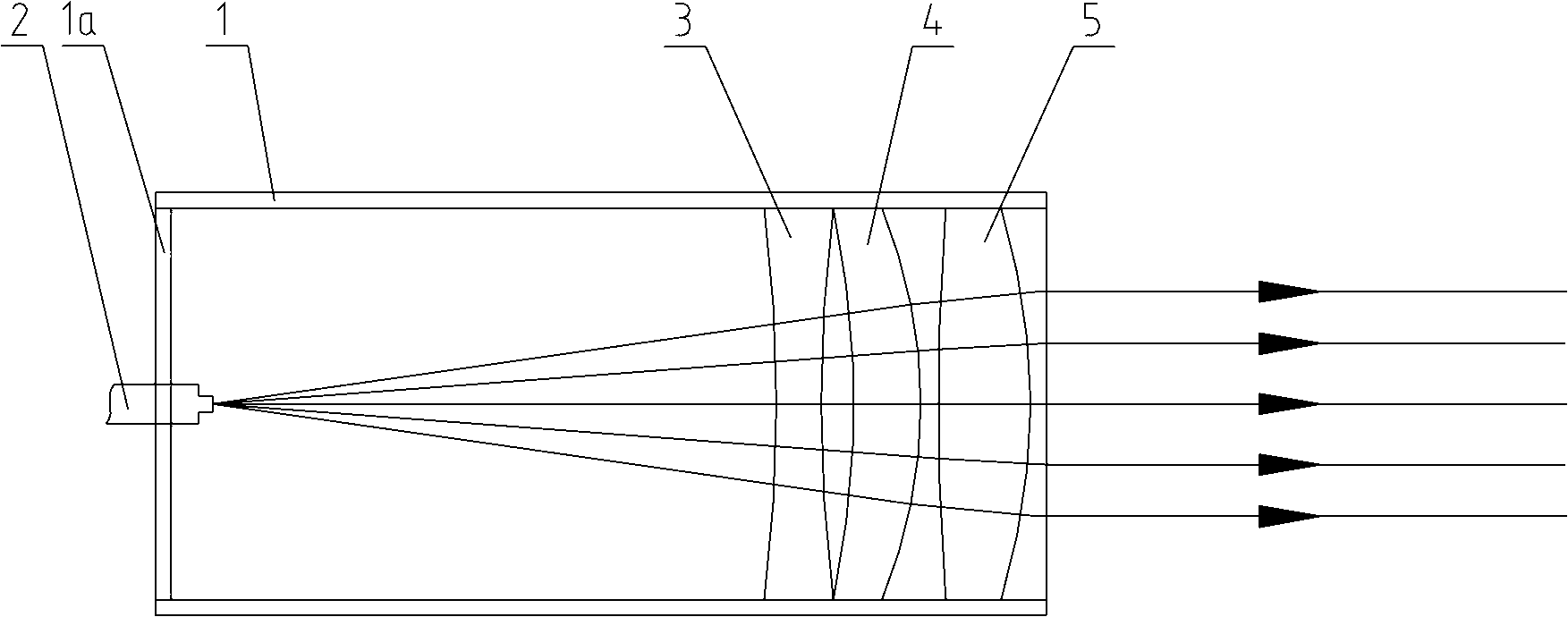
[0029] The structure diagram of one of the embodiments of the collimator of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, the collimator consists of a lens barrel 1, an output pigtail 2 fixed to the front end of the lens barrel 1, and a biconcave lens 3, a meniscus lens 4 and a biconvex lens 5 fixed in the lens barrel 1. The front end of the lens barrel 1 is closed by a support plate 1a, and the rear end of the output pigtail 2 extends into the lens barrel 1 from the middle of the support plate 1a. Biconcave lens 3, meniscus lens 4 and biconvex lens 5 are sequentially fixed in lens barrel 1 along the optical path, output pigtail 2 and three lenses 3, 4, 5 form a coaxial optical system, and the rear end surface of output pigtail 2 is located at The focal positions of groups 3, 4, and 5 of the three-piece lens. For ease of description, the surface of each lens that is closer to the output pigtail 2 along the optical path is defined as the front surface. Similarly, the surface ...
