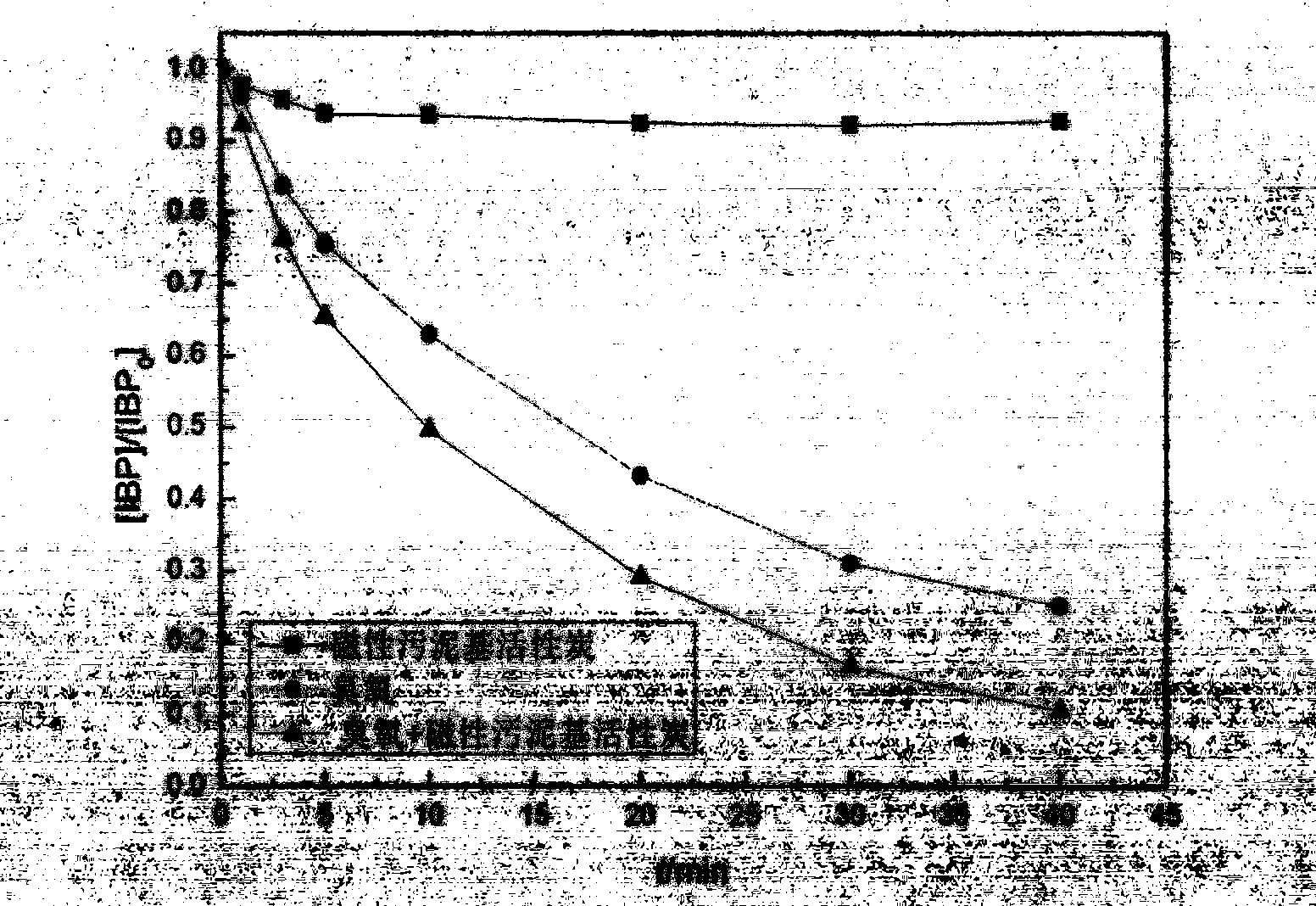
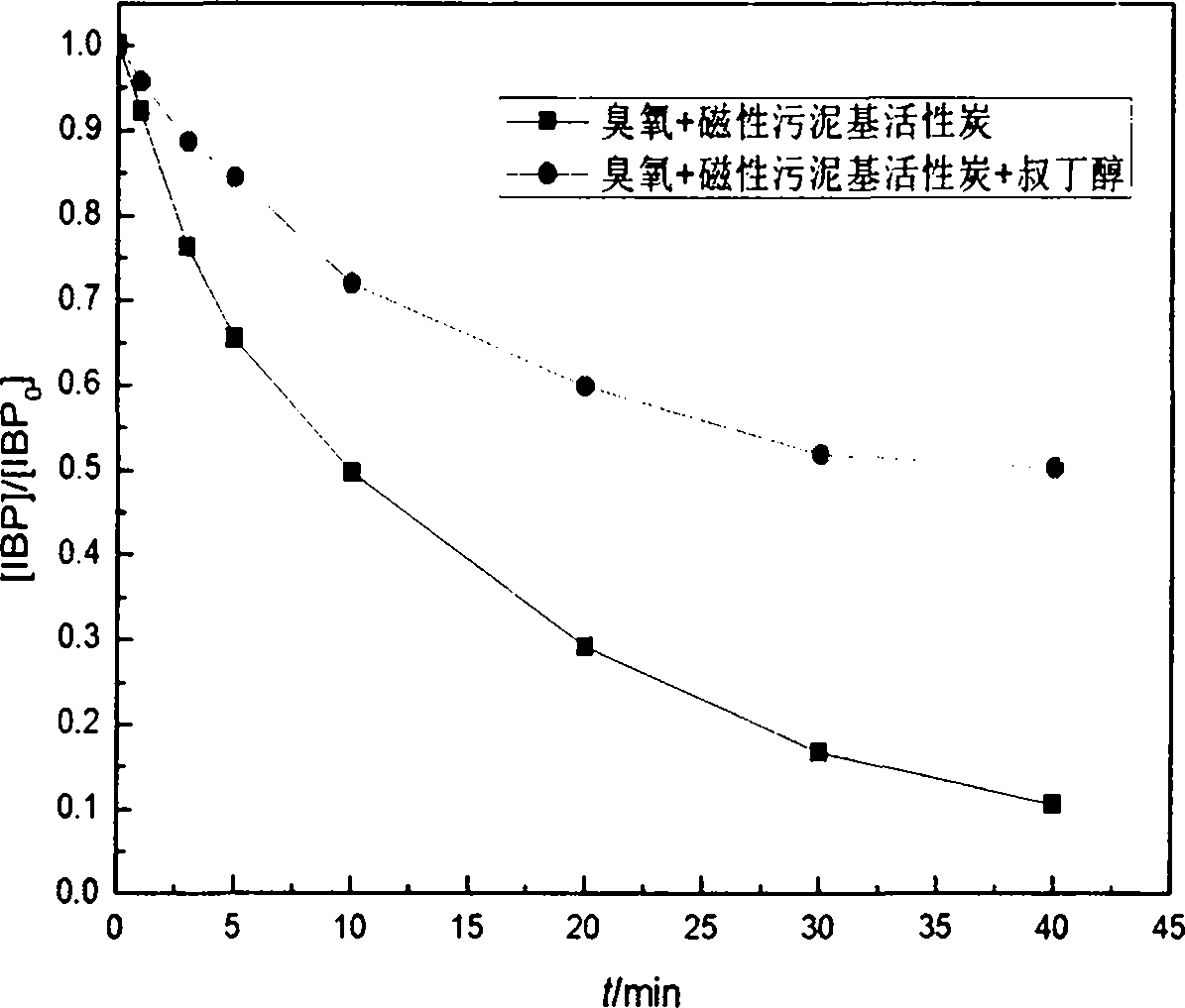
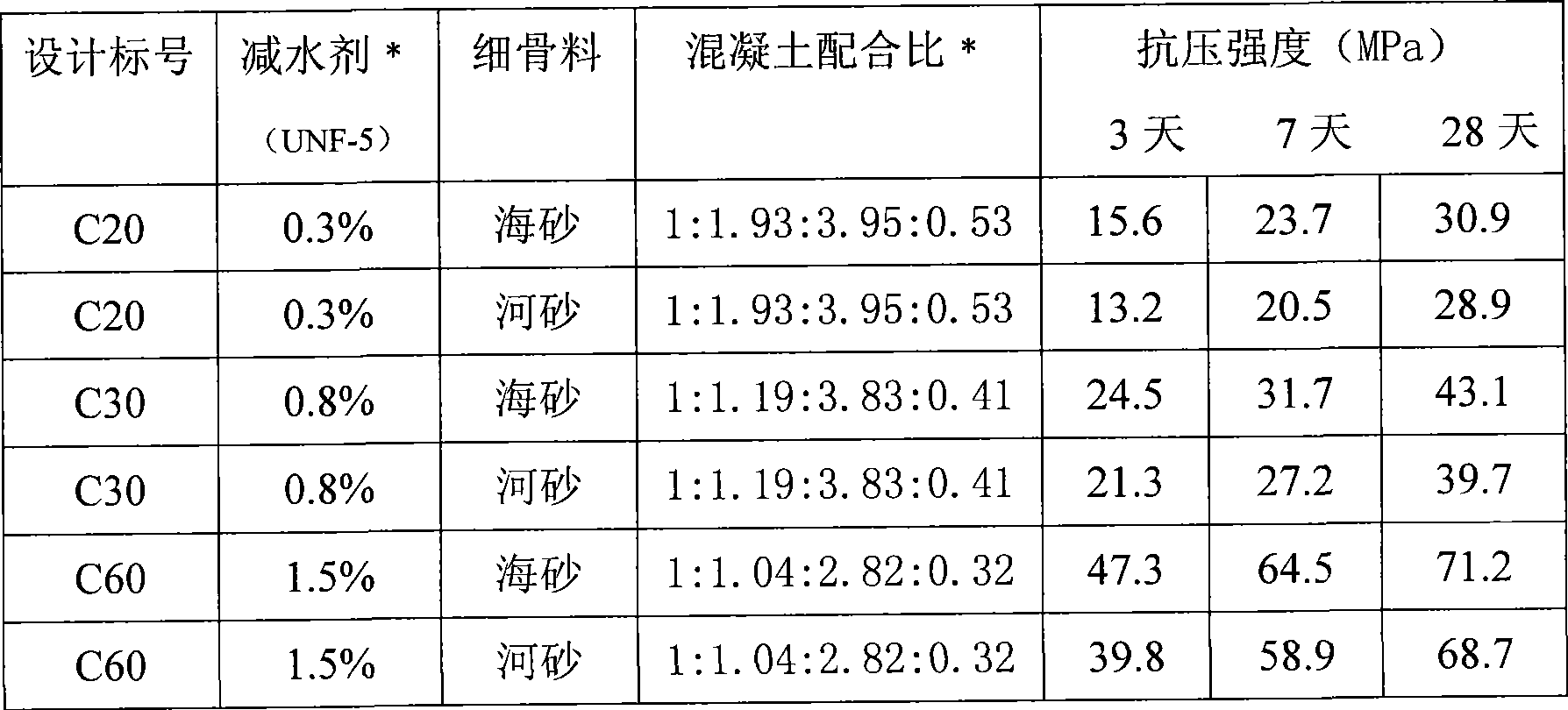
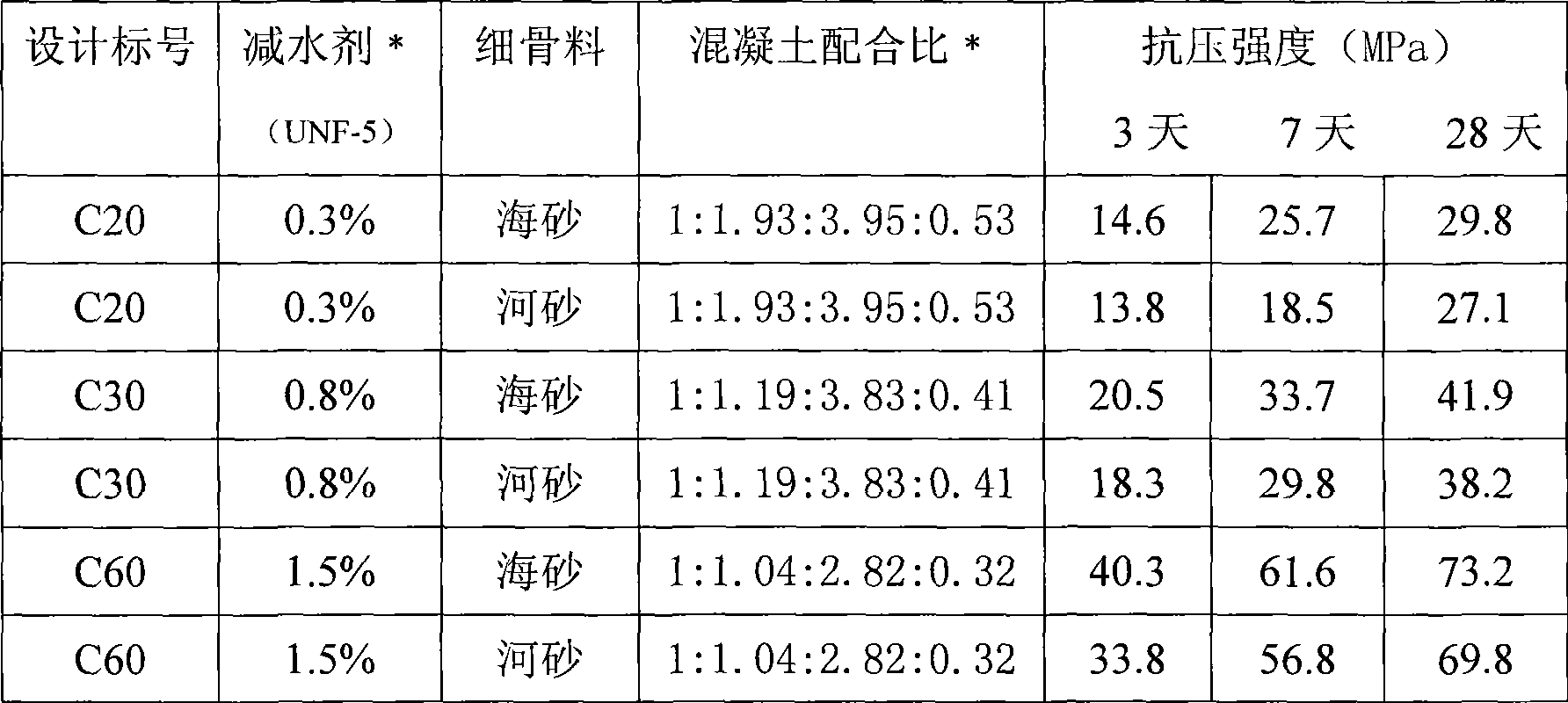
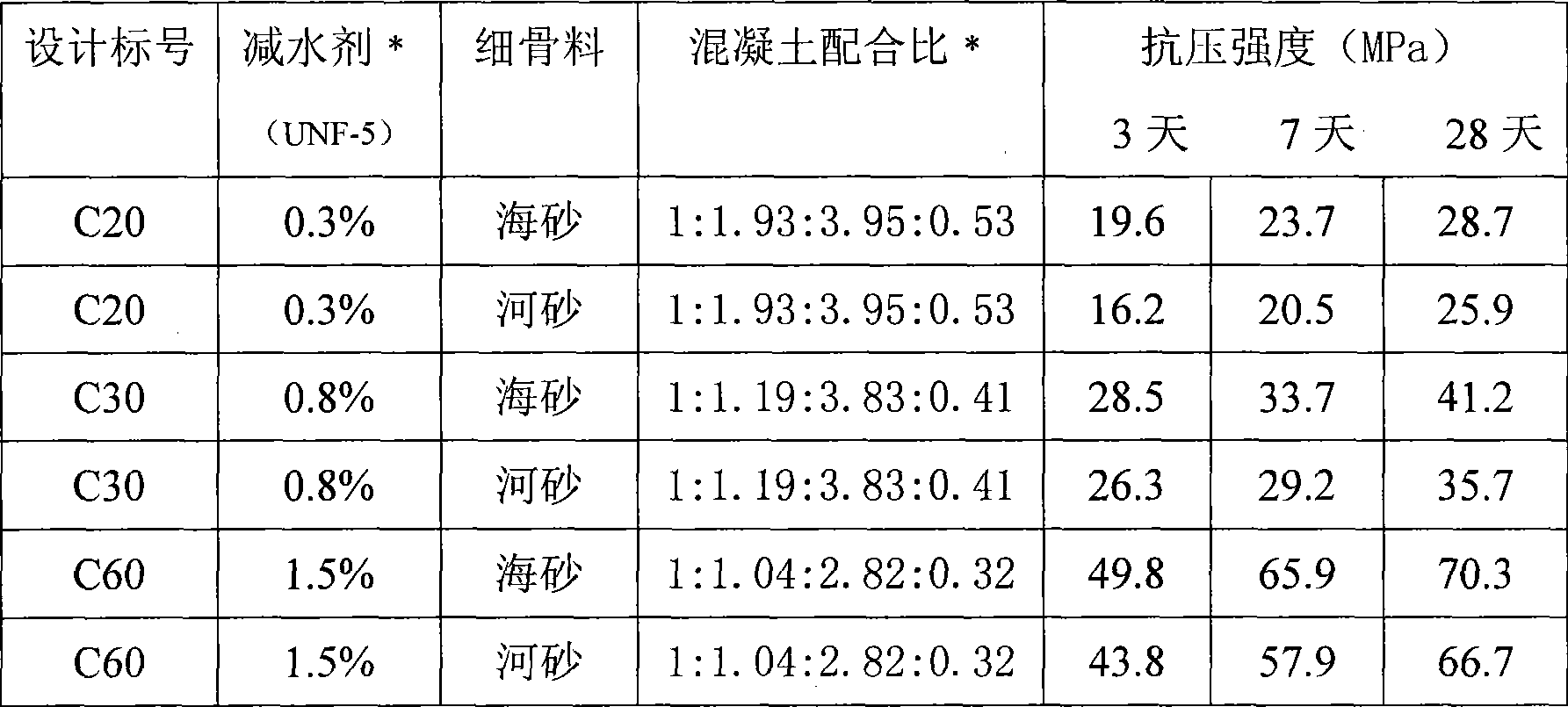
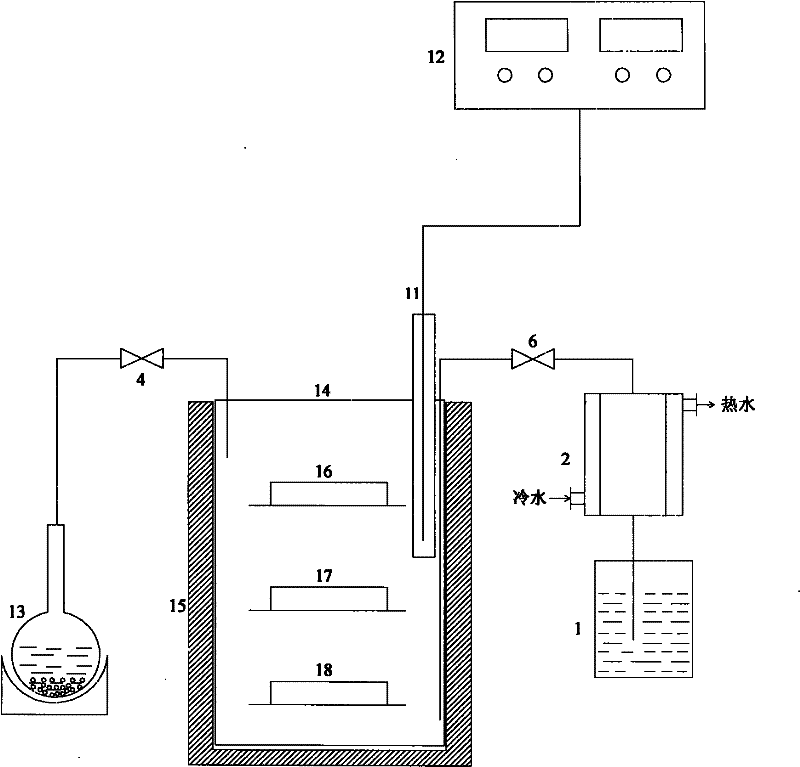
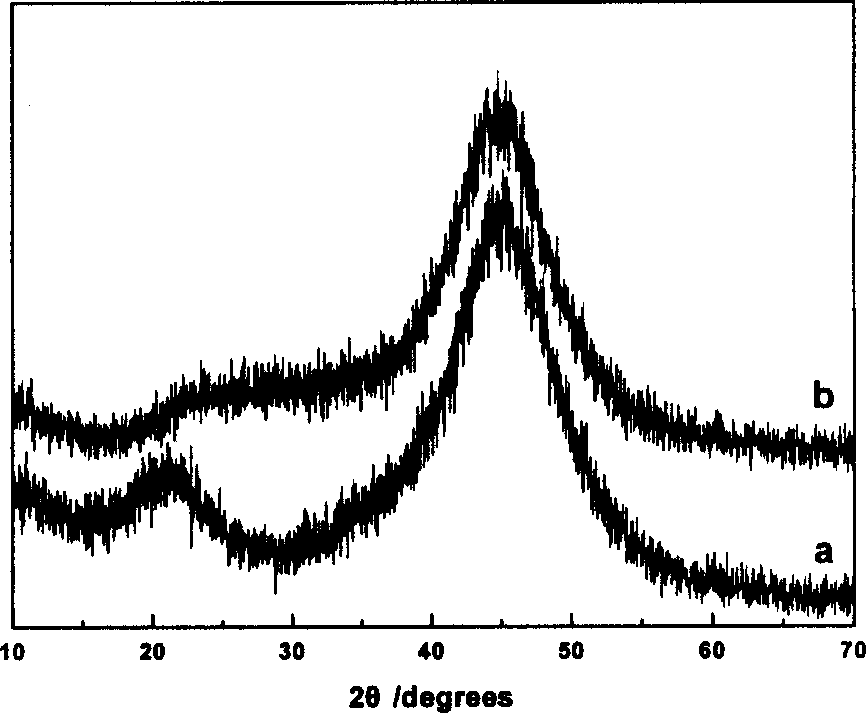
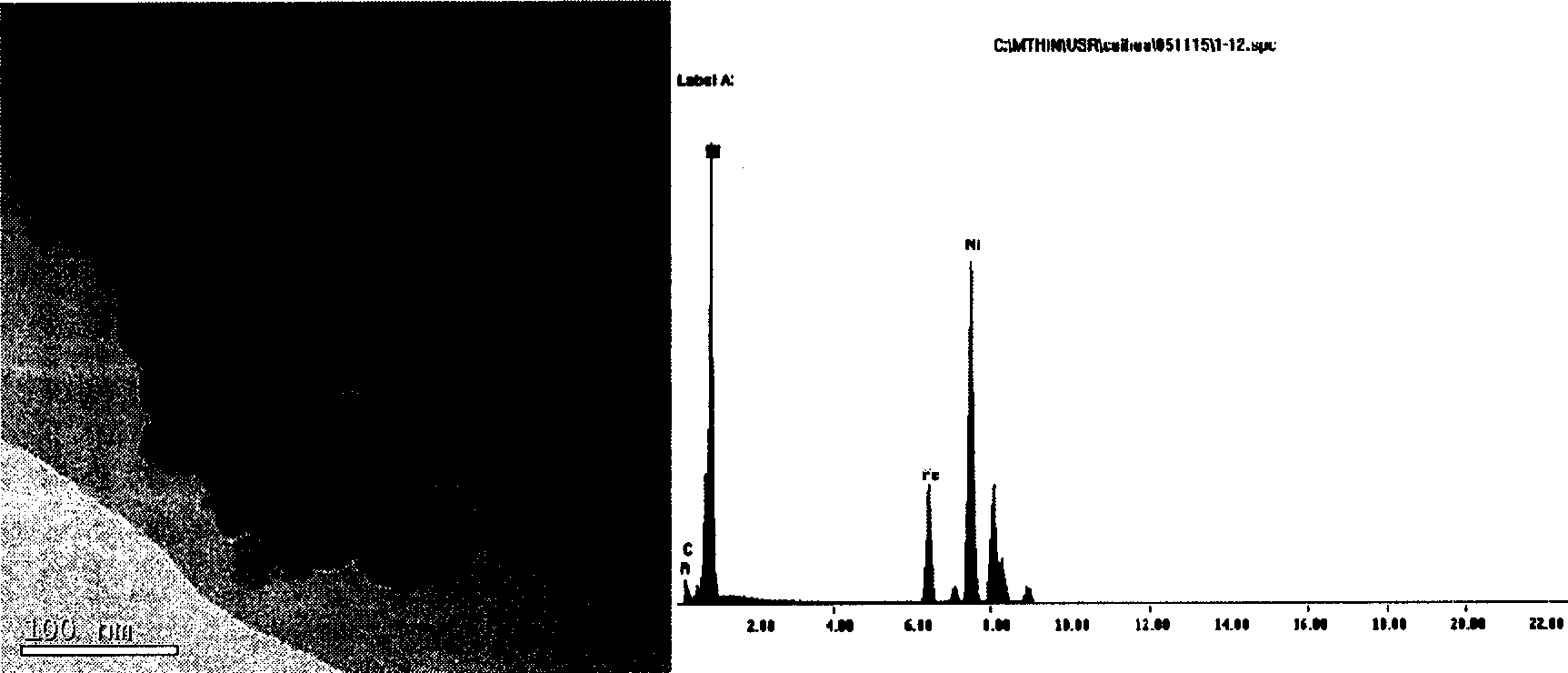
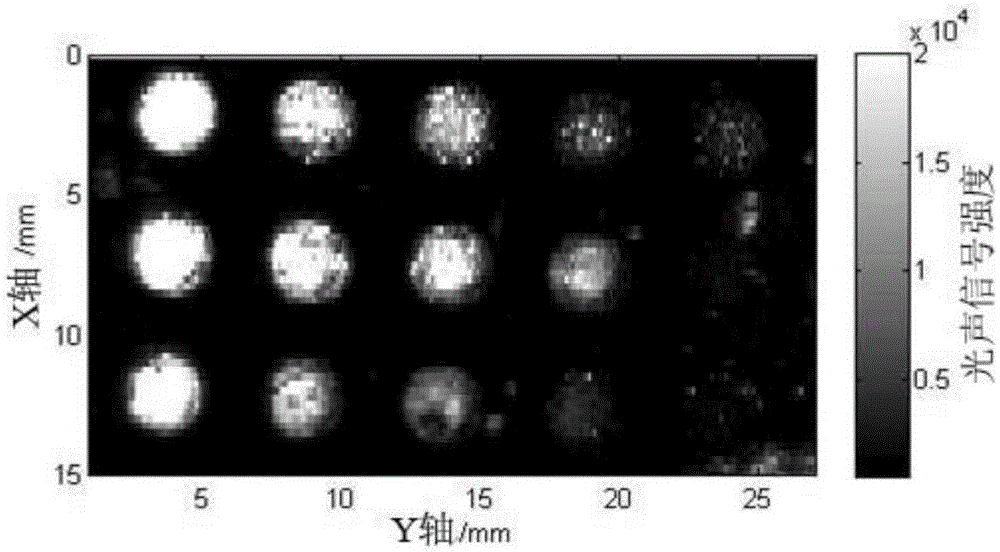
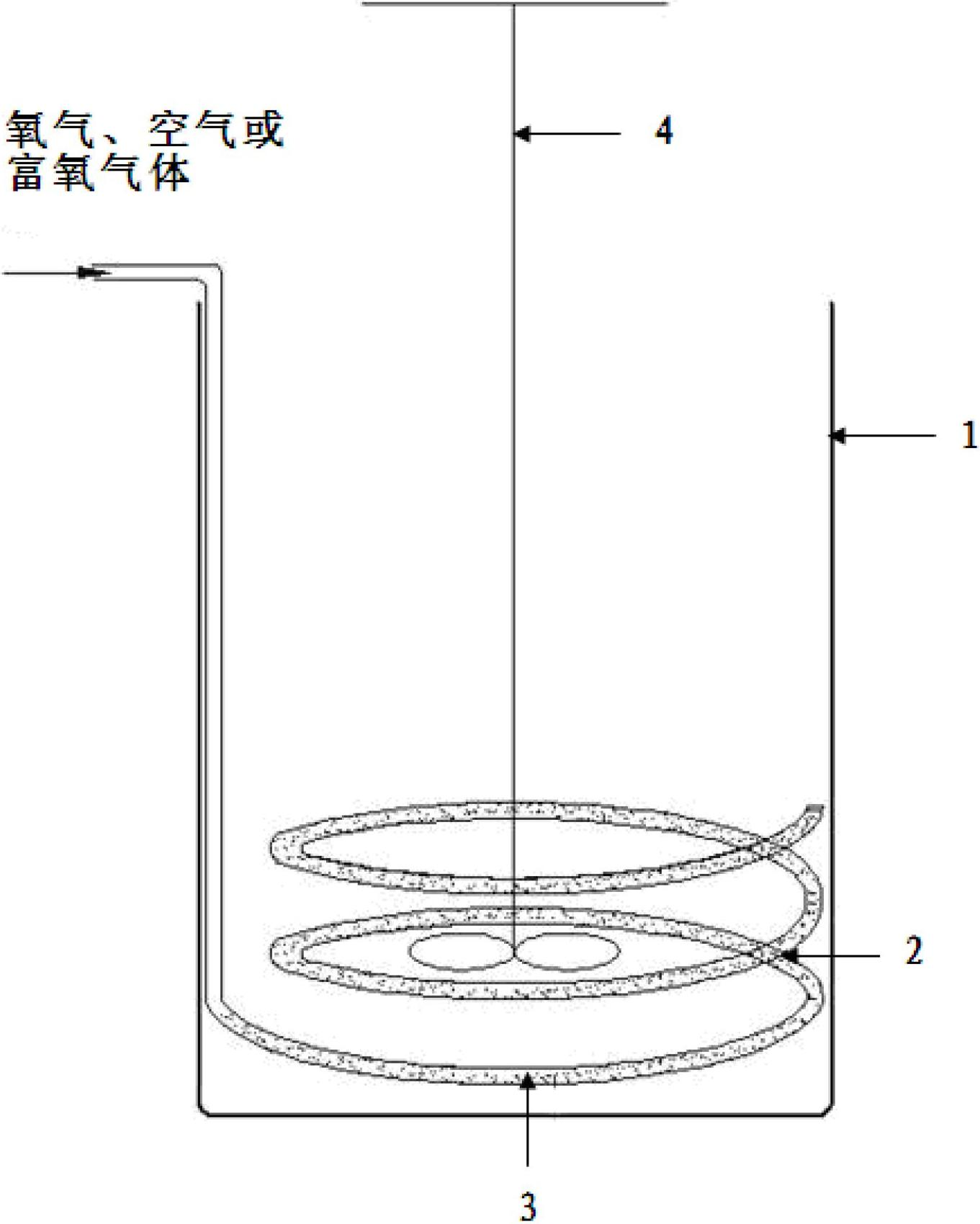
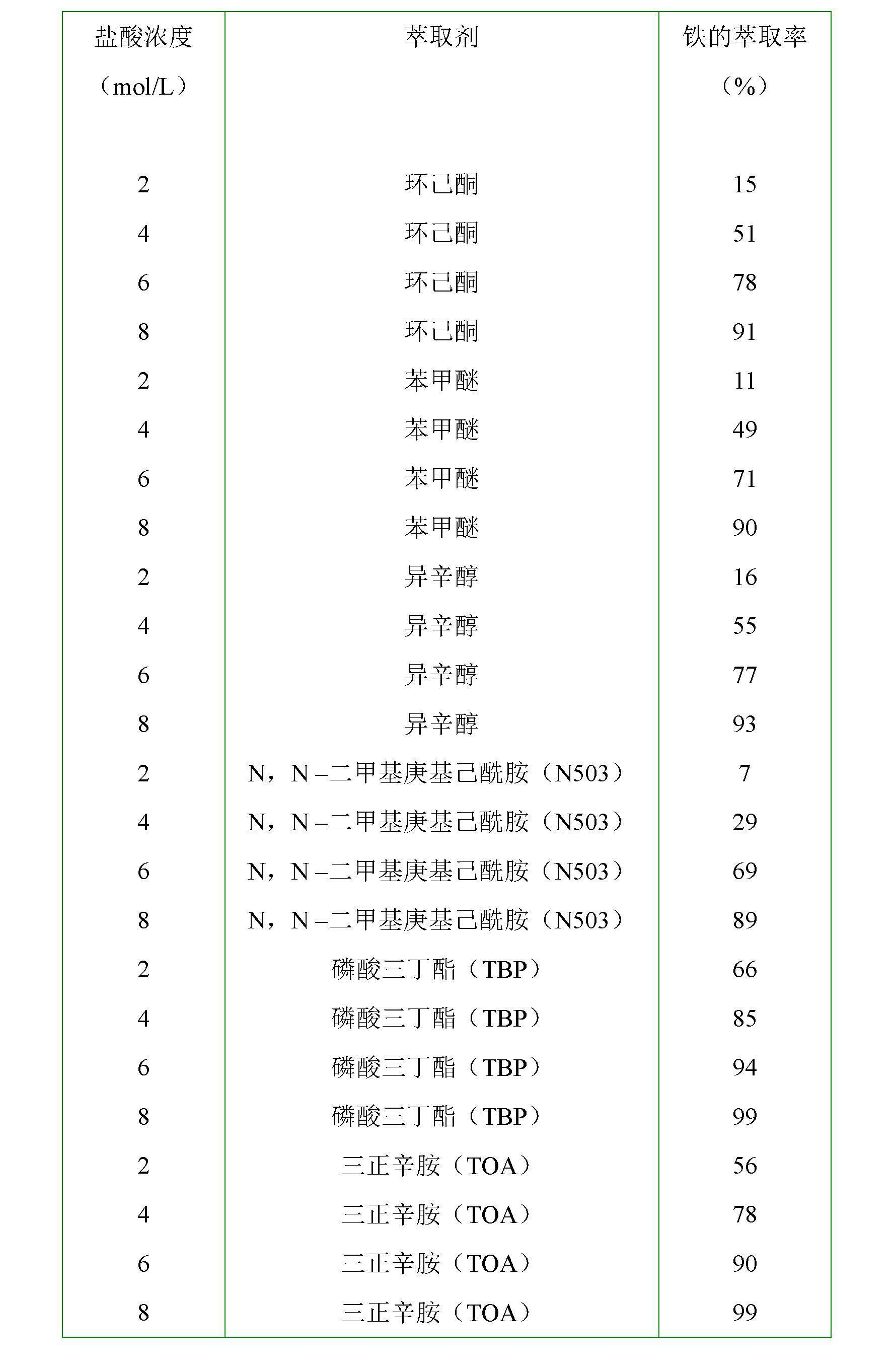
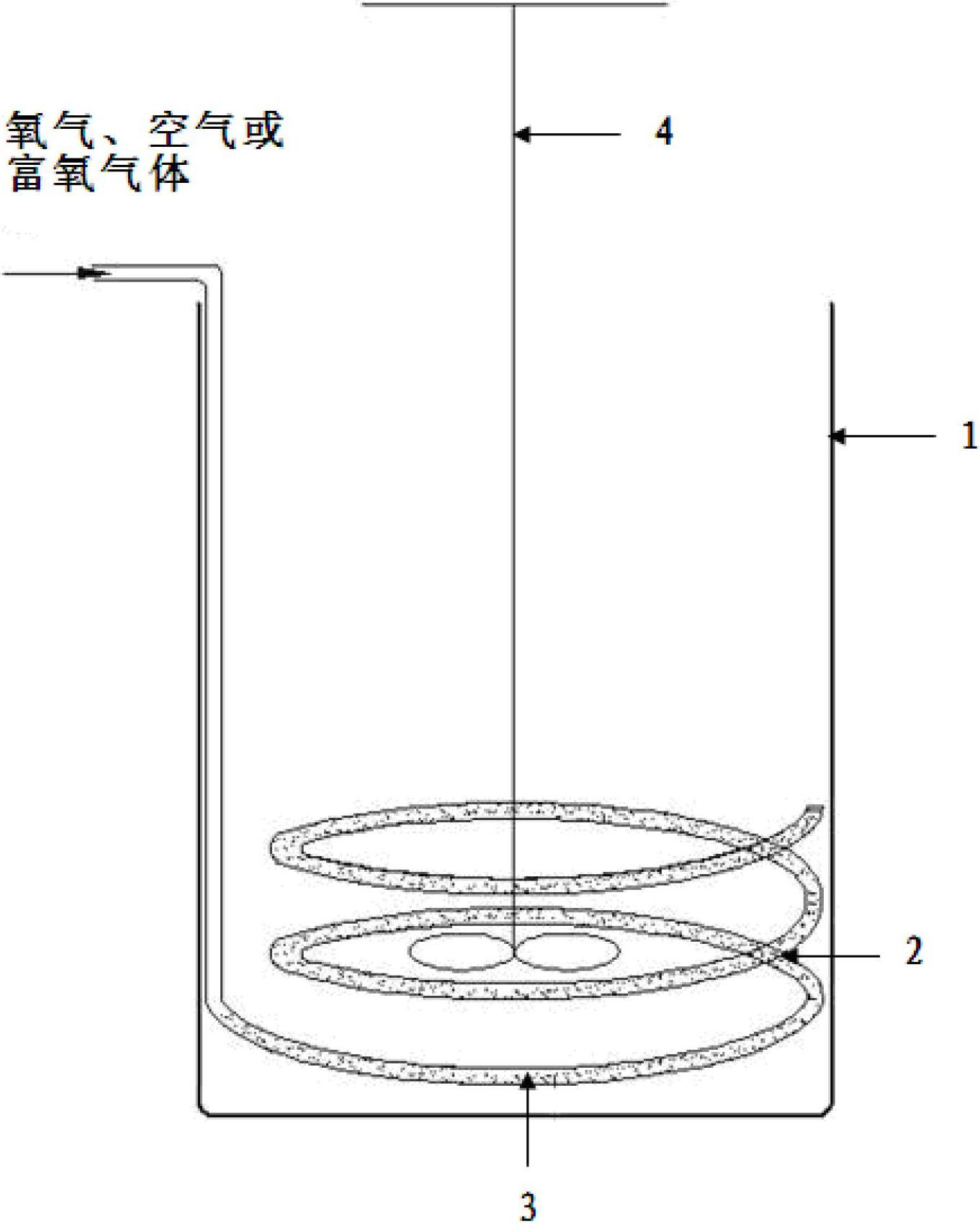
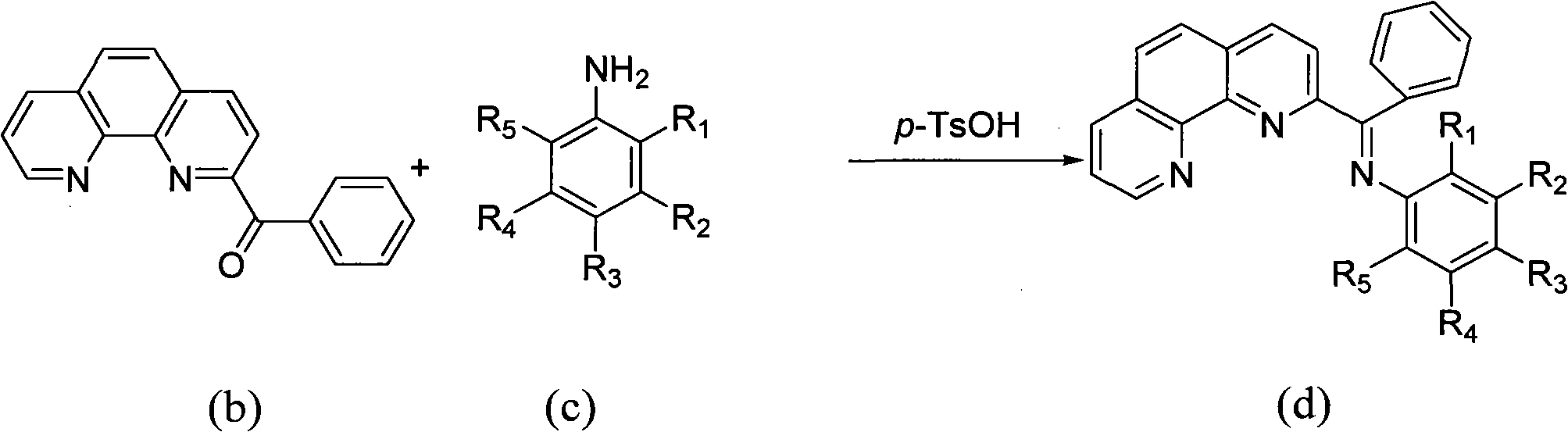
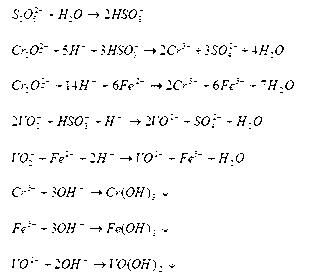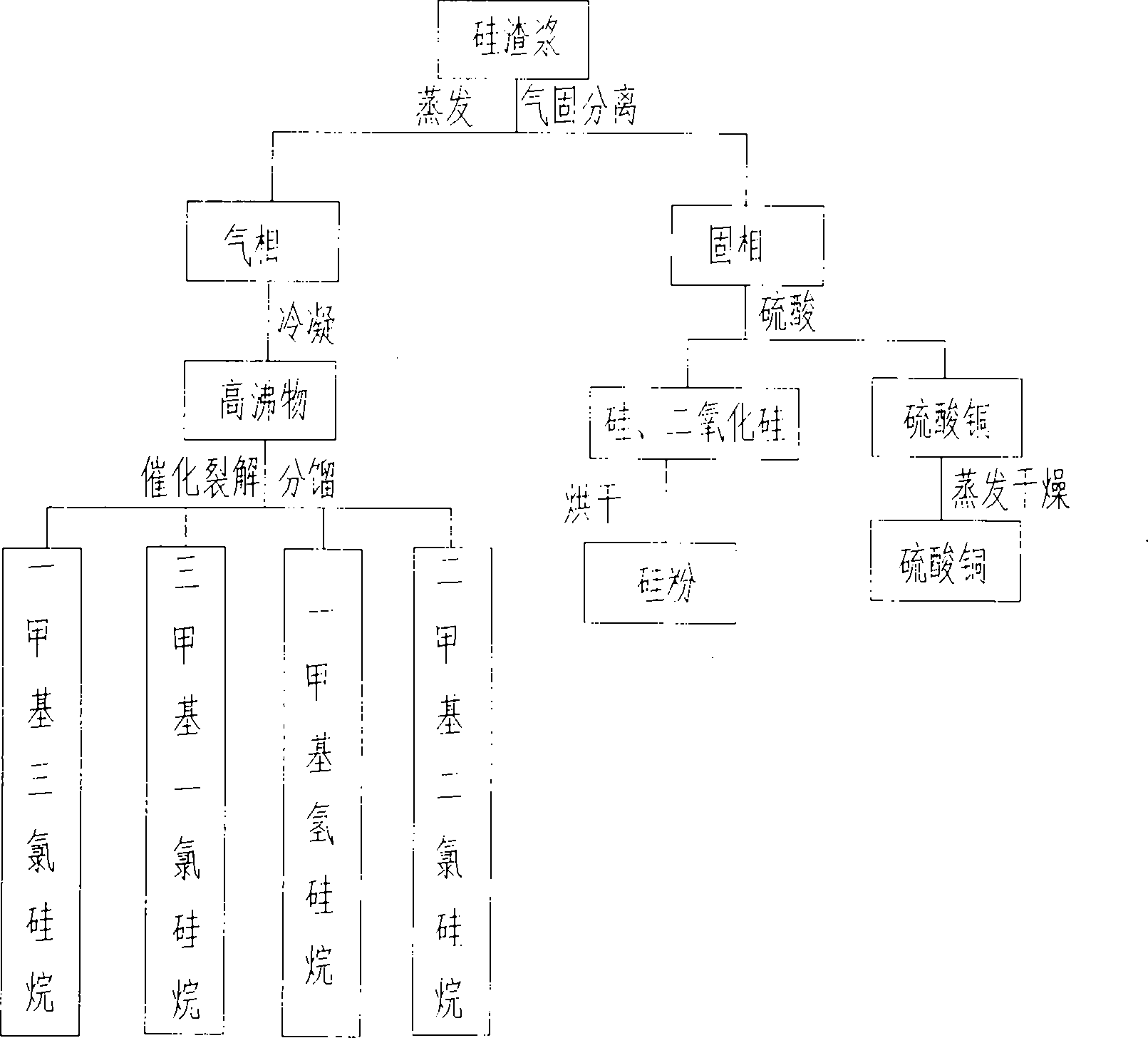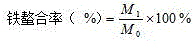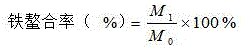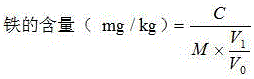Patents
Literature
524 results about "Iron(II) chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl₂. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl₂ crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
Method for manufacturing magnetic sludge-based active carbon
InactiveCN103406094ASolve environmental problems caused by improper disposalLow running costSludge treatmentOther chemical processesSludgeCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing magnetic sludge-based active carbon by taking redundant sludge in an urban sewage treatment plant as main raw materials and aims to solve the problem that existing active carbon catalysts are difficult to be recycled. The method comprises the steps of immersing the dried redundant sludge in a ferric chloride and ferrous chloride mixing solution activation agent for activating for 24 hours, dripping ammonia water, putting the mixture into a drying box with the temperature of 105 DEG C for drying, carbonizing and activating the mixture in a muffle furnace, cleaning the mixture with distilled water, grinding and screening products, and performing magnetic separation to obtain the magnetic sludge-based active carbon. The magnetic sludge-based active carbon manufactured by the method is very convenient to separate and recycle and is extremely high in catalytic oxidation capacity and heavy metal adsorption capacity.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Low alkalinity gel material for preparing concrete artificial reef and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a low-alkalinity gel material for manufacturing artificial concrete fishing rocks and a preparation method thereof. The low-alkalinity gel material for manufacturing the artificial concrete fishing rocks is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by weight percentage: 40 to 80 percent of blast-furnace water-granulated slag, 5 to 25 percent of fly ash, furnace slag, self-igniting coal slack or oil shale slag, 10 to 30 percent of natural dihydrate