Method for separating and recovering valuable elements from neodymium-iron-boron wastes
A technology for separation and recovery, valuable elements, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as affecting product purity, and achieve the effect of improving purity
Inactive Publication Date: 2011-10-05
林剑
View PDF2 Cites 52 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
However, during the process of dissolving the rare earth elements in the waste into ions in the hydrochloric acid solvent, some iron elements in the waste are still dissolved into ions, which affects the purity of the product.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment
[0032]
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
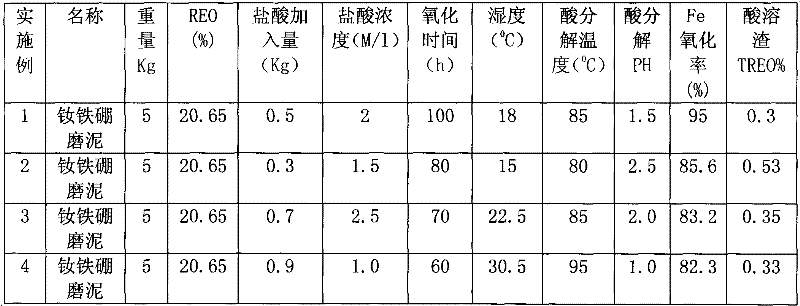
The invention relates to a method for separating and recovering valuable elements from neodymium-iron-boron wastes, comprising the following steps of: with the neodymium-iron-boron wastes as raw materials, carrying out air oxidation; finely grinding; carrying out acid decomposition; purifying iron slag; extracting, and separating; precipitating through carbonic acid; washing, and dewatering; burning rare earth; extracting and recovering cobalt and copper; precipitating the cobalt through the carbonic acid, and the like so as to obtain high-purity single rare earth oxide and high-purity cobaltcarbonate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the preferential leaching of rare earth elements contained in the neodymium-iron-boron wastes is realized and the leaching of iron is inhibited in the acid decomposition process; after hydrochloric acid is added to the neodymium-iron-boron wastes, air oxidation pretreatment is carried out so that a part of metallic iron powder is transformed into iron dichloride which is then oxidized into iron oxide red difficult to dissolve in the hydrochloric acid; and iron elements are mostly separated in the shape of the iron slag in the acid decomposition process, and therefore the purity of products is greatly enhanced.
Description
Technical field [0001] The invention relates to a rare earth metallurgy technology, in particular to a method for separating and recovering valuable elements from NdFeB waste. Background technique [0002] Rare earth resources are strategic resources and non-renewable resources. With the sharp increase in the demand for rare earths in color developers, magnets and electronics industries, it is particularly important to reasonably and effectively improve the utilization of rare earth resources. Using NdFeB waste to recover rare earth elements is one of the important means. Moreover, the use of NdFeB waste to recover rare earth elements has many advantages, such as shortened procedures, reduced costs, and reduced "three wastes" compared with the use of ore to produce rare earth products. At present, the main sources of NdFeB waste are: (1) the furnace pool produced by vacuum smelting, the ultrafine powder produced in the milling process, and the grinding mud produced in the g...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): C22B7/00C22B3/10C22B3/22C22B3/38C22B3/46C22B23/00C22B59/00
CPCY02P10/20
Inventor 林剑
Owner 林剑
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com