Patents
Literature
71 results about "Potassium peroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Potassium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula K₂O₂. It is formed as potassium reacts with oxygen in the air, along with potassium oxide (K₂O) and potassium superoxide (KO₂). Potassium peroxide reacts with water to form potassium hydroxide and oxygen: 2K₂O₂+2H₂O->4KOH+O₂()
Method for the preparation of reactive hydrogen peroxide in deep eutectic solvents
The subject invention provides a potentially economically viable method for the preparation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in deep eutectic solvents (DES). H2O2 is then used for the destruction of small to large quantities of sulfur and nitrogen mustards and lewisite, their homologous / analogues, and similar chemical warfare agents at ambient conditions in DES without producing any toxic by-products. Furthermore, H2O2 has been used for the destruction of small to large quantities of halogenated hydrocarbons, their homologous / analogues, and similar hazardous chemicals at ambient conditions. H2O2 can be formed by either the electrochemical reduction of oxygen in DES in the presence of water or by dissolving Group 1 (alkali metals) or Group 2 (alkaline earth metals) superoxides, e.g. potassium superoxide, in DES in the presence of water, with / without chemicals used for the enhancement of the solubility of the metal superoxide in the DES, e.g. crown ethers.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
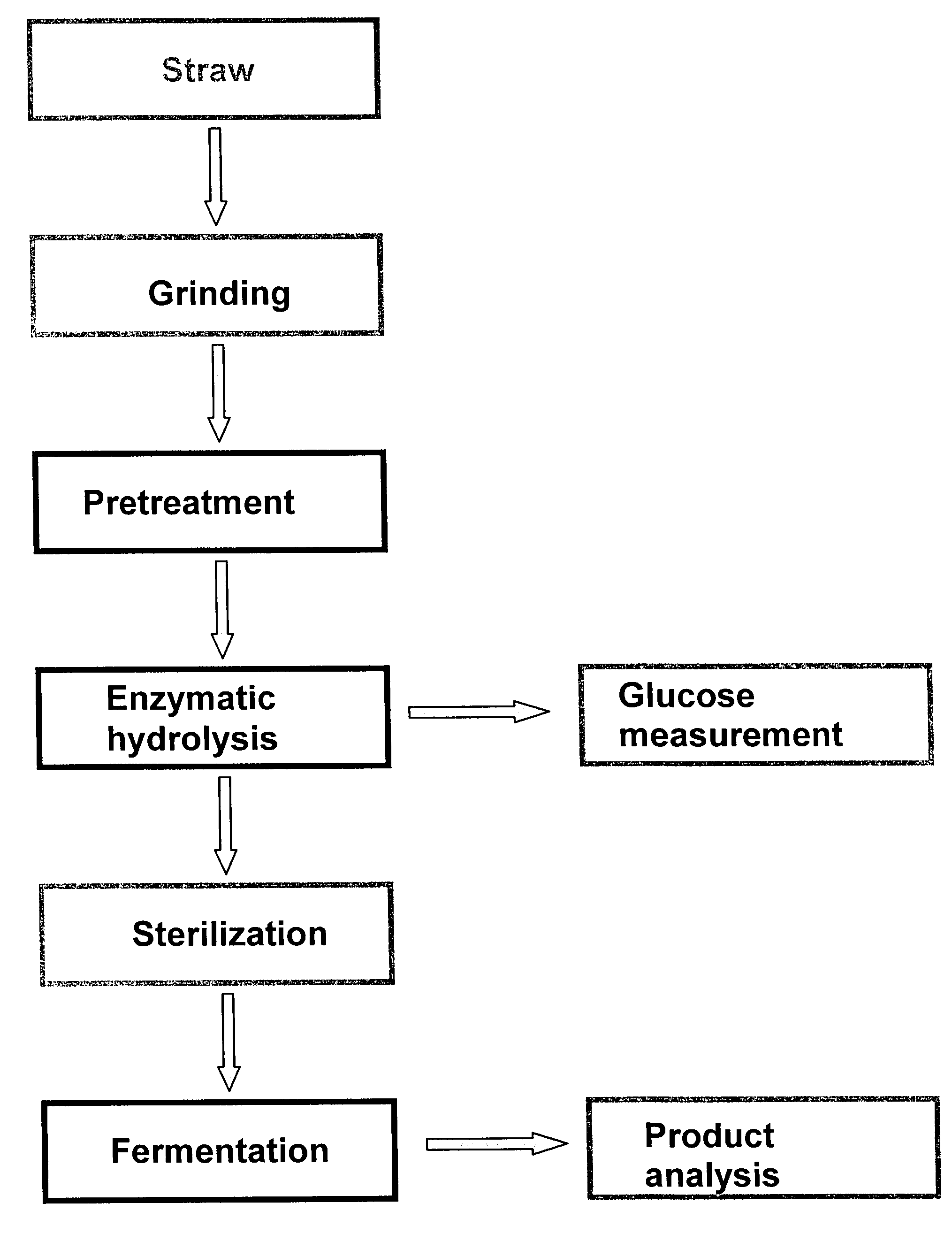
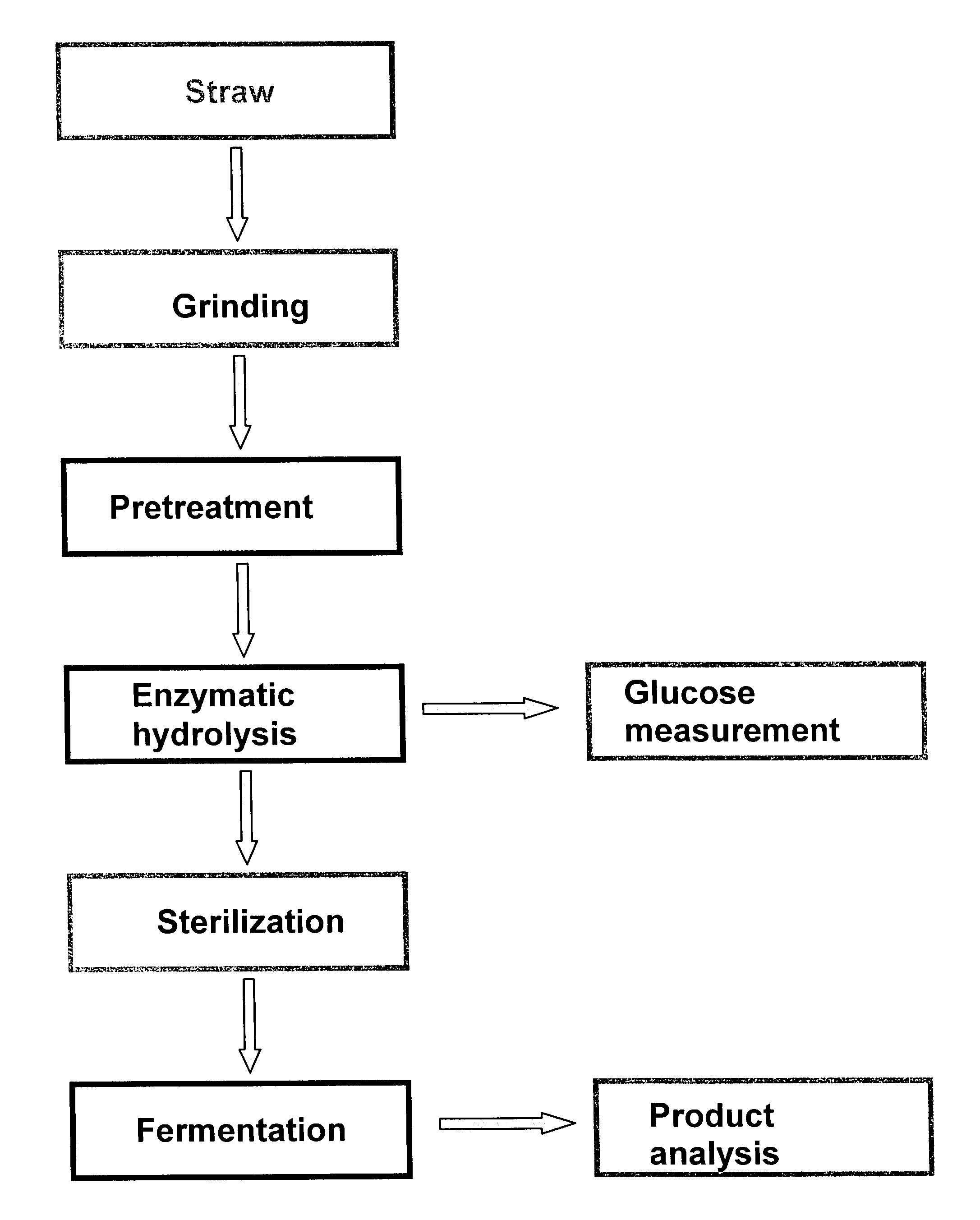
Process for preparing sugar-containing hydrolyzates from lignocellulose
A sugar-containing hydrolyzate is produced from a lignocellulose-containing material by a) pretreating the lignocellulose-containing material with a chemical compound selected from sulphuric acid, alkali, peroxodisulphates, potassium peroxide, potassium hydroxide, and mixtures thereof, in the presence of water, thereby obtaining an aqueous phase, and b) after removing of the aqueous phase and washing the resulting product, treating said product with an enzyme suitable for hydrolysis in the presence of water, thereby obtaining a hydrolyzate, the hydrolyzate being suitable as a carbon source for fermentation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method combining oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water
InactiveCN102642951AQuick removalWater safetyWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPotassium persulfateChlorine dioxide