gypsum, anhydrite, semi-hydrated gypsum, desulfurated gypsum, phosphogypsum or fluorgypsum, and 1 to 5 percent of ferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric chloride, ferrous chloride, ferric nitrate or ferrous nitrate. The raw materials are independently ground or mixed and ground until the specific surface area is between 500 and 800 square meters per kilogram, and uniformly mixed to obtain the low-alkalinity gel material for manufacturing the artificial concrete fishing rocks. The gel material can not generate Ca(OH)2 after hydration. The pH value of the surface of concrete prepared by the gel material can be the same as that of seawater in natural sea areas, so that the concrete is favorable for propagation of algae, microorganisms and hydrophyte which are favorable for fish, shrimps and seashells; and simultaneously, the concrete has high strength, so as to meet the demands of constructing the artificial fishing rocks and resisting impact of ocean tides and ocean waves.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Prussian-blue type sodium ion battery positive electrode material and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN106920964AImprove performanceImprove structural stabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsOctahedronConcentration gradient
The invention discloses a prussian-blue type sodium ion battery positive electrode material and a preparation method therefor. According to the material, iron ions in iron-nitrogen octahedron in prussian-blue crystal lattices are substituted by transitional metal elements from the interiors to the surfaces of crystal particles based on concentration gradient; the molecular formula of the positive electrode material is Na<x>M<y>Fe<1-y>[Fe(CN)<6>]<z>.nH<2>O, wherein M is a substituting element. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving sodium ferrocyanide, ferrous chloride, and a mixture of substituting element chloride and ferrous chloride into deionized water separately to obtain each precursor solution; then performing a co-precipitation reaction to obtain a prussian-blue turbid liquid, wherein the substituting element is distributed from the interiors to the surfaces of the crystal particles based on concentration gradient; and performing centrifuging, washing and vacuum drying to prepare the positive electrode material. The positive electrode material has the characteristics of high capacity, high cycling stability, simple preparation and the like.
Owner:湖州超钠新能源科技有限公司
Preparation method of roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite and application of roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite in adsorption of arsenic-polluted wastewater