Embodiment 2
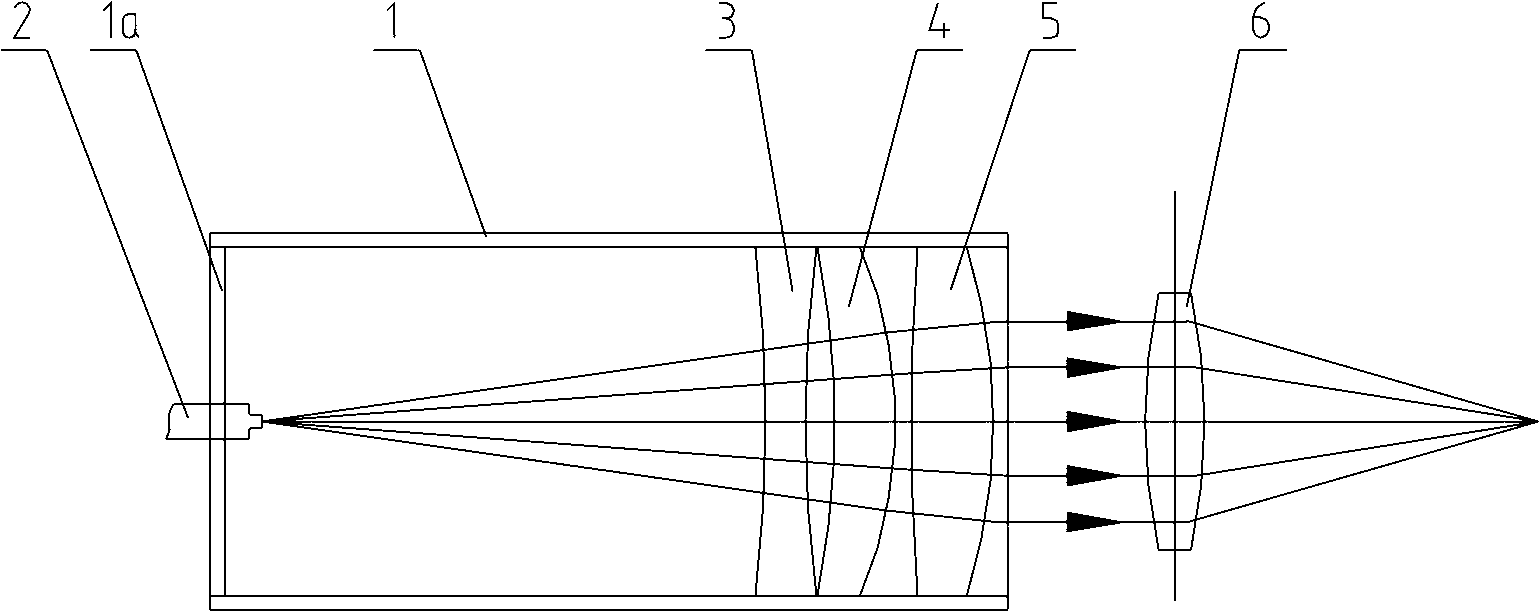
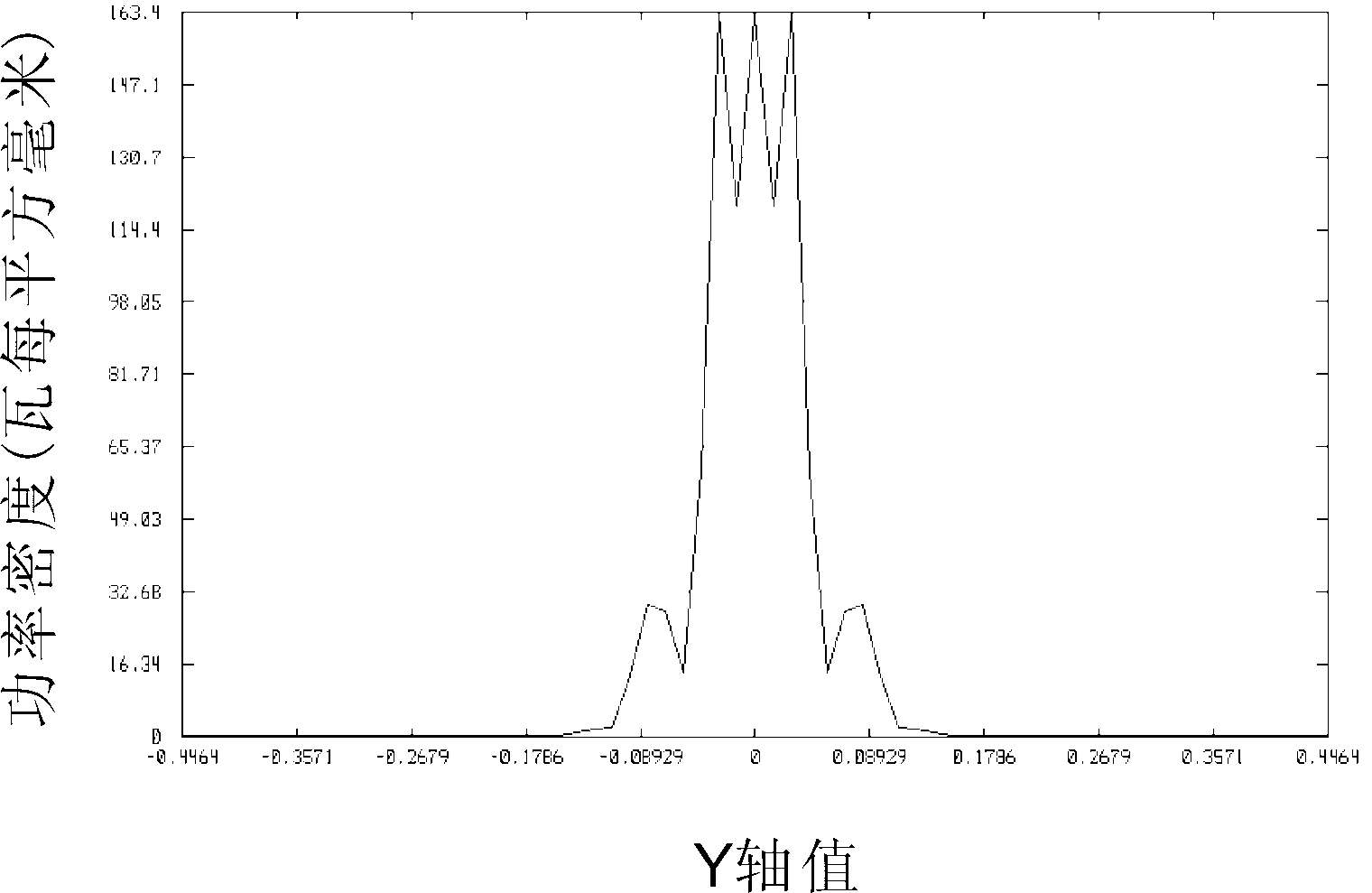
[0033] The structure diagram of one embodiment of the fiber laser of the present invention is as follows figure 2 As shown, the fiber laser comprises the collimator described in Embodiment 1 and a biconvex lens 6 with spherical aberration arranged behind the optical path of the collimator, the biconvex lens 6 with spherical aberration and the three lenses 3 of the collimator, 4, 5 groups with the same optical axis. The biconvex lens 6 with spherical aberration has a front and back curvature radius of 25 mm, a middle thickness of 2 mm, and is made of fused silica. The light beam output by the collimator passes through the biconvex lens 6 with spherical aberration and is focused at a place 26.67mm away from the rear surface of the lens. image 3 It is the power density distribution diagram at 26.67mm from the rear surface of the lens. It can be seen that the power density is approximately uniform. Figure 4 It is the light distribution diagram at 26.67mm from the rear surface...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as Figure 7As shown, the difference from Embodiment 2 is that the output pigtail 2 of the fiber laser in this embodiment is formed by fusing and connecting the single-mode optical fiber 21 at the front and the multi-mode optical fiber at the rear. The single-mode optical fiber 21 has a core diameter of 5um and a numerical aperture of 0.14. The core diameter of the multimode fiber is 50um and the numerical aperture is 0.22. After the single-mode laser coming from the single-mode fiber 21 enters the multi-mode fiber through the fusion point, multiple modes are excited, the power distribution tends to be uniform, and the homogenized beam is output through the collimator. The single-mode optical fiber 21 and the multi-mode optical fiber are connected by fusion, so there is little light loss.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com