The invention provides a method combining an oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water. The oxidizing composite reagent is added into the water and stirred, and then the activated carbon is utilized to adsorb the arsenic. The oxidizing composite reagent is formed by compositing potassium ferrate, chlorine dioxide, sodium peroxide, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, or is formed by compositing potassium peroxide, sodium peroxide, sodium monopersulfate, iron chloride and hydroxylaminehydrochloride, or is formed by compositing calcium peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, calcium monopersulfate, calcium persulfate, cerium chloride, ferric chloride, cerous sulfate and humus, or is formed by compositing cobalt chloride, ammonium monopersulfate, ammonium persulfate, cerous sulfate, sodium peroxide and hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The method can not only remove the arsenic in drinking water, underground water and surface water rapidly, efficiently, conveniently and safely, but also effectively reduce concentration of the arsenic in sewage containing arsenic and effluent of sewage secondary sedimentation tanks, and simultaneously can have good recovery effect on lakes and inland seawater polluted by the arsenic.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A method of reclaiming rhodium from carbonylation reaction organic waste liquid
The invention discloses a method for recovering rhodium from organic waste liquid produced in a carbonyl synthesis reaction. The method comprises: adding rhodium-containing organic waste liquid produced in a reaction for synthesizing octanol by using carbonyl into an inorganic acid; acidifying with stirring at 25 to 60 DEG C for 1 to 3 hours; adding oxidation accelerator after acidification, and reacting under a condition of a temperature of 50 to 100 DEG C for 1 to 5 hours; after the reaction is finished, standing reaction solution for 4 to 10 hours, demixing and obtaining a water phase and an oil phase; adding inorganic alkali into the water phase under a stirring condition; regulating the pH value of the reaction solution to 7.0 to 9.5; reacting at 60 to 110 DEG C for 1 to 2 hours; standing, precipitating, filtering out the precipitate, and drying; and thus, obtaining coarse rhodium. The maximum rhodium recovery rate reaches 99.4 percent, the oxidation accelerator may be oxygen, air, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, sodium peroxide, potassium peroxide or sodium hypochlorite; and the rhodium content in the rhodium-containing organic waste liquid is 100 to 600 ppm. The method disclosed by the invention can reduce energy waste, improve total metal rhodium recovery rate, has low equipment requirement, and is suitable for large-volume solution treatment, low in investment, simple in process flow, environment-friendly, quick, high in recovery rate and easy to industrialize.