InactiveCN103769037AReduce processing costsEasy to recycleOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionFiltrationCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method for roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite and application of the roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite in the adsorption of arsenic-polluted wastewater. According to the preparation method for synthesizing the roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite, manganese chloride and ferrous chloride are used as raw materials, and a required product is obtained by the steps of co-precipitation, crystallization, centrifugation, filtration, washing, drying, grinding, roasting and the like. When the roasted ferro-manganese hydrotalcite is used for adsorbing arsenic-containing wastewater, the adsorption capacity reaches 6.8mg / g, and high adsorption performance is exhibited. In addition, 95 percent of saturated adsorbing capacity can be achieved within 2 hours, so that the time cost of arsenic-containing wastewater treatment is greatly lowered. The adsorbed material can be separated from a water body for recycling in a centrifugation way, so that secondary pollution is alleviated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for recycling iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution
ActiveCN105696010ATake advantage ofSolve the problem of no separation and recyclingProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideChloride
The invention discloses a method for recycling an iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution. The method specifically comprises the following steps that 1, acid consuming and reducing are carried out, acidity is made to meet the requirement, and ferric iron in waste acid is reduced into ferrous iron; 2, zinc and iron are extracted and separated, and a ferrous chloride solution is obtained; 3, an organic phase transfers zinc into a strip liquor through reverse extraction, and the organic phase is extracted for reuse; and 4, the strip liquor is subjected to subsection kalizing treatment, zinc hydroxide is obtained, and the strip liquor is reused. According to the method, iron and zinc are separated through different extracting capacities of N235 to the ferrous iron and zinc, and therefore pure ferrous chloride liquid and zinc hydroxide solids are obtained. Ferrous chloride can be oxidized into ferric trichloride, and ferrous chloride and ferric trichloride both can be used as a water treatment agent; and zinc hydroxide can be used as a raw material for preparing zinc oxide or zinc chloride.
Owner:3R ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Method for recycling traditional chromium residue
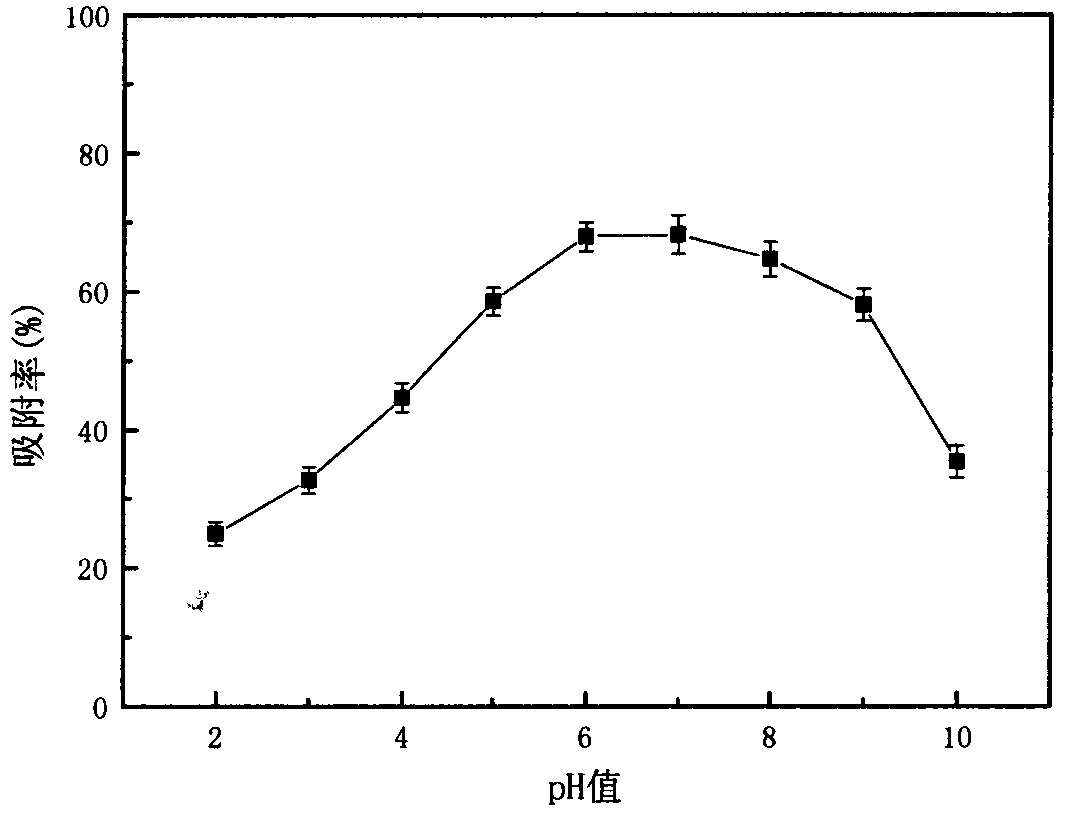
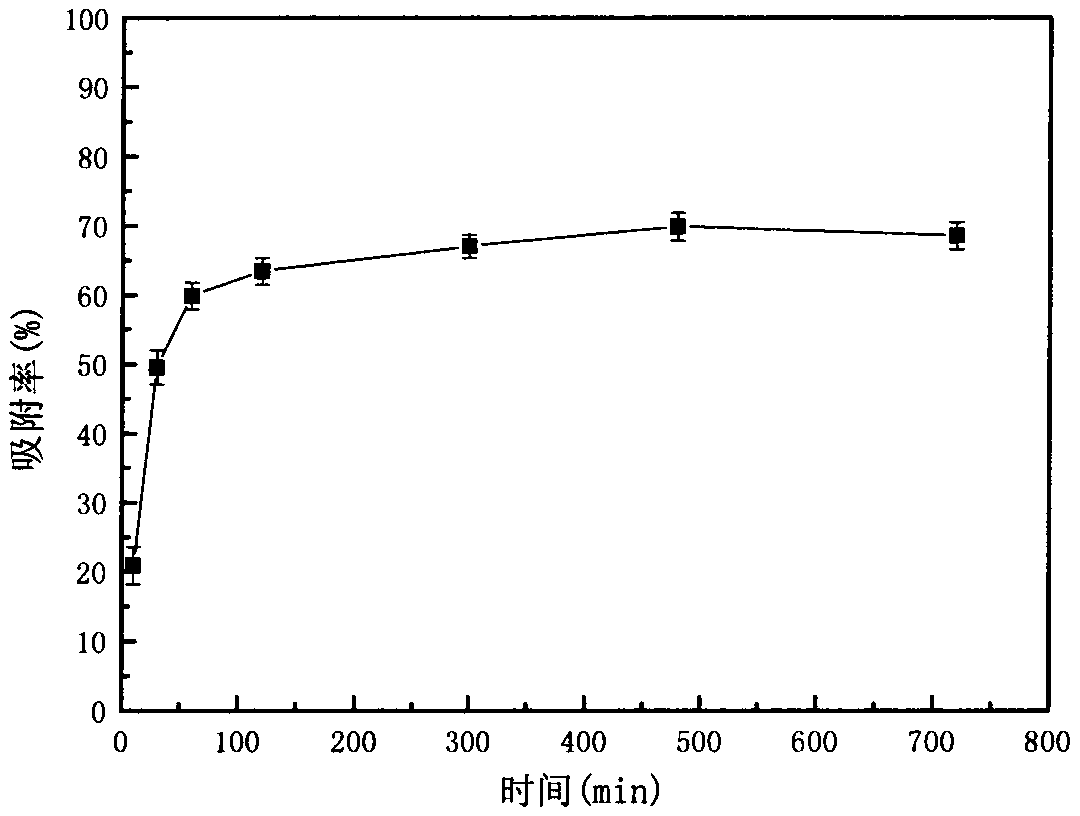
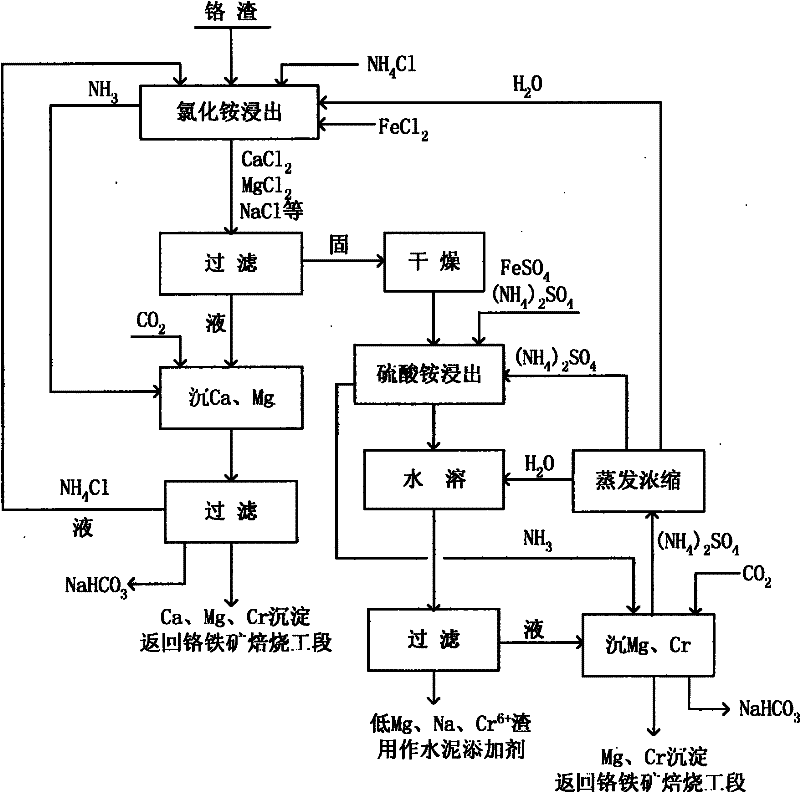
