Production method of low-carbon olefin
A technology of low-carbon olefins and production methods, which is applied in ethylene production, biological raw materials, molecular cracking to hydrocarbons, etc., and can solve the problem of low selectivity of low-carbon olefins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~2
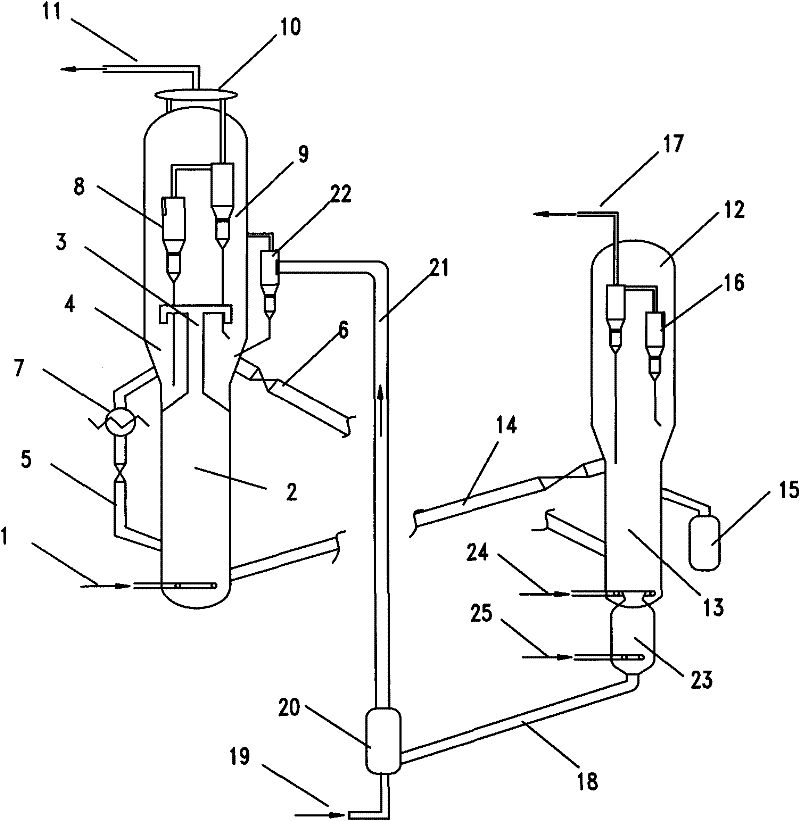
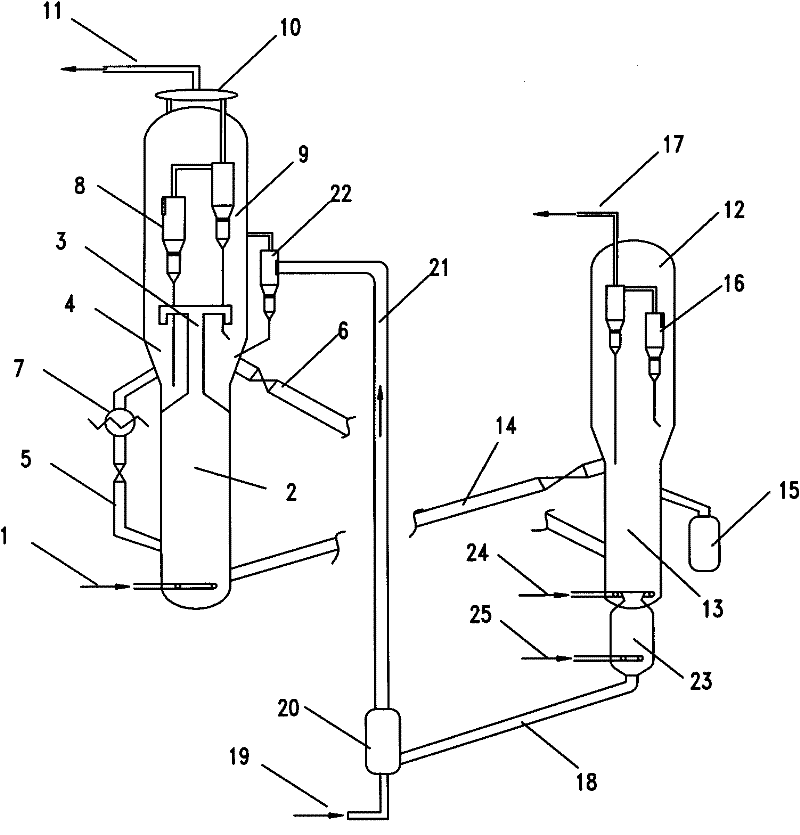
[0021] In a fast fluidized bed reactor, such as figure 1 As shown, the first reaction zone is a fast fluidized bed, the second reaction zone is a riser, and both the first regeneration zone and the second regeneration zone of the regenerator are turbulent fluidized beds. The raw material including methanol enters the first reaction zone of the reactor, and reacts to generate light olefins, and the gas phase product enters the subsequent separation section. After being stripped, part of the separated catalyst to be used is returned to the first reaction zone, and the other part enters the first regeneration zone to be regenerated by burning charcoal, and the regenerated catalyst in the first regeneration zone is returned to the first reaction zone. The rest of the catalyst in the first regeneration zone enters the second regeneration zone, the regenerated catalyst enters the second reaction zone to contact with raw materials, and the catalyst and product enter the separation zo...
Embodiment 3
[0025] According to the conditions described in Example 2, the average temperature in the first reaction zone is 400° C., the reaction pressure is 0.3 MPa in gauge pressure, pure methanol is fed, the methanol feed is 4.2 tons / hour, and the methanol weight hourly space velocity is 6 Hour -1 , the average carbon deposit of the catalyzer is 1% (weight), the catalyzer is SAPO-34, the reaction temperature in the second reaction zone is 500 ° C, the raw material is mixed carbon four, wherein the olefin content is 87%, and the mixed carbon four feed rate is 0.4 tons / hour, the reaction pressure is 0.3 MPa in gauge pressure, and the gas phase velocity is 5 m / s. Palladium / alumina CO combustion aid is added to the first regeneration zone, the content of palladium is 0.05% (weight), and the added amount accounts for 1% (weight) of the catalyst storage in the first regeneration zone. The carbon deposition amount of the regenerated catalyst in the first regeneration zone is 0.8% (weight), ...
Embodiment 4
[0027] According to the conditions described in Example 2, the average temperature in the first reaction zone is 460° C., the reaction pressure is 0.15 MPa in gauge pressure, pure methanol is fed, the methanol feed is 4.2 tons / hour, and the methanol weight hourly space velocity is 10 Hour -1 , the average carbon deposit of the catalyst is 2.7% (weight), the catalyst is SAPO-34, the reaction temperature in the second reaction zone is 620 ° C, the raw material is mixed carbon four, wherein the olefin content is 87%, and the mixed carbon four feed rate is 0.4 tons / hour, the reaction pressure is 0.15MPa in gauge pressure, and the gas phase velocity is 7 m / s. The carbon deposit of the regenerated catalyst in the first regeneration zone is 1.5% by weight, and the carbon deposit of the regenerated catalyst in the first regeneration zone is 0.05% by weight. The experimental results are: the yield of low carbon olefins at the outlet of the first reaction zone is 82.54% (weight), the y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com