Owner:杭州凯大催化金属材料股份有限公司
Method of fast degradation of organic phosphorus pesticide
InactiveCN1752025AWide variety of sourcesHigh catalytic efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationUltrasound - actionOrganophosphorus pesticides
A method for quickly degradating the residual agricultural chemical containing organophosphorus in sewage or on vegetable or fruit includes such steps as preparing the aqueous solution from nano-TiO2 catalyst and water-soluble peroxide (potassium peroxide or sodium peroxide), and degradating under the action of ultrasonic wave.
Owner:段晓军 +1
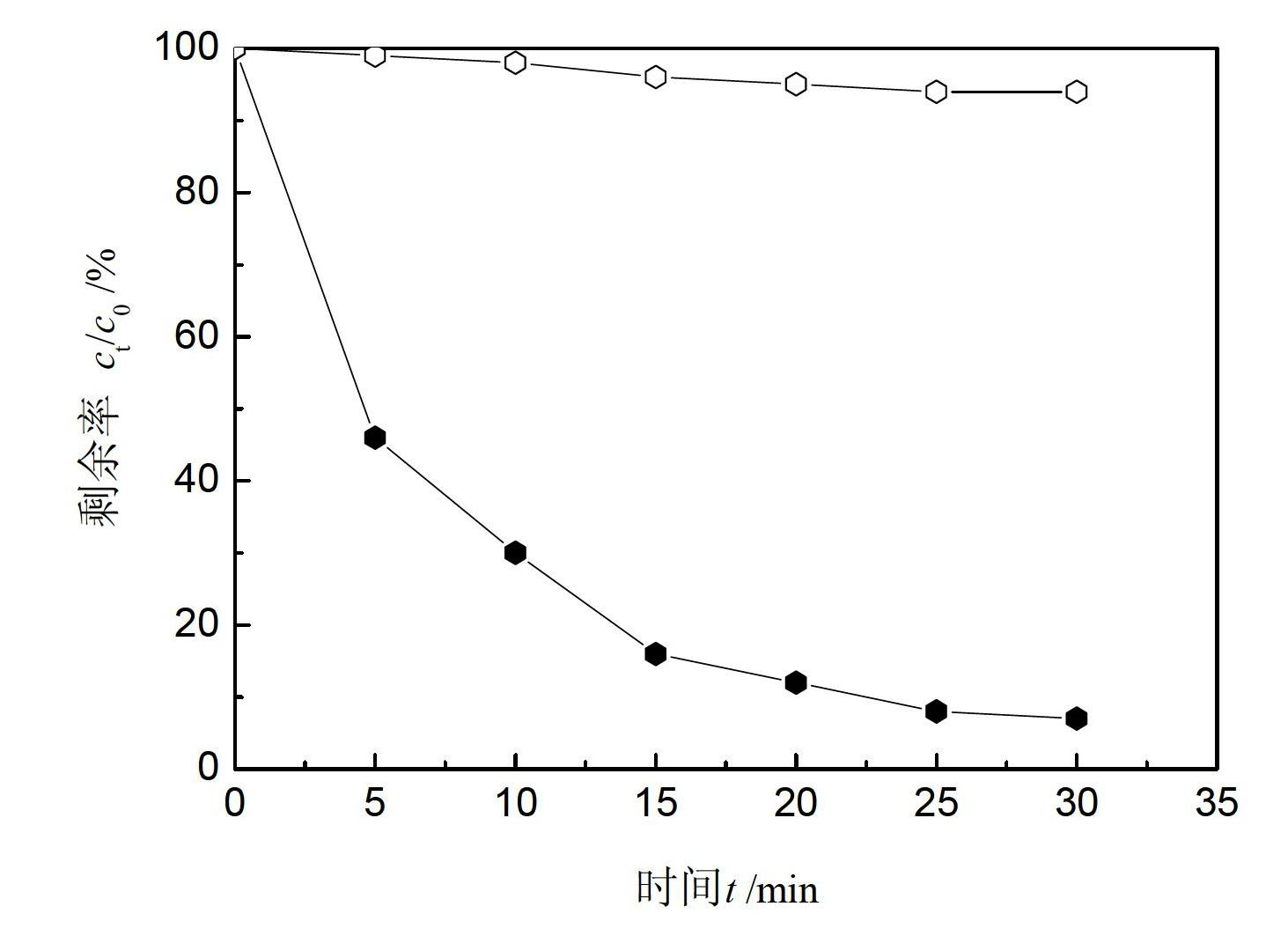
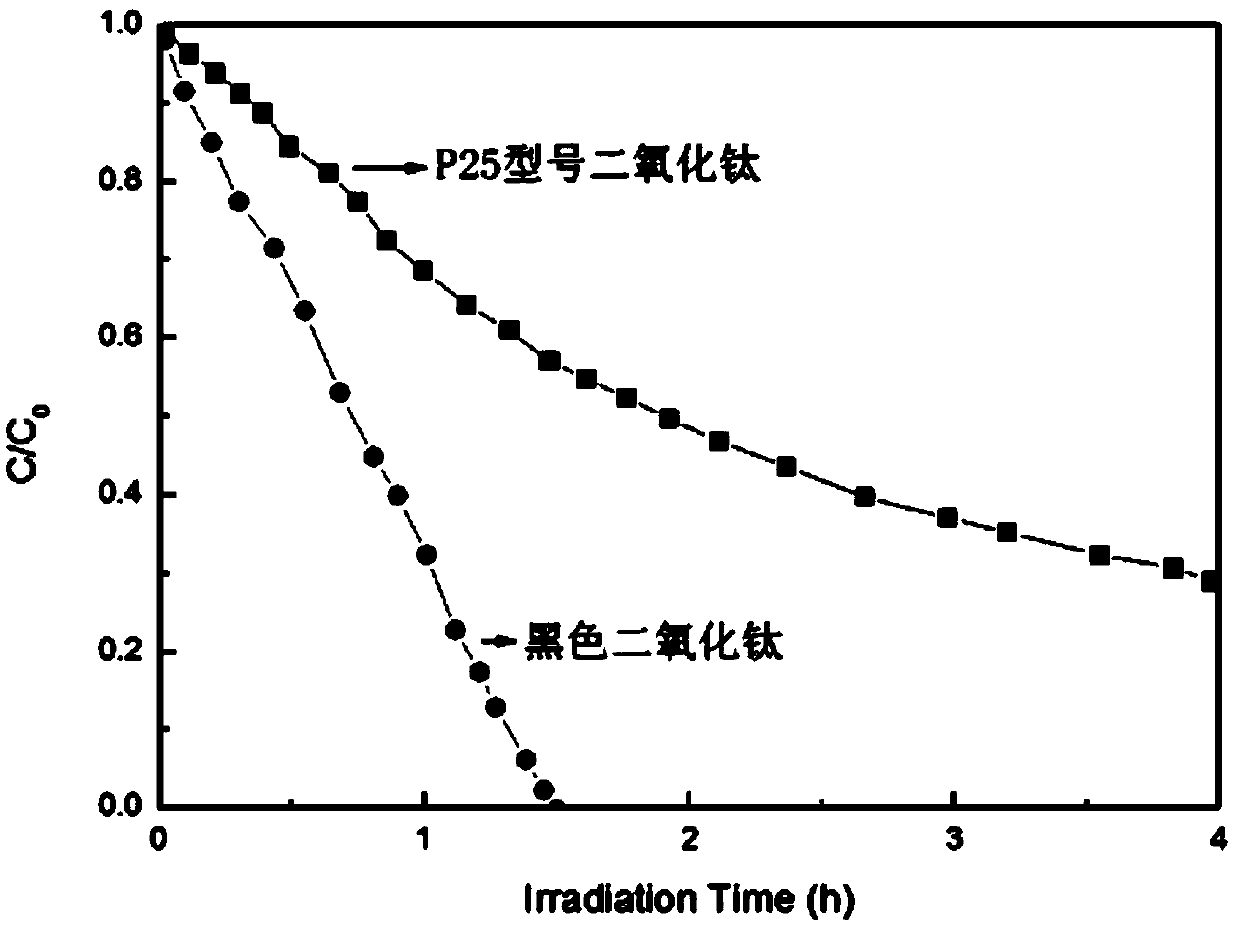
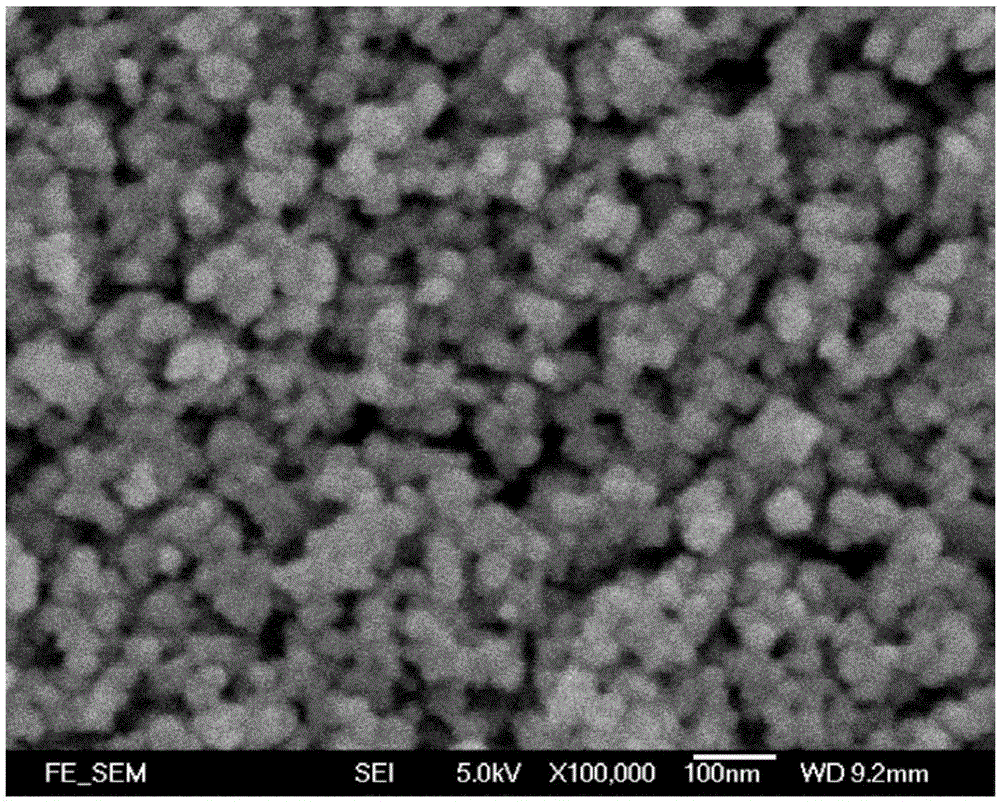
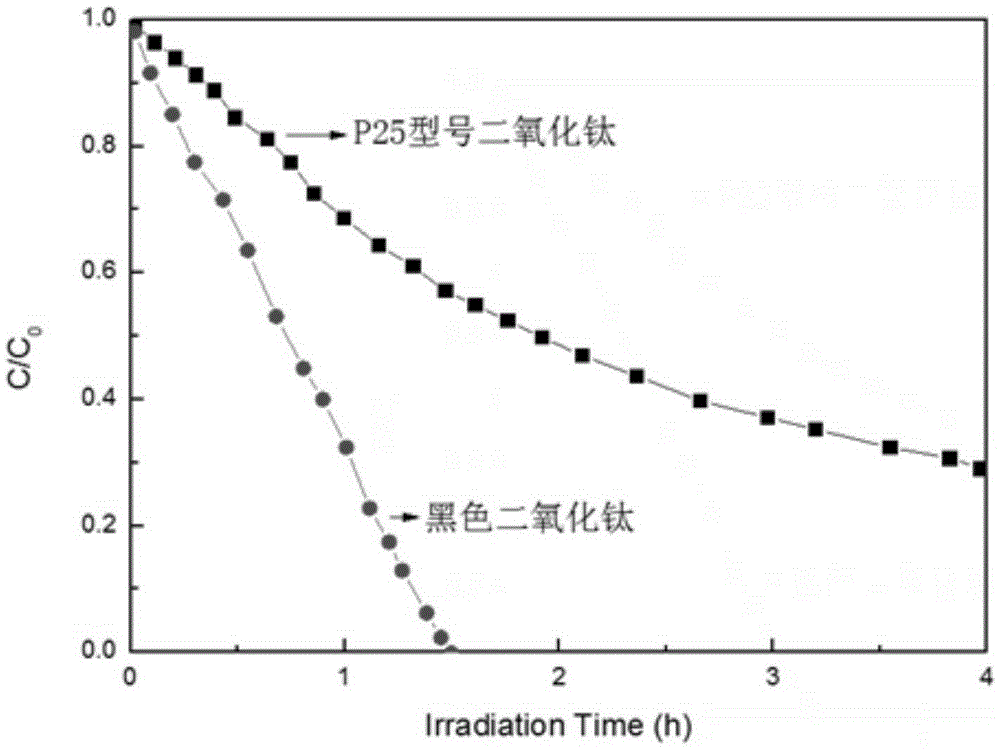
Method for preparing black titanium dioxide by using hydrothermal synthesis method