The invention relates to a method for recycling traditional chromium residue, in particular to a method for recycling the traditional chromium residue by replacing strong acid (hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid) with an ammonium salt (ammonium chloride or ammonium sulfate) of the strong acid. In the method, chromium residue generated in the traditional calcium roasting production process for sodium bichromate is taken as a treatment object, ammonium salts (including ammonium chloride and ammonium sulfate) of the strong acid and reducing ferrous salts (including ferrous chloride and ferrous sulfate) are adopted to make calcium, magnesium, sodium, chromium and the like in the chromium residue form soluble chloride or sulfate, then the calcium, the magnesium and the chromium are precipitated by utilizing ammonia released by decomposing the ammonium salts and adding carbon dioxide, and are returned to the calcium roasting production process for the sodium bichromate to realize the circulation, ammonium chloride and ammonium sulfate regenerated by reacting with the chloride and the sulfate are recycled, and final slag is used as a raw material of cement after the treatment. In the method, the strong acid is not added, so the requirements on equipment materials are reduced; and the recycling of elements such as calcium, magnesium, chromium and the like greatly reduces the amount of the final slag, and greatly improves the utilization rate of traditional chromium residue raw materials.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing mica titanium nacreous material
InactiveCN101235227ANo sintering phenomenonIdeal powder productInorganic pigment treatmentIron saltsSulfate
The invention belongs to the pearlescent pigment preparation process field, particularly relating to a preparation process of mica titanium pearlescent pigment. The process of the invention comprises adopting titanium tetrachloride solution which is partially transformed into titanyl sulfate, ferric trichloride solution and ferrous chloride solution or mixed solution of titanium salt and iron salt as deposition agent, adopting carbamide as neutralizing agent, wherein carbamide adopts the way of filling in batch, and hydrolyzing titanium salt, iron salt or mixed salt of titanium salt and iron salt to prepare mica pearlescent pigment. The process of the invention has the advantages of simple making art and easy operation, and the mica pearlescent pigment product which is prepared has even and compact titanium dioxide, di-iron trioxide film structure on the surface of the product, silver white product has high whiteness and strong pearlescent effect, and neon or color product has saturated color and strong pearlescent effect.
