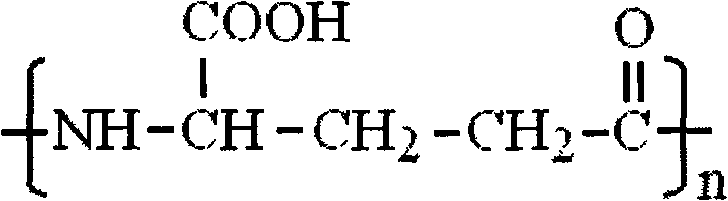Gamma-polyglutamic acid synthetic bacteria and fermentation method thereof
A technology of polyglutamic acid and fermentation products, applied in the field of γ-polyglutamic acid, which can solve the problems of difficult chemical reagent modification, difficult control of rheology, and restrictions on the application of γ-polyglutamic acid, and achieves a simple fermentation method Ease of operation, narrow molecular weight distribution, and easy-to-control conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
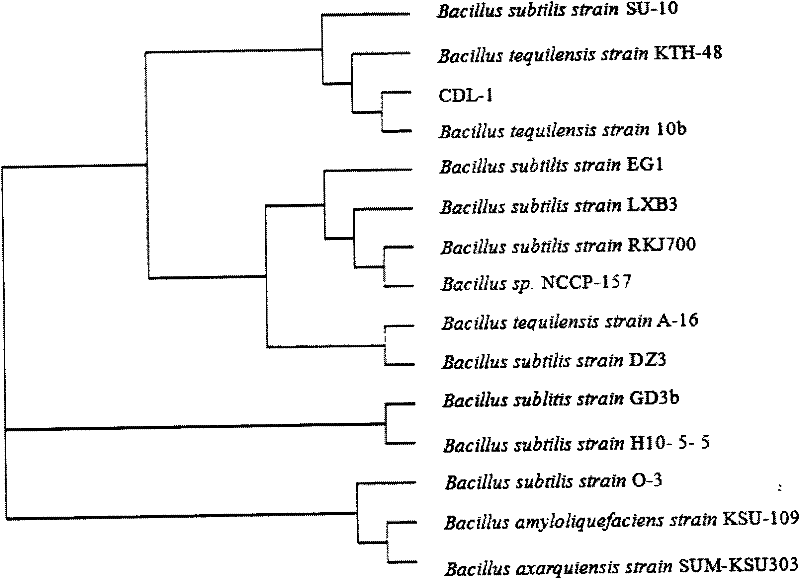
[0026] Example 1. Isolation and identification of Bacillus lincheniformis CDL-1
[0027] The strain was isolated from bean curd fermented food.
[0028] The specific implementation steps are as follows: take 1 g of the experimental material from the fermented food and put it into 100 ml of sterilized LB culture solution, and stir it magnetically for 30 minutes to make it evenly dispersed. Treat at 100°C for 15min, then place the Erlenmeyer flask in a shaker at 37°C, and shake at 170r / min for 12h to enrich the strains. Then use 0.85% physiological saline to dilute the bacterial solution 10 times. will be 10 -2 , 10 -3 200 μL of the two gradients were drawn from the coated solid plate, and placed in a 37°C incubator for 24 hours. Then observe the viscous single colony, pick it out and streak it on the solid plate for purification. The strain was identified as Bacillus licheniformis by Gram staining, 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis and BIOLOG microbial taxonomic identificati...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2. Fermentation of γ-polyglutamic acid by Bacillus lincheniformis CDL-1 and detection of physicochemical properties of fermentation products
[0030] 1) Strain activation: Bacillus lincheniformis CDL-1 preserved at -80°C was inoculated onto LB solid plates, and cultured at a constant temperature of 37°C for 24 hours;
[0031] (2) Seed culture: transfer the activated bacteria on the solid plate to 5ml seed culture medium, and culture at 37°C and 170rpm for 12 hours with shaking;
[0032] (3) Shake flask fermentation: insert the seed solution into the fermentation medium with an inoculum size of 1%, and shake and culture at 170 rpm for 24 hours at 37°C;
[0033] (4) Determination of the yield of γ-polyglutamic acid: adjust the pH of the fermented liquid to 6, 8000rpm, centrifuge at 4°C for 20 minutes to take out the bacteria, precipitate the supernatant with 4 times the volume of absolute ethanol, centrifuge at 6000rpm, and centrifuge at 4°C for 20 minutes. minut...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3. Determination of the molecular weight of the product after fermentation of Bacillus lincheniformis CDL-1 for 48 hours.
[0037] Shake flask fermentation, shaking culture 48 hours, other conditions are the same as embodiment 2. The results showed that the molecular weight of gamma-polyglutamic acid obtained by fermentation of Bacillus lincheniformis CDL-1 after 48 hours of cultivation was 347KD.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com