The invention discloses a method for preparing black titanium dioxide by using a hydrothermal synthesis method. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) adding sodium peroxide or potassium peroxide into titanium hydride or titanium nitride powder, mixing the materials uniformly, adding water, and stirring the materials uniformly; (2) soaking the polytetrafluoroethylene lining of a reaction kettle into aqua regia at the room temperature for 1 hour, boiling the polytetrafluoroethylene lining with distilled water for three times, putting a powder mixed solution prepared in the step (1) into the polytetrafluoroethylene lining, putting the polytetrafluoroethylene lining into a matched steel casing, and tightening the steel casing; (3) putting the reaction kettle into a constant-temperature reactor, and reacting at the temperature of 150-250 DEG C for 3-7 hours; (4) after the reaction, centrifuging a product obtained in the step (3), discarding supernatant, taking precipitate out, and washing the precipitate with deionized water; and (5) drying the precipitate obtained in the step (4) to obtain the black titanium dioxide powder.
Owner:重庆深盟新材料科技有限公司
Super-thin artificial stone sheet and its prepn process
The super-thin artificial stone sheet is prepared with material including epoxy resin, unsaturated resin, emulsifier, potassium peroxide-acetone paste, acid cobalt compound solution, quartz powder, quartzite, mica and titanium white powder in certain proportion. The super-thin artificial stone sheet has color similar to natural stone material, and may be used in decorating wall, ceiling, surface of furniture, door, etc.
Owner:杨世杰
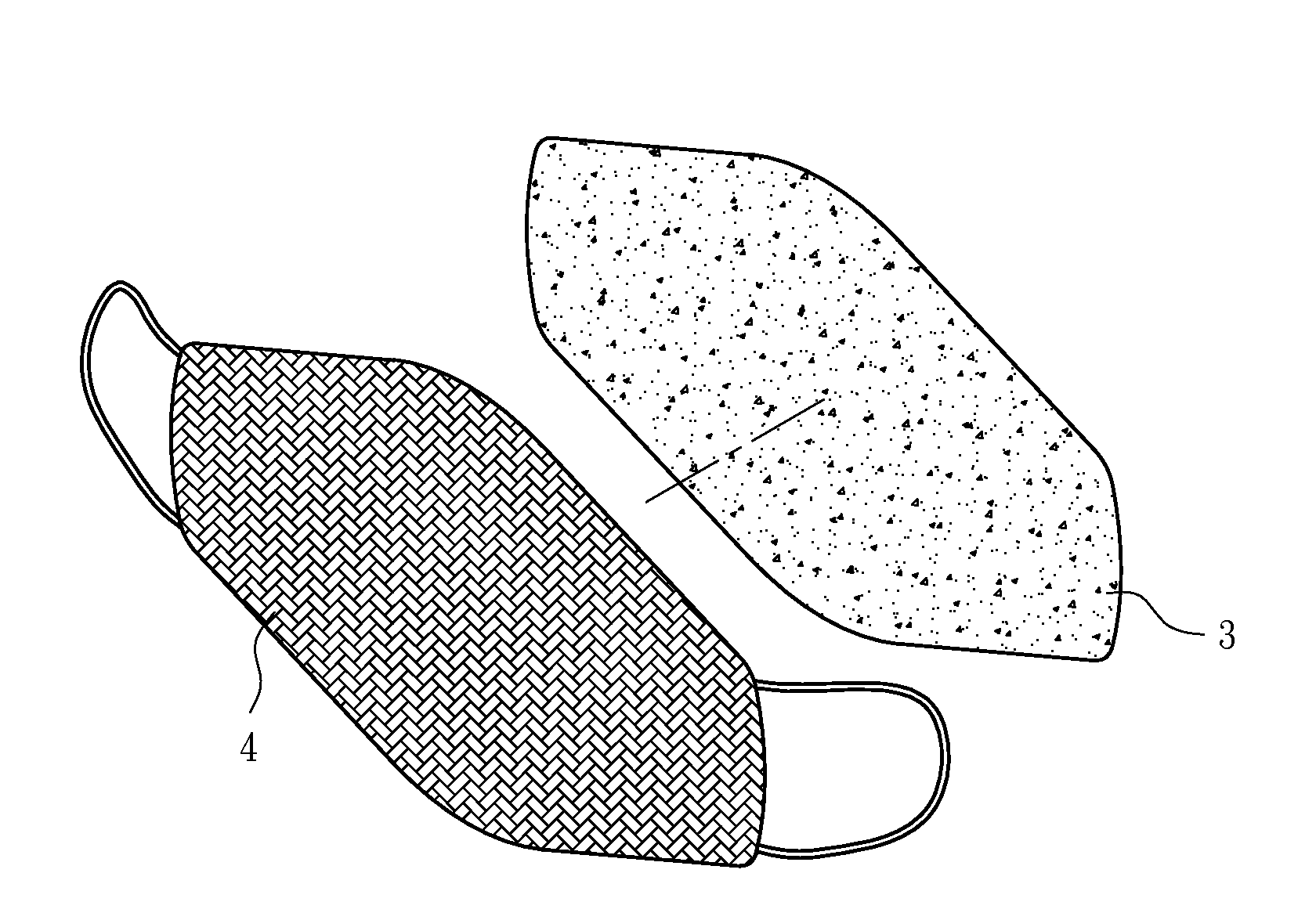
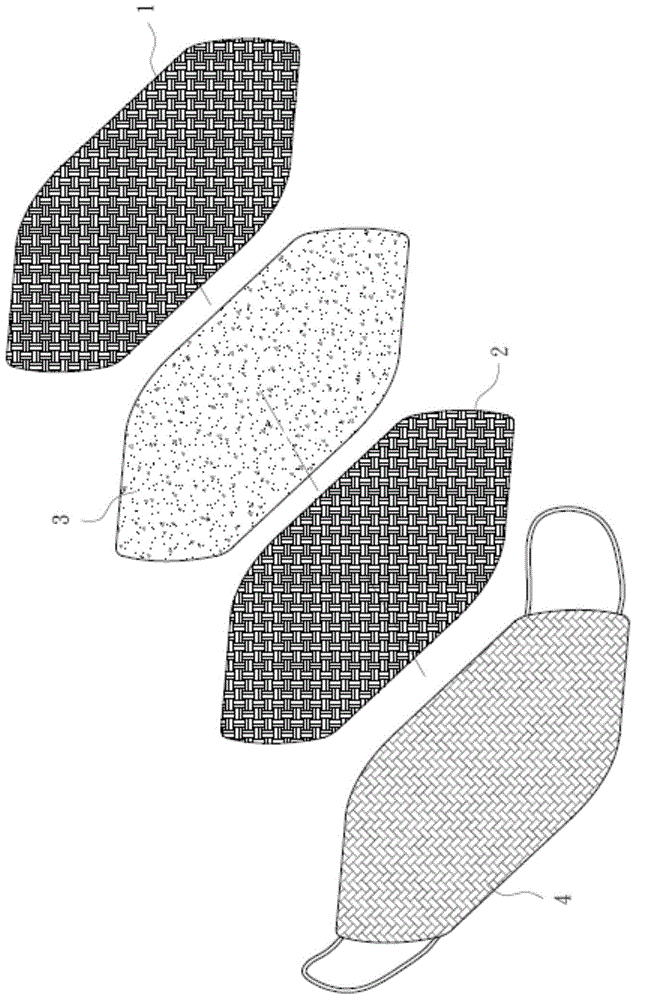
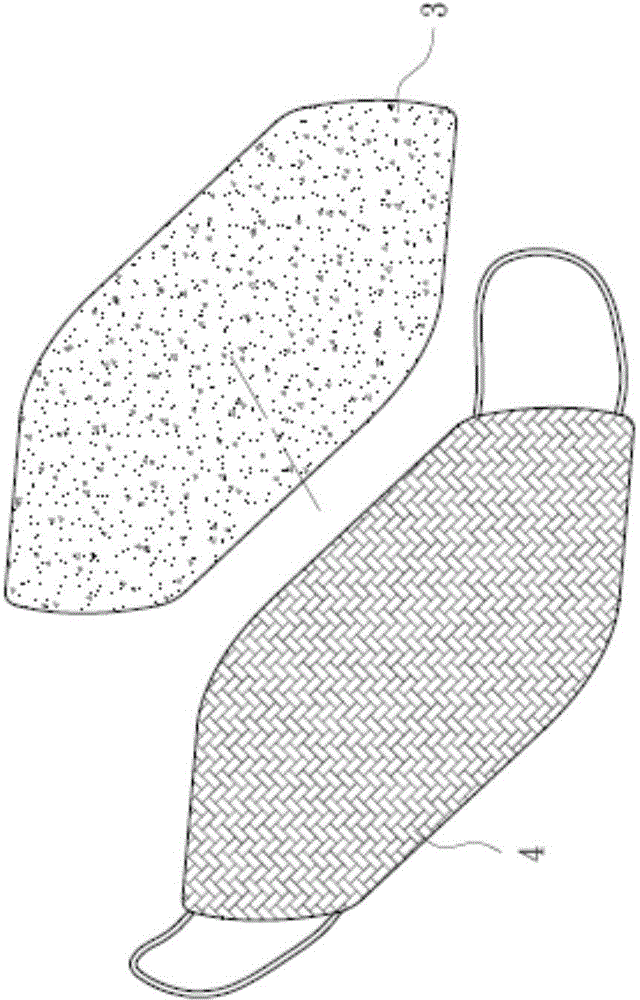
Air permeable mask
The present disclosure relates to a mask providing oxygen and removing water vapor in which a functional layer for oxygen production, moisture removal and better air quality is embedded; the functional layer can be inserted between an outer layer and an inner layer of the mask, taken as an inner layer or a sole layer, or held in a receiving pocket or attach / adhere to an innermost side of the mask; the functional layer comprises metal peroxide, metal superoxide, metal oxide and nonmetal oxide to remove water vapor and provide oxygen; the metal peroxide is selected from the group consisting of magnesium peroxide, potassium peroxide, sodium peroxide and calcium peroxide; the metal superoxide comprises potassium superoxide or sodium superoxide; the metal oxide is selected from the group consisting of magnesium oxide, calcium oxide and sodium oxide; the nonmetal oxide can be silicon dioxide.