Owner:北京首纳东方科技有限公司
Method for preparing NiB non-crystalline alloy catalyst with the aid of microwave
InactiveCN1792440ACluster size controllableGood dispersionCatalyst carriersHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical platingIron(II) chloride
A microwave aided process for preparing the catalyst of non-crystalline NiB alloy suitable for catalytic hydro-reaction with high catalytic active features that the chemical reduction and chemical plating in microwave field is used, KBH4 is used as reducer, its primary salt is chosen from nickel sulfate, nickel acetate, etc, its secondary salt is chosen from cobalt chloride, iron chloride, etc, its carrier is chosen from oxide, molecular sieve, etc, its solvent is chosen from water, tetrahydrofuran, etc and the complex agent, stabilizer and additive is used.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation of acetyl-substituted-1,10-phenanthroline complex and application of prepared complex as catalyst
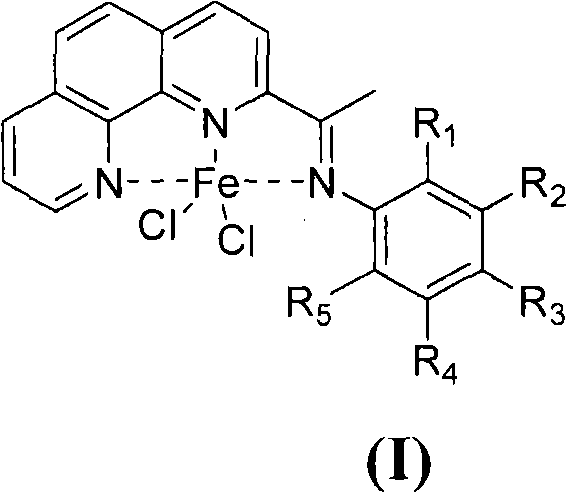
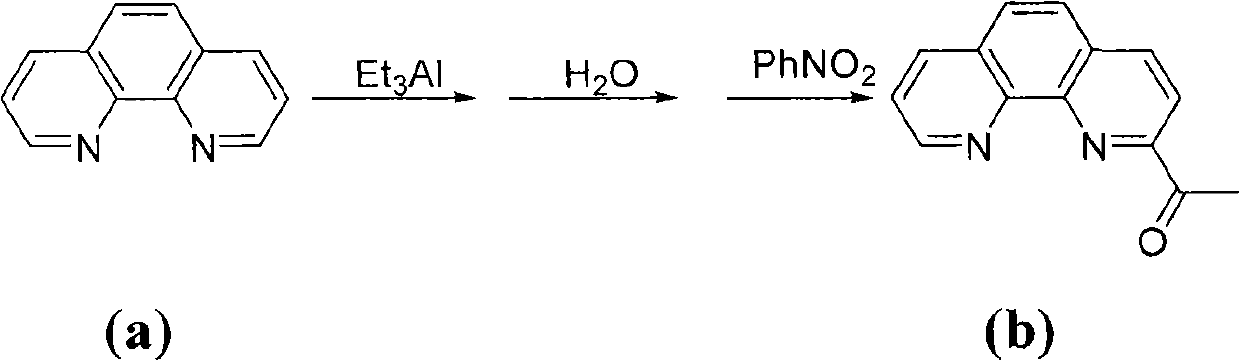
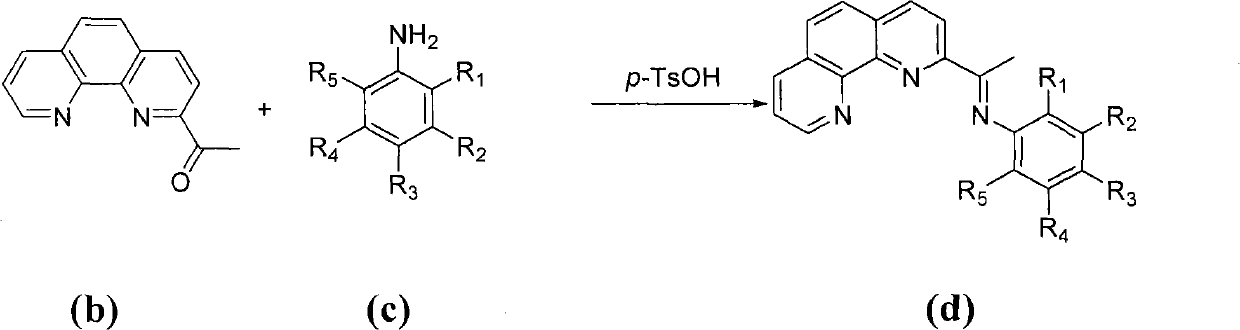
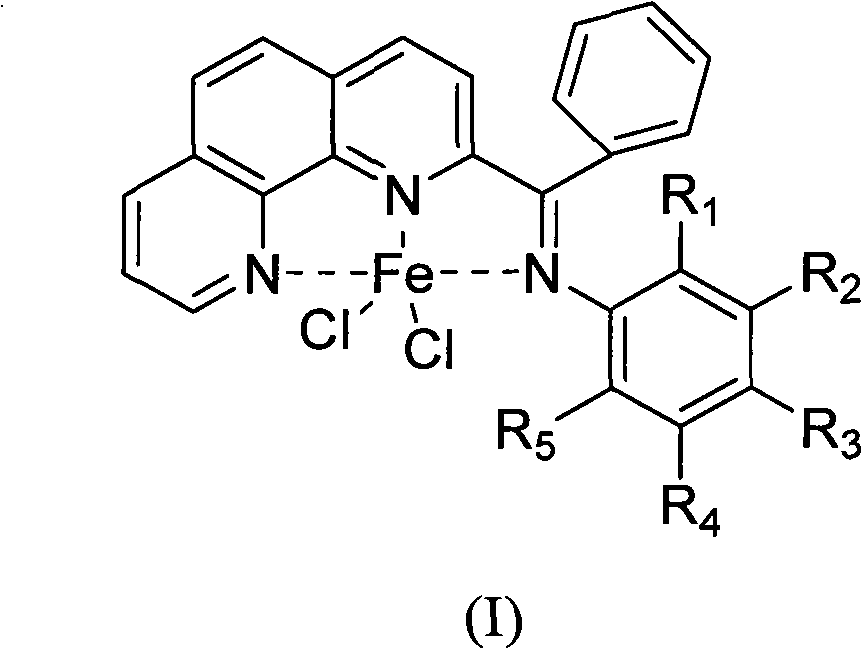
ActiveCN102485733AReduce manufacturing costLess varietyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron organic compoundsPotassium cyanidePhenanthroline
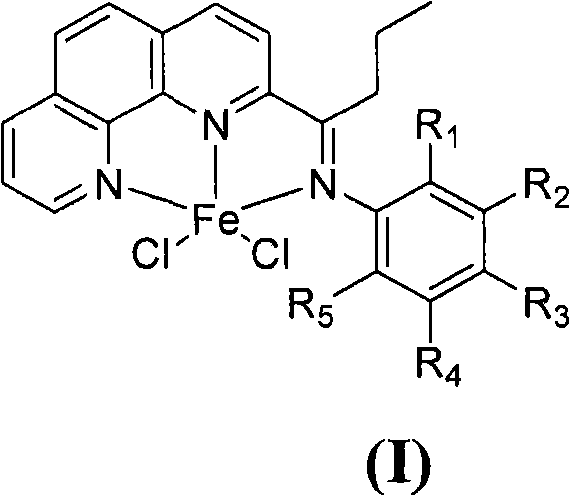
The invention provides a method for preparing chlorinated-2-acetyl-1,10-phenanthroline amine iron (II) complex with the structural formula of formula (I) and an application of the obtained complex as an ethylene oligomerization catalyst, wherein variables in the formula (I) are defined in the specification. According to the method, triethyl aluminum which is adopted as an initial raw material in the process of the preparation of 2-acetyl-1,10-phenanthroline from 1,10-phenanthroline is hydrolyzed and undergoes an oxidation reaction with nitrobenzene to obtain 2-acetyl-1,10-phenanthroline, 2-acetyl-1,10-phenanthroline is condensed with substituted aniline to obtain a 2-acetyl-1,10-phenanthroline amine ligand, and the ligand is reacted with iron dichloride to obtain the complex. The synthetic method of the invention, which has the advantages of less step, simple technology, and catalyst preparation cost reduction, and adopts nontoxic triethyl aluminum to replace potassium cyanide used in routine preparation methods, has a wide industrialization prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of mulberry stem active carbon/ferrum and manganese oxide composite adsorbent
ActiveCN104888704ASimple processReduce manufacturing costOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentWastewater
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mulberry stem active carbon / ferrum and manganese oxide composite adsorbent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding 10g of dried and broken 20-mesh mulberry stems into 100ml of 20g / L-50 / L potassium permanganate solution, mechanically stirring for 10 minutes, dipping for 12-48 hours, and filtering; putting filter residue into a beaker, adding 100mL of 10g / L-40g / L ferrous chloride solution, stirring for 10 minutes, dipping for 12-48 hours, and filtering; putting filter residue into the beaker, adding 50mL of 7% sodium hydroxide solution, stirring evenly, dipping for 6 hours, filtering, and washing fully by ultrapure water; drying obtained filter residue at 60 DEG C-70 DEG C for 12 hours, putting an obtained dried mixture into a crucible, forging at 400 DEG C-550 DEG C for 1-4 hours, cooling, grinding, and sieving by a 100-mesh sieve so as to obtain the mulberry stem active carbon / ferrum and manganese oxide composite adsorbent. By the method provided by the invention, the device is simple, the cost is low, and the obtained composite adsorbent has a good effect of treatment of wastewater containing arsenic.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
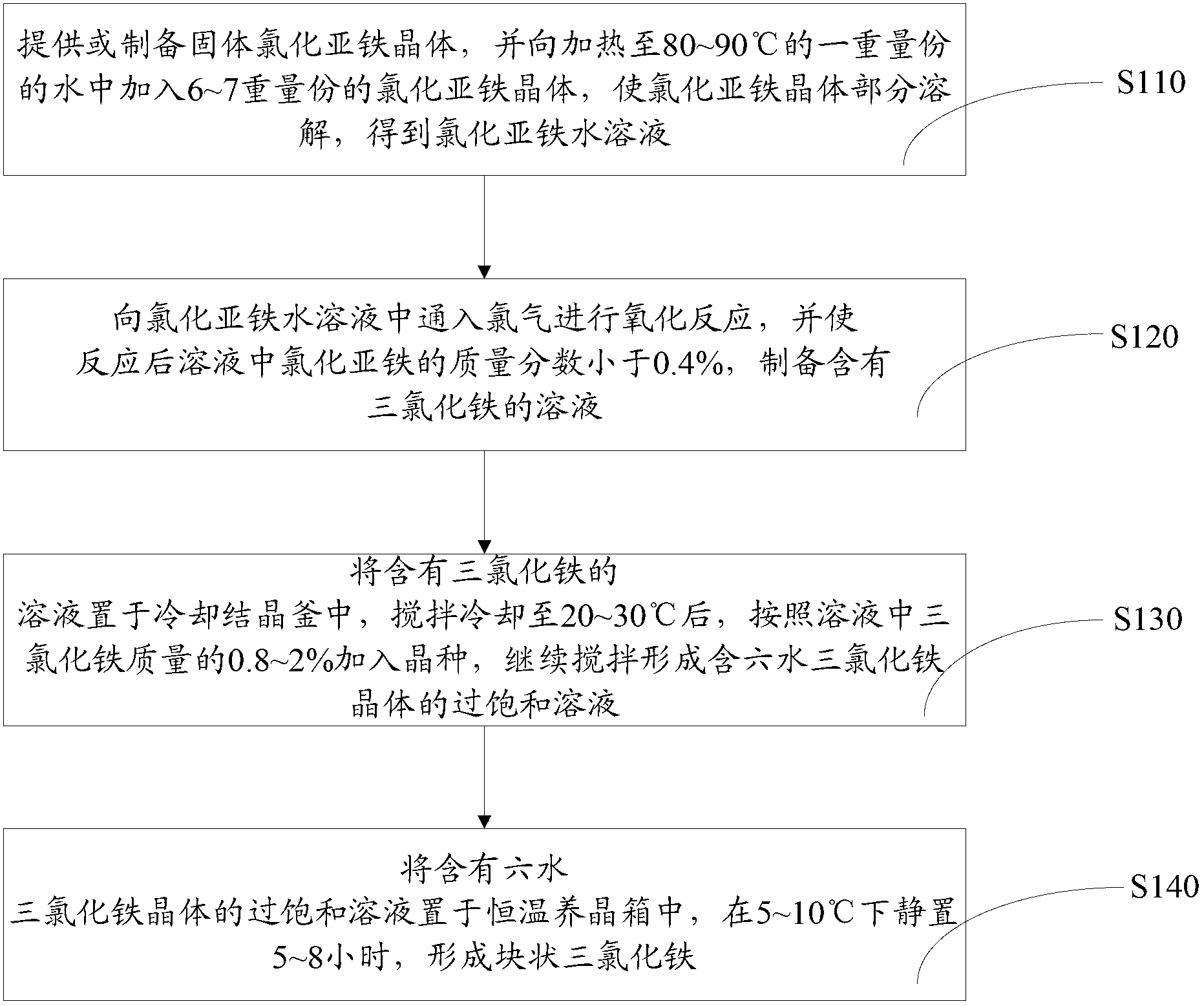
Method for preparing blocky ferric trichloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing blocky ferric trichloride. Blocky ferric trichloride can be produced both under constant-temperature crystal growing condition at 5-10 DEG C and at high-temperature environment temperature by adjusting the parameters of crystal cooling and crystal growing. In addition, solid ferric trichloride is used as a raw material, and impurities in the traditional pickling waste liquid are prevented from being mixed into a product; and chlorine gas is used as an oxidizing agent and does not contain any impurity. Finally, the blocky ferric trichloride can be directly obtained through crystal growing, the area of blocky ferric trichloride in direct contact with the air is small, the problem that ferric trichloride absorbs moisture easily can be effectively solved, the quality guarantee period of the product is prolonged, and the blocky ferric trichloride is easy to store and transport.
Owner:3R ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
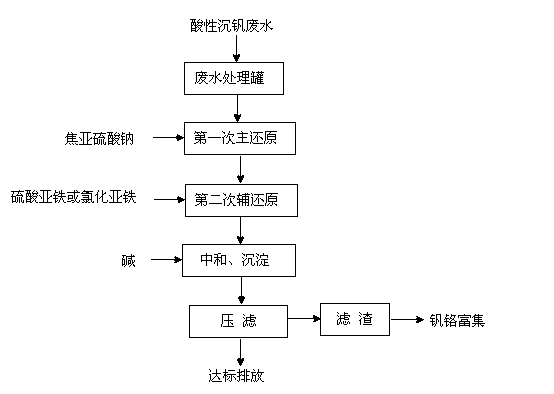
Treatment method for wastewater after vanadium precipitation
InactiveCN102795721AAchieve emission standardsReduce CODWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandSulfite salt
A treatment method for wastewater after vanadium precipitation comprises: detecting the concentrations of chromium (VI) and vanadium (V) in the wastewater after vanadium precipitation, and adding solid sodium pyrosulfite according to the total mass of the chromium (VI) and the vanadium (V) for a first reduction reaction; detecting the concentrations of the chromium (VI) and the vanadium (V) in the wastewater after vanadium precipitation and after the first reduction reaction, and adding ferrous sulphate or ferrous chloride according to the total mass of the chromium (VI) and the vanadium (V) for a second auxiliary reduction reaction; and adjusting pH value by using alkali, neutralizing, precipitating, press filtering, and the wastewater reaching the discharge standard for discharging. The indexes of chemical oxygen demand (COD), the suspension solids (SS), the total chromium (TCr) and the chromium (VI) are easy to control after the wastewater after vanadium precipitation being treated by using the method, and all the indexes meet the wastewater discharge standard of the nation. By using the method, a small quantity of waste residue is produced, the chromium and the vanadium are fully enriched in waste residue, and the waste residue can be used as the raw material for producing the vanadium and chromium, realizing the recycle of resource, eliminating environmental pollution and reducing wastewater treatment cost.
Owner:CITIC JINZHOU METAL
Production method of nano medicine carrier
InactiveCN1476896APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMicroparticleIron chloride
The preparation method of nano medicine carrier includes the following steps: utilizes the iron chloride and ferrous chloride mixed liquor and ammonia water to make them produce reaction to obtain tri-iron tetroxide solution; mixing said tri-ion tetroxide solution with amycin and albumen, adding cotton seed oil, placing them into cell disintegrator to make ultrasonic uniformly-mixing and make theparticles in which the amycin and albumen are covered with magnetic iron be dispersed in the oil and fat, then using ethyl ether to dissolve the oil and fat so as to obtain the invented product.
Owner:张阳德
Composite high polymer flocculant for coking wastewater and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106335988AReduce secondary pollutionWide variety of sourcesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationCoking wastewaterIron(II) chloride
The invention discloses a composite high polymer flocculant for coking wastewater and a preparation method thereof. The composite high polymer flocculant adopts non-ionic modified starch, cationic modified starch, anionic modified starch, and amphoteric modified starch as the raw materials, in the presence of an initiator and under a weak acid condition, the raw materials undergo graft copolymerization with acrylamide, acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, acrylonitrile, acrylic ester, styrene, methylene acrylamide, maleic anhydride and other monomers to obtain a modified starch graft copolymer, and the copolymer is blended with an inorganic flocculant ferric sulfate, ferric silicate, ferric chloride, ferrous sulfate and ferrous chloride to obtain the composite high polymer flocculant. The composite high polymer flocculant has the characteristics of long molecular chain, compact floccules, wide source of raw materials, low price, biodegradability, and little secondary pollution, etc., and is a real efficient and environment-friendly flocculant. During use, the dosage of the composite high polymer flocculant accounts for 0.1-1% of the volume fraction of the treated coking wastewater, the COD removal rate of the treated coking wastewater reaches 85% or more, the decolorization rate is 95% or more, and the removal rate of suspended solids reaches 95% or more.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGFU ENG TECH
Method combining oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water
InactiveCN102642951AQuick removalWater safetyWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPotassium persulfateChlorine dioxide
The invention provides a method combining an oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water. The oxidizing composite reagent is added into the water and stirred, and then the activated carbon is utilized to adsorb the arsenic. The oxidizing composite reagent is formed by compositing potassium ferrate, chlorine dioxide, sodium peroxide, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, or is formed by compositing potassium peroxide, sodium peroxide, sodium monopersulfate, iron chloride and hydroxylaminehydrochloride, or is formed by compositing calcium peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, calcium monopersulfate, calcium persulfate, cerium chloride, ferric chloride, cerous sulfate and humus, or is formed by compositing cobalt chloride, ammonium monopersulfate, ammonium persulfate, cerous sulfate, sodium peroxide and hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The method can not only remove the arsenic in drinking water, underground water and surface water rapidly, efficiently, conveniently and safely, but also effectively reduce concentration of the arsenic in sewage containing arsenic and effluent of sewage secondary sedimentation tanks, and simultaneously can have good recovery effect on lakes and inland seawater polluted by the arsenic.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Preparation of butyryl-substituted 1,10-phenanthroline complex and application of prepared complex as catalyst
ActiveCN102485732AReduce manufacturing costFew synthetic stepsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron organic compoundsPotassium cyanideNitrobenzene
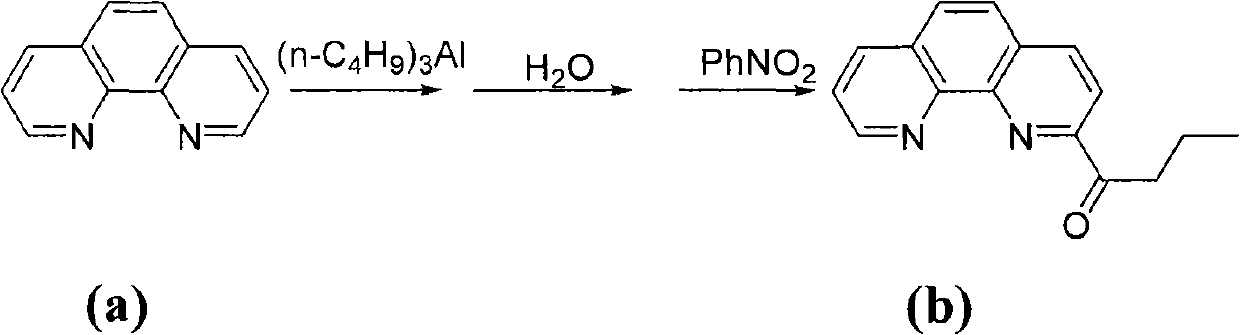
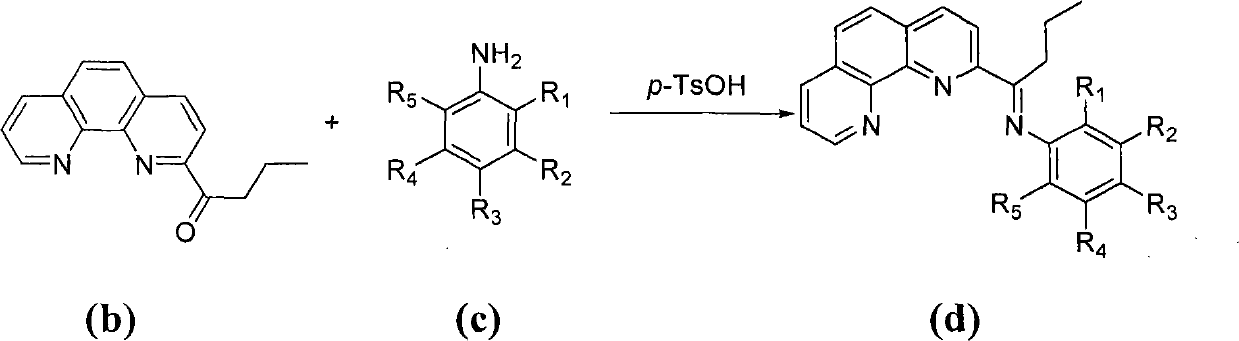
The invention provides a method of preparing a complex represented by formula (I) of 2-n-butyryl-1,10-phenanthroline condensation amine ferric chloride (II) and application of the prepared complex as a catalyst for ethylene oligomerization, wherein variables in formula (I) are defined in the specification. According to the method, in the process of preparing 2-n-butyryl-1,10-phenanthroline from 1,10-phenanthroline, tri-n-butylaluminum is used as a starting material, then hydrolysis and an oxidation reaction with nitrobenzene are sequentially carried out so as to obtain 2-n-butyryl-1,10-phenanthroline, 2-n-butyryl-1,10-phenanthroline and substituted aniline undergo a condensation reaction so as to prepare 2-n-butyryl-1,10-phenanthroline condensation amine ligand, and the ligand reacts with ferrous chloride so as to obtain a target product. The synthetic method comprises a few procedures, is a simple process, enables preparation cost for the catalyst to be reduced and uses nontoxic tri-n-butylaluminium to substitute potassium cyanide used in normal preparation methods, thereby having a wide industrial prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Prussian blue nano-particle contrast agent, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105288665AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a prussian blue nano-particle contrast agent, a preparation method and application thereof. The contrast agent includes a core of prussian blue nano-particle and a polyethylene glycol shell clad on the surface of prussian blue nano-particle. The preparation method of the contrast agent comprises dissolving hexacyanoferrate and organic acid in a solvent to obtain solution A; dissolving ferric chloride or ferrous chloride and organic acid in a solvent to obtain solution B; adding polyethylene glycol into the solution A to obtain solution C; adding the solution B into the solution C to obtain solution D; performing solvothermal synthesis reaction of the solution D, drying the solid product obtained by the reaction to obtain the prussian blue nano-particle contrast agent. The prussian blue nano-particle contrast agent has good water solubility and biocompatibility, and is benefit for the application in vivo.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for selectively separating iron from hydrochloric acid solution containing ferrous chloride