Owner:TSAUR GARRY +2
Papermaking wastewater treatment agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105399194AEfficient removalEasy to transportWater treatment compoundsSpecific water treatment objectivesTert butylPolyacrylamide
The invention relates to a papermaking wastewater treatment agent and a preparation method thereof. The treatment agent comprises the following components in parts by mass: 90-115 parts of tetraethylene pentamine, 30-50 parts of sodium carbonate, 15-30 parts of diatomite, 4-12 part of powdered carbon, 0.001-0.005 part of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt, 0.0001-0.0005 part of polyacrylamide, 0.0003-0.0007 part of dimethyl ethanolamine, 0.08-0.35 part of tertiary butyl hydrogen, 0.3-0.9 part of mercaptobenzothiazole, 0.00005-0.00015 part of potassium peroxide, 0.002-0.004 part of calcium hydroxide, 0.00005-0.00015 part of dithiothreitol, 0.2-0.55 part of zinc sulfate, and 0.03-0.06 part of tetradecyltributylphosphonium chloride. The treatment agent provided by the invention can effectively remove harmful substances in papermaking wastewater.
Owner:JIANGSU GAIYA ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
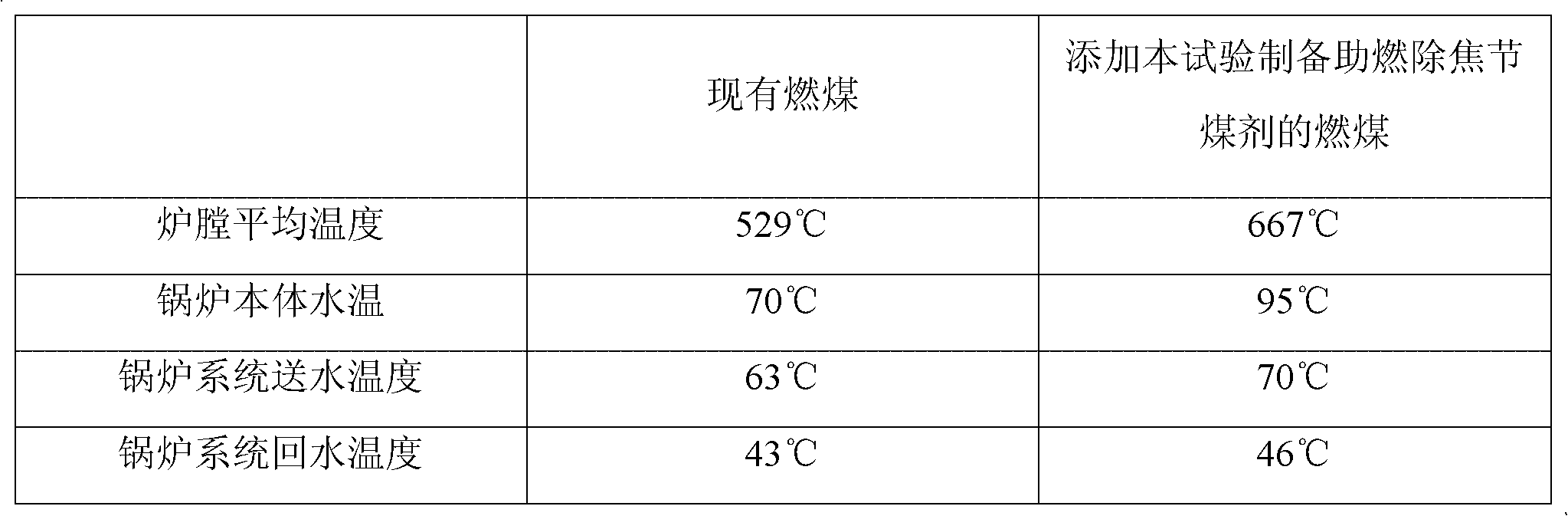
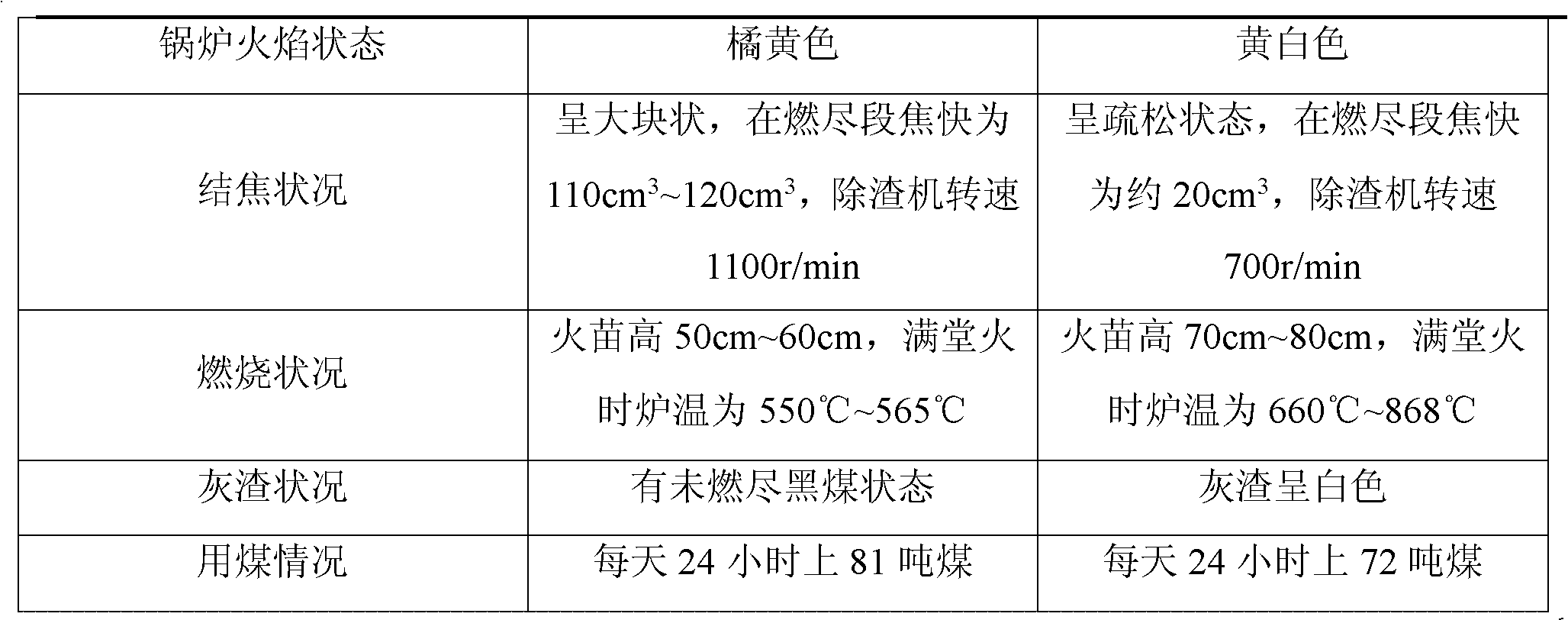
Combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent
The invention provides a combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent, relating to a coal saving agent. The invention aims at solving the problems that coal cost of an enterprise is high and a coked block is produced in a combustion process. The combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent provided by the invention is formed by mixing potassium hypermanganate, sodium chloride, dimethylcarbinol-ethanol, rare earth lanthanum, dispersing agent, calcium chloride, high-alumina vanadine, olefine acid-dimethylbenzene acrylate copolymer, methylisobutylketone, potassium peroxide, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monostearate, sulphur-fixing agent, Tween-60, tributyl phosphate, diisopropyl ether, descaling agent and penetrant. The combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent provided by the invention has