InactiveCN102660678AReduce concentrationThe driving force of the oxidation reaction is largeProcess efficiency improvementReaction temperatureHydrochloric Acid Liquid
The invention discloses a method for selectively separating iron from hydrochloric acid solution containing ferrous chloride. The method comprises the following steps of: with hydrochloric acid solution containing ferrous chloride as a water phase, adding the water phase and an organic phase into extraction equipment to form a mixed solution; introducing gas containing oxygen into the mixed solution; simultaneously oxidizing and extracting by stirring, wherein the reaction temperature is 25-40DEG C and the reaction time of each stage of extraction is at least 15 minutes; after the reaction time reaches, stopping stirring and introducing the gas containing the oxygen; standing a reaction solution for at least 3 minutes; and then separating an extraction solution and the organic phase, wherein the mixture ratio of the organic phase to the water phase is in the limit of the mol ratio of an extraction agent in the organic phase to an iron ion in the water phase being (2-5) to 1 and the total introduction quantity of the gas containing the oxygen is 2-10 times the theoretical quantity of the gas containing the oxygen required by complete oxidation of ferrous chloride in the mixed solution into ferric trichloride.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Processing and recycling process for silicon slurry
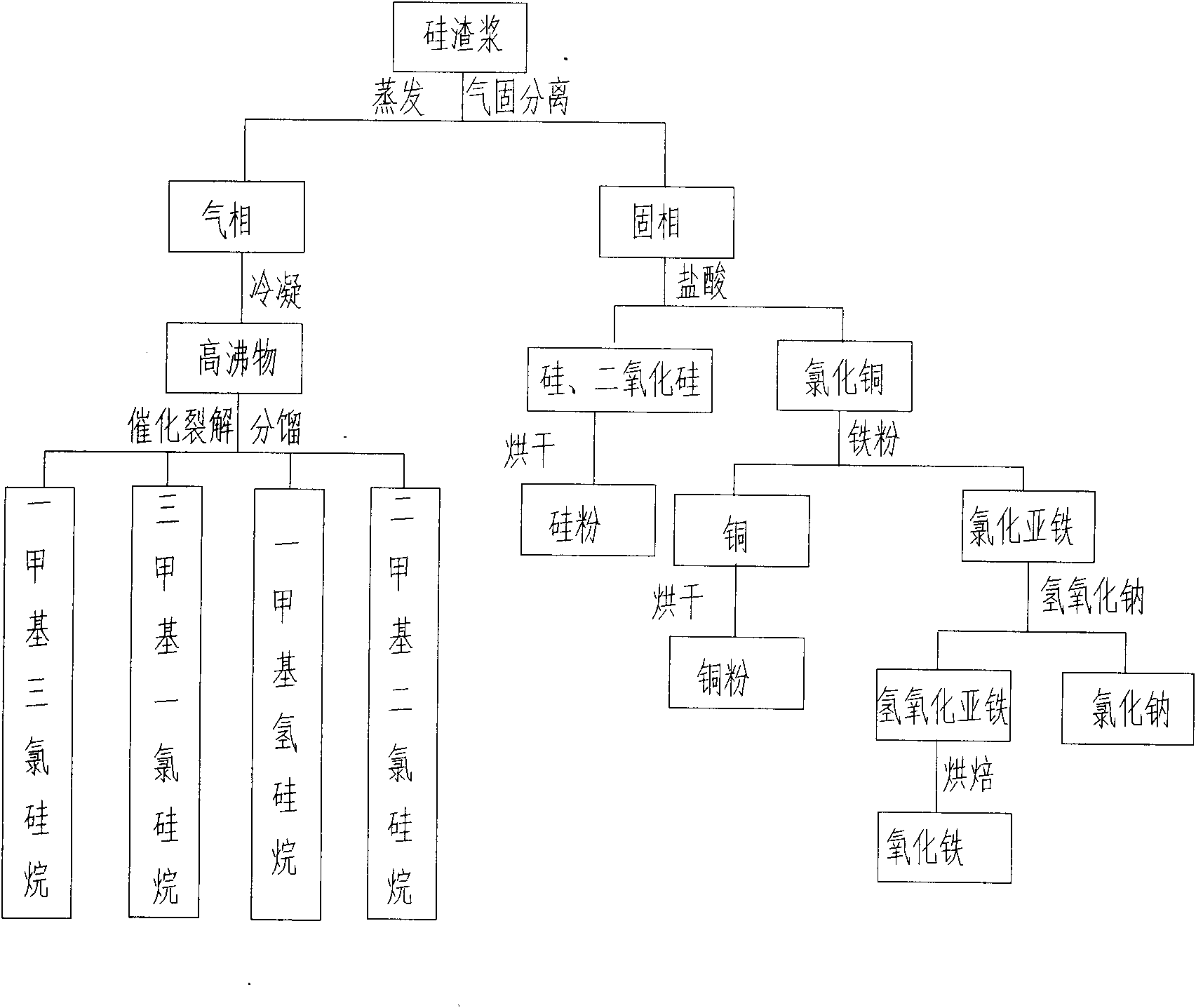
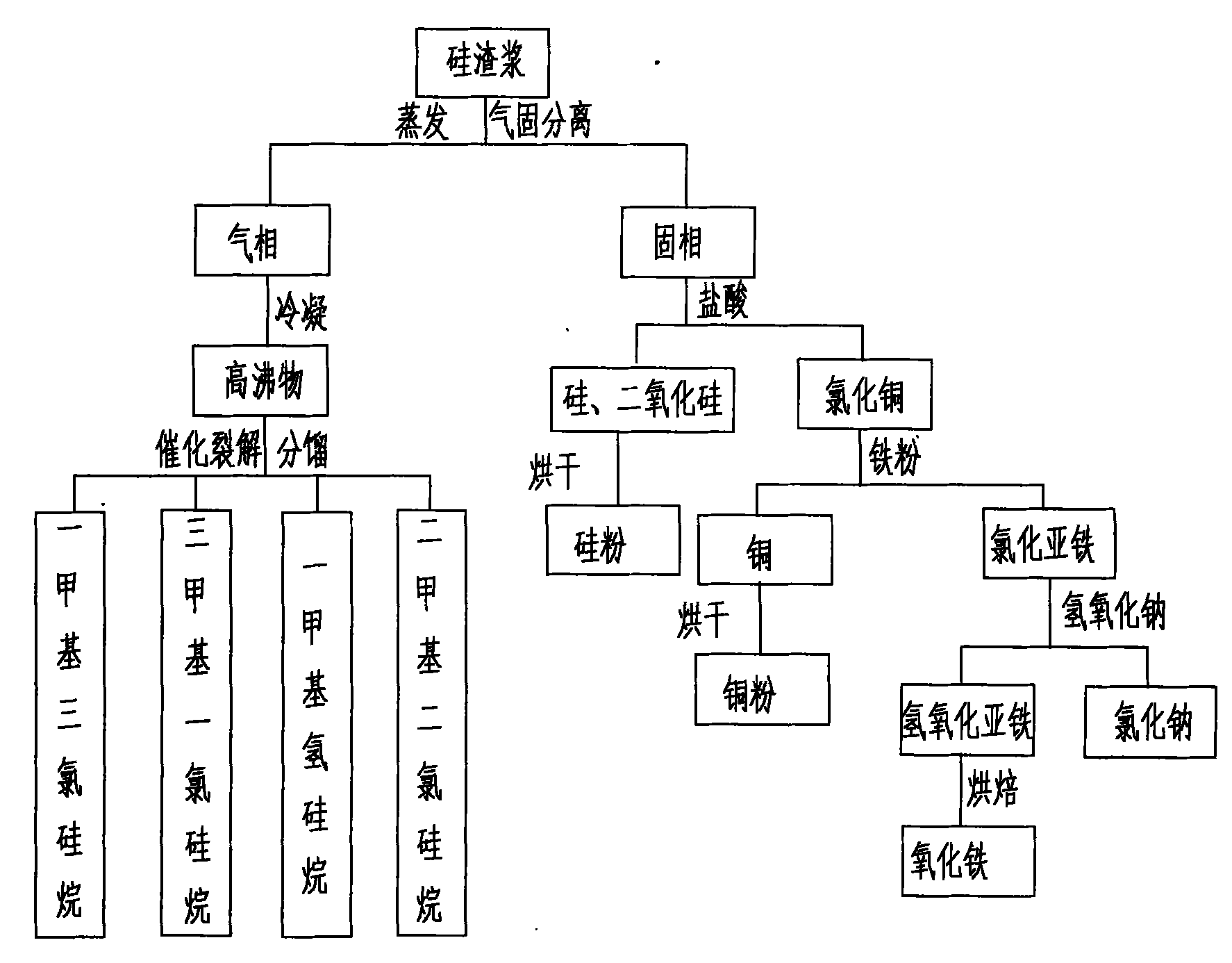
PendingCN102174674AGuaranteed to drive normallyEliminate pollutionSilicon organic compoundsFerrous oxidesGas phaseSilanes
The invention provides a processing and recycling process for silicon slurry, which comprises the steps as follows: silicon slurry is evaporated for gas and solid separation; high boiling point substances are obtained after the gas phase is condensed; the high boiling point substances react with hydrogen chloride to be cracked into mixed monomers such as methyl trichloro silicane, trimethyl chloro silicane, methyl silane, dimethyl dichloro silicane and the like; and after the fractionation, each pure monomer product can be obtained. The solid phase separated through evaporation mainly contains cuprous oxide, silicon, silicon dioxide and the like; hydrochloric acid (or sulfuric acid) is added into the solid phase to extract copper chloride (or copper sulfate, which can be sold directly) by a chemical method; and silicon and silicon dioxide are separated out. Iron powder is added into a copper chloride solution for extracting copper and ferrous chloride, and sodium hydroxide is added into the ferrous chloride solution for extracting ferrous oxide. The processing and recycling process is environment-friendly and can eliminate pollution, and meanwhile can recover various by-products from silicon slurry, thereby having well economic benefits.
Owner:上海竟茨环保科技有限公司
Treatment method of ferrous waste hydrochloric acid
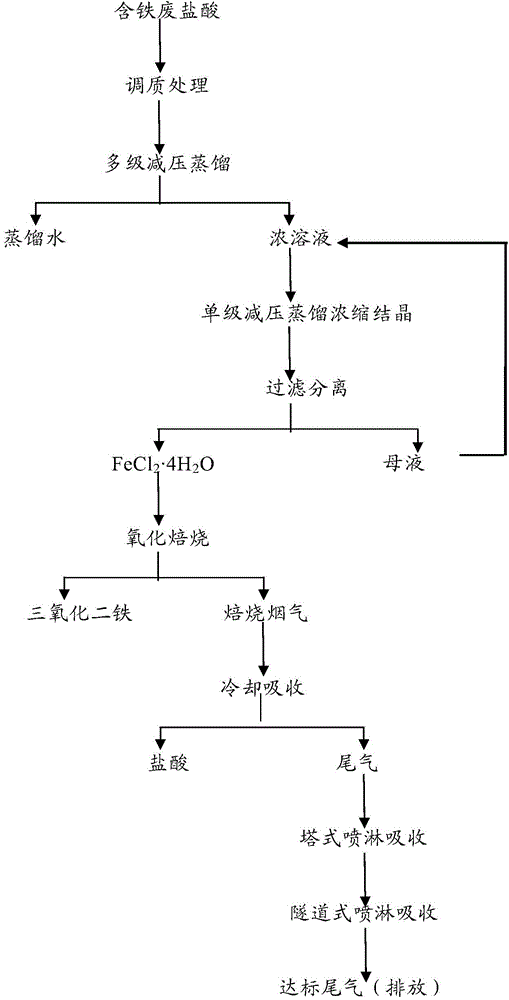
ActiveCN104828995AReduce energy consumptionLow costChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideCombination devicesScrapIron(II) chloride
The invention provides a treatment method of ferrous waste hydrochloric acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling the ferrous waste hydrochloric acid to react with plenty of scrap iron until complete solute in the solution is ferrite ferrous chloride; (2) concentrating and crystallizing the ferrous chloride solution obtained from the step (1) through a multi-stage vacuum distillation device and a single-stage vacuum distillation device, so as to obtain a ferrous chloride crystal; (3) calcining the ferrous chloride crystal obtained from the step (2) through a rotary kiln, decomposing to obtain hydrogen chloride gas, water vapor and a ferric oxide solid, collecting the ferric oxide solid to obtain a ferric oxide product, and exhausting mixed gas containing the hydrogen chloride gas, the water vapor, a little of ferric oxide dust and combustion tail gas; and (4) cooling the mixed gas obtained from the step (3) through a heat exchanger to form hydrochloric acid droplets.
Owner:BERIS ENG & RES CORP
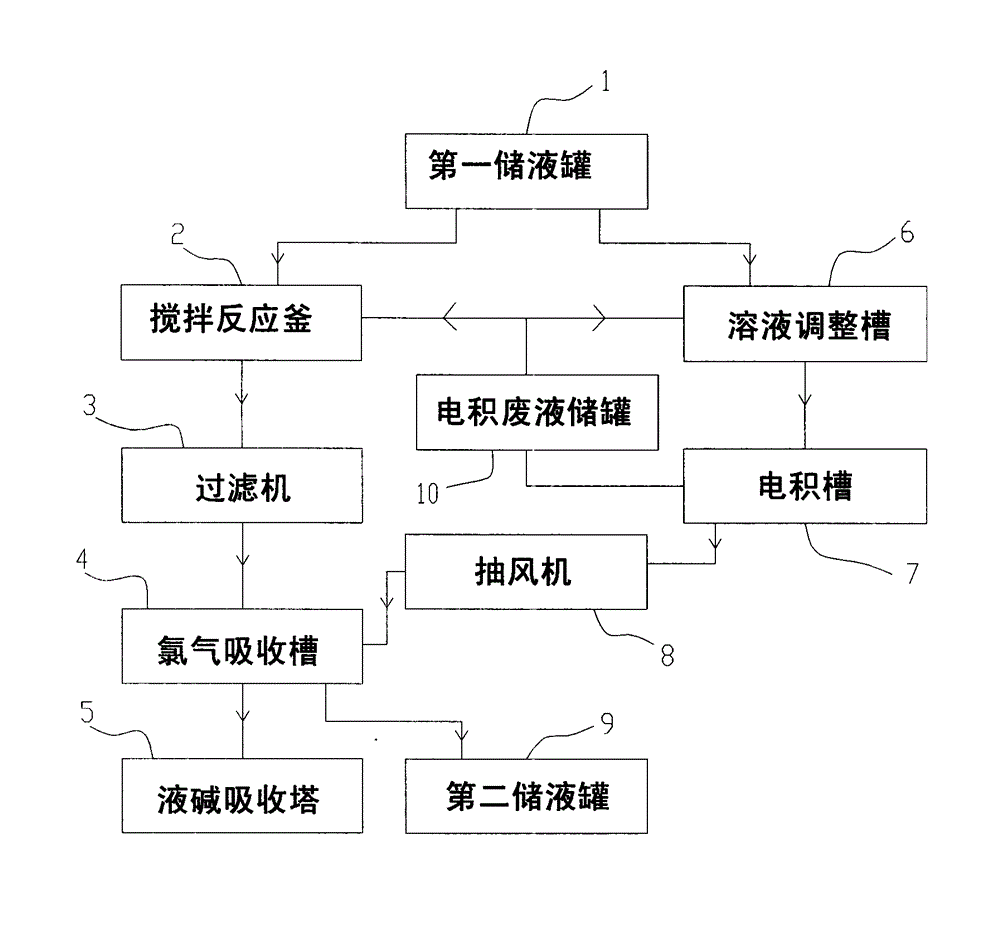
Method and system for preparing ferric chloride, electrodeposited copper and copper powder from copper-containing hydrochloric acid waste liquid
ActiveCN103936081ASolve pollutionHigh pricePhotography auxillary processesIron halidesLiquid storage tankIron(II) chloride
The invention provides a method and a system for preparing ferric chloride, electrodeposited copper and copper powder from copper-containing hydrochloric acid waste liquid. The system comprises a first liquid storage tank, a stirring reactor, a filter, a chlorine absorption tank, a caustic soda solution absorption tower, a solution adjusting tank, an electrodeposition cell and an exhaust fan, wherein the first liquid storage tank is used for storing the copper-containing hydrochloric acid waste liquid; the stirring reactor is used for carrying out replacement reaction between ferrum and copper chloride; the filter is used for filtering a solution obtained through the replacement reaction; the chlorine absorption tank is used for enabling the solution filtered by the filter to absorb chlorine, so that ferrous chloride is oxidized into ferric trichloride; the caustic soda liquid absorption tower is used for treating tail gas emitted from the chlorine adsorption tank; the solution adjusting tank is used for adjusting the concentration of a solution in the electrodeposition cell; the electrodeposition cell is used for an electrodeposition reaction; and the exhaust fan is used for conveying chlorine gas produced by the electrodeposition cell to the chlorine absorption tank. According to the method and the system provided by the invention, replacement of copper ions from ferrous powder is combined with the electrodeposited copper, so that the wastewater discharge problem of the copper-containing hydrochloric acid waste liquid and the pollution problem of the chlorine gas to the environment can be solved, and the phenomenon that the power consumption sharply rises is avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN YUEPENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Superparamagnetic nano-ferroferric oxide and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102234134ASmall granularityHigh saturation magnetizationNanostructure manufactureFerroso-ferric oxidesDispersityMean diameter
The invention provides a nano-ferroferric oxide sol-gel method production process which adopts ferrous chloride, ferric chloride, ammonia water and oleic acid as main raw materials to synthesis of nano-ferroferric oxide, and adopts the oleic acid to carrying out modification. The method provided by the present invention has advantages of simple experiment equipment, convenient operation and large output. The nano-ferroferric oxide provided by the present invention has characteristics of uniform particle size, good dispersity, stable magnetism, a mean diameter of 15 nm, a saturation magnetization of 55 emu / g. In addition, due to presenting the superparamagnetic, the nano-ferroferric oxide materials can be applicable for a plurality of fields such as chemical engineering, machinery, electronic industry, printing, medicine and the like; meanwhile, due to remarkable magnetic susceptibility and gas and humidity sensing properties, the nano-ferroferric oxide provides great application prospects for a plurality of the fields such as high-density magnetic recording materials, air and humidity sensor parts, magnetic separation of immune cells, magnetic resonance imaging, drug controlled release and the like.
Owner:张永昶
Method for producing polymerized iron chloride by utilizing acid-washing waste liquid of steel
InactiveCN102603015AReduce post-processing costsTake advantage ofIron halidesAfter treatmentSodium chlorate
The invention discloses a method for producing polymerized iron chloride by utilizing the acid-washing waste liquid of steel. The method for producing the polymerized iron chloride by utilizing the acid-washing waste liquid of the steel comprises the following steps of: (1) adding the acid-washing waste liquid of steel and a stabilizing agent into a reaction tank and fully stirring evenly so as to obtain a liquid material 1; (2) adding a sodium chlorate solution into the liquid material 1 continuously for reacting until the content of ferrous chloride in the mixture is lower than 0.5 percent so as to obtain a liquid material 2; and (3) adding a polymerization initiator into the liquid material 2 for carrying out a polymerizing reaction so as to obtain a polymerized iron chloride product after finishing the reaction. According to the method for producing the polymerized iron chloride by utilizing the acid-washing waste liquid of the steel, the polymerized iron chloride is prepared by utilizing the acid-washing waste liquid of the steel, the after-treatment cost of the acid-washing waste liquid of the steel industry is lowered, and resources are fully utilized; sodium chlorate is adopted as an oxidizing agent, the use of chlorine gas is avoided, a favorable production environment is formed, and the potential safety hazard is eliminated; and the method disclosed by the invention has simple technological process and low equipment investment and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:蓝保(厦门)水处理科技有限公司
Preparation method of benzoyl-substituted 1,10-phenanthroline complex and catalytic application in ethylene oligomerization
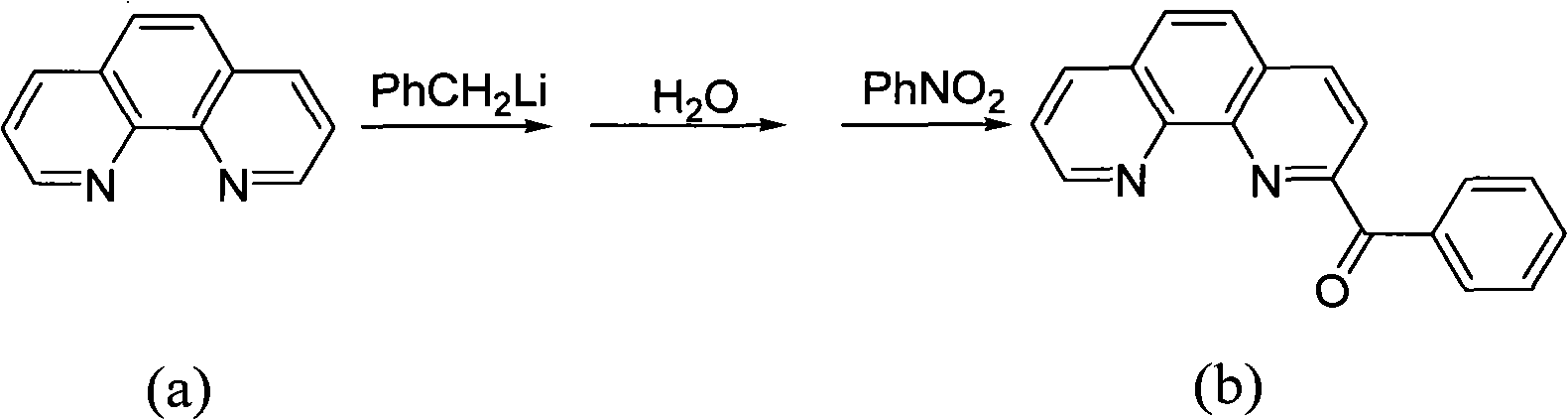
ActiveCN102964388AReduce manufacturing costLow priceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron organic compoundsPotassium cyanidePhenanthroline
The invention provides a method for preparing a chlorinated 2-benzoyl-1,10-phenanthroline condensed amine iron (II) complex shown in formula I, and its catalytic application in ethylene oligomerization. The preparation method comprises the following steps: orderly performing hydrolysis and an oxidation reaction with nitrobenzene of initial reaction raw materials of 1,10-phenanthroline and benzyl lithium to obtain 2-benzoyl-1,10-phenanthroline, then performing condensation of 2-benzoyl-1,10-phenanthroline with substituted aniline to obtain 2-benzoyl-1,10-phenanthroline condensed amine ligand, and reacting the ligand with ferrous chloride to obtain a target product I. The synthetic method provided by the invention is few in steps, and simple in process, substitutes nitrobenzene for selenium dioxide in the prior art for the oxidation reaction, substitutes nontoxic benzyl lithium for hypertoxic potassium cyanide in the prior art, reduces the preparation cost of the catalyst, and has wide industrialization prospects.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of edible and medicinal fungus protein peptide-ferrous chelate
InactiveCN105852135AHigh extraction rateHigh ferrous chelating activityProtein foodstuffs working-upNeutral proteaseHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the field of food biotechnology, and specifically relates to a preparation method of edible and medicinal fungus protein peptide-ferrous chelate, comprising: extracting protein from edible and medicinal fungi by alkali-dissolving acid precipitation method or ammonium sulfate precipitation method; Proteases, neutral proteases or complex proteases restrict the enzymolysis of edible and medicinal fungal proteins, and then inactivate the enzymes to prepare edible and medicinal fungal protein enzymatic hydrolysates; use inorganic ferrous chloride or ferrous sulfate in ferrous and Edible and medicinal mycoprotein peptide chelation to obtain edible and medicinal mycoprotein-ferrous chelate. The invention can significantly improve the extraction rate of edible and medicinal mycoprotein by alkali-soluble acid precipitation method or ammonium sulfate precipitation method; the degradation degree of protein can be effectively controlled by controlling the enzymatic hydrolysis time; the preparation process of the whole polypeptide-ferrous chelate is simple. The ferrous-peptide chelate prepared by the present invention has a unique chelation system and transport mechanism, is easily absorbed, safe and non-toxic, low in price, can supplement amino acids and ferrous at the same time, and will definitely become the first choice for ferrous supplements; The invention provides a new idea for the application of edible and medicinal fungi.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
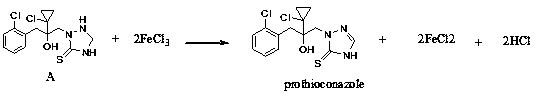
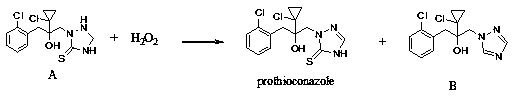
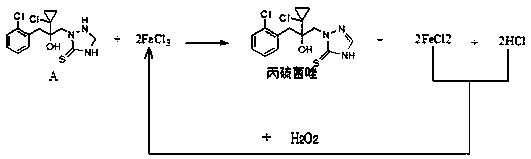
Synthetic method of prothioconazole
ActiveCN111303059AAvoid the three wastesDesulfurization impurities are reducedOrganic chemistryProcess engineeringEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a synthetic method of prothioconazole. The method specifically comprises the following steps: oxidizing an intermediate A by ferric chloride to generate prothioconazole and simultaneously generate ferrous chloride and hydrogen chloride, oxidizing the ferrous chloride and the hydrogen chloride by hydrogen peroxide dropwise added into the system to regenerate ferric chloride, continuing to oxidize the intermediate A by the generated ferric trichloride to obtain prothioconazole, and repeating the steps until the intermediate A is completely converted into the prothioconazole. According to the synthesis method of prothioconazole, only a catalytic amount of ferric chloride is needed, a byproduct is water, a large amount of three wastes generated by a traditional ferricchloride oxidation method are avoided, and a mild oxidant ferric chloride is adopted, so that desulfurization impurities are greatly reduced, and the yield is high.
Owner:JIANGYIN SULI CHEM
Ferrous disulfide semiconductor film preparation method
ActiveCN102642874AThickness is easy to controlEasy for large-scale continuous productionIron sulfidesVulcanizationIron(II) chloride
The invention discloses a ferrous disulfide semiconductor film preparation method, which relates to the field of preparation of compound semiconductor films for solar cells and the like. The method includes: by an aqueous solution deposition method, using ferrous sulfate or ferrous chloride aqueous solution as cation precursor solution, and using sodium polysulfide aqueous solution as anion precursor solution; controlling immersion time of a substrate in the precursor solution and circulation times to deposit a ferrous disulfide film premade layer; and subjecting the premade layer to vulcanization heat treatment at the high temperature to obtain a ferrous disulfide film. The ferrous disulfide semiconductor film preparation method is short in procedure, low in cost, high in reproducibilityand easy in massive continuous production, and the film is controllable in component and suitable for large-area growth. The deposition substrate can be normal soda lime glass, conductive glass, flexible stainless steel plates, titanium plates, molybdenum plates or plastic plates. The film prepared by the method is controllable in thickness and component, compact and uniform in appearance, high in crystallizing performance and photoelectric property and applicable to thin film solar cells.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of sodium ion battery based on graphite/prussian blue anode material
InactiveCN107039622AImprove cycle stabilityPositive electrode capacity is not easy to decayCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureFreeze-dryingArgon atmosphere
The invention provides a preparation method of a sodium ion battery based on a graphite / prussian blue anode material. The preparation method comprises the specific steps of mixing a ferrous chloride solution and a sodium ferrocyanide solution, performing programmed heating to be 70-90 DEG C, performing programmed cooling to be a room temperature, performing washing and drying to obtain a prussian blue nanosphere, adding the prussian blue nanosphere to a graphite oxide solution, performing stirring and mixing, performing separation, cold quenching and freeze-drying to obtain a graphite oxide cladded prussian blue nanosphere, performing reduction in hydrazine hydrate to obtain graphite / prussian blue, performing grinding, vacuum drying and tabletting on the graphite / prussian blue, a conductive agent, isopropanol and polytetrafluoroethylene to serve as an anode, taking a metal sodium sheet as a cathode, taking NaClO4 as an electrolyte, taking a chitosan film as a membrane, and then performing assembling in an argon atmosphere to form the sodium ion battery based on the graphite / prussian blue. The sodium ion battery prepared by the method has stable cycle performance; and a capacity maintenance rate is above 90%.
Owner:DONGGUAN JIAQIAN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Phytochelatin iron supplementation powder containing iron and preparation method of phytochelatin iron supplementation powder
InactiveCN105420323AFast absorptionPrevent oxidationHydrolysed protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFiltrationHydrolysate
The invention provides phytochelatin iron supplement powder which contains iron and has an iron supplementation function and a preparation method of the phytochelatin iron supplementation powder and belongs to the technical field of health-care food. The preparation method includes the steps that fresh pig blood is centrifuged, lower-layer blood cells are obtained, wall breaking is conducted on blood cell homogeneity, hemoglobin is obtained, the hemoglobin is subjected to enzymolysis with alkaline protease, after enzyme deactivation is conducted, enzymatic hydrolysate is subjected to decoloration with a decolorising agent, and liquid supernatant is dried after decoloration, and porcine hemoglobin polypeptide is obtained; chelation with ferrous chloride is conducted, reactant is treated through an ethanol solution, sediment is obtained, suction filtration is conducted repeatedly till filter residues are not separated out any more, freezing and drying are conducted, powder is obtained, and porcine hemoglobin iron phytochelatin is obtained; then 0.2-0.4 part of porcine hemoglobin iron phytochelatin , 30-50 parts of red bean powder, 20-30 parts of jujube powder, 8-10 parts of glucose and 0.3-0.5 part of glucose are fully mixed to be uniform, and the phytochelatin iron supplement powder containing iron and with the iron supplementation function is obtained. Through in-vitro simulation digestion and absorption inspection, the iron absorption rate of a product to which the porcine hemoglobin iron phytochelatin is added is 14-31% higher than that of a product to which ferrous chloride is added, a high iron absorption rate is achieved, and a good iron supplementation function can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for producing industrial grade calcium chloride by taking calcium carbide slurry as raw material
InactiveCN102910665AShort processEasy to operateCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesHydration reactionMagnesium phosphate
The invention discloses a method for producing industrial grade calcium chloride by taking calcium carbide slurry as raw material, comprising the following steps: firstly, the calcium carbide slurry and hydrochloric acid are reacted to produce calcium chloride, secondly, Fe<2+> produced by oxidation-reduction reaction is oxidized into Fe<3+> by bleaching powder, H2S produced in the reaction is partially removed, and then calcium carbonate and ammonium phosphate in NP residues are reacted with free hydrochloric acid, FeCl3 and MgCl2 in the reaction completion solution to produce calcium chloride, iron phosphate octahydrate and magnesium phosphate hexahydrate, calcium chloride thin slurry is subjected to sedimentation, rough filtration and fine filtration, so fine calcium chloride solution is obtained, the fine calcium chloride solution is subjected to evaporative concentration and granulation drying, so granular calcium chloride product is prepared, and finally, ferrous chloride solution containing sodium hydroxide is adopted to absorb hydrogen sulfide in the tail gas, and the tail gas is enabled to reach the treatment standard. According to the method for producing industrial grade calcium chloride by taking calcium carbide slurry as the raw material, wastes are treated by using wastes, the wastes are turned into useful things, and the serious pollution problem caused by calcium carbide slurry and by-product hydrochloric acid is radically solved, the benefit of environmental protection is very remarkable, the technological process is short, the product quality is good, and the economic benefit is high.
Owner:荣殿相
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com