the advantages that: firstly, after the combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent is used, furnace box temperature is improved, slag carbon content is reduced, and dust and harmful gases such as carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide are removed; and secondly, the combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent provided by the invention also has decoking function, thus deslagging labour intensity is reduced, comprehensive fuel coal saving rate is 7-16%, and production cost is reduced. The combustion-supporting decoking coal saving agent provided by the invention is mainly used for preparing the coal saving agent.
Owner:哈尔滨巨龙节能设备经销有限责任公司
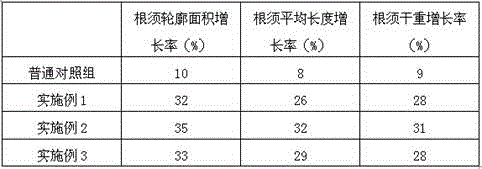
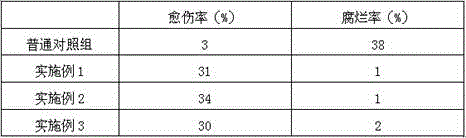
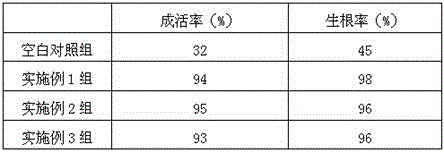
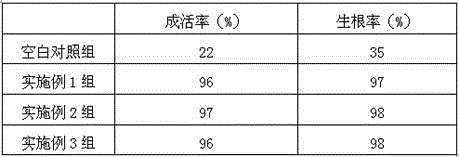
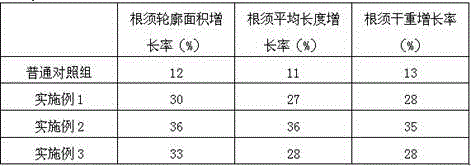
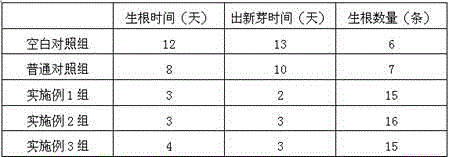
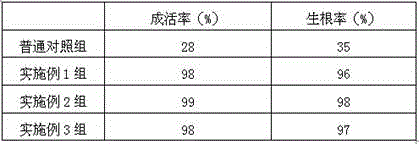
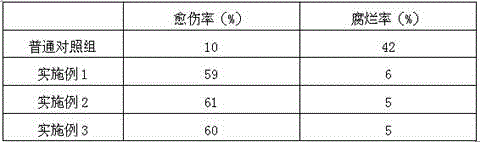
Rooting agent containing ferric citrate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106376619ASolve the problem of high incidence of rot diseaseThe effect of promoting wound healingPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant rootsPolyacrylamide
The invention relates to a rooting agent containing ferric citrate. The rooting agent comprises ferric citrate, ethanolamine, a Chinese gall extract product, a garlic extract product, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, polypropylene carbonate resin, polyacrylamide, 6-aminofurfurylpurine, a brown sugar solution, sodium alginate, potassium peroxide, ferric citrate, magnesium carbonate, and a slow release material. The invention also provides a preparation method of the rooting agent containing ferric citrate. The rooting agent solves the problem of large probability of rot disease of Salix babylonica planted in saline land. The rooting agent has the effect for promoting cutting callus effect of Salix babylonica, and can greatly increase the growth vitality of the plant roots when used for cottage of Salix babylonica in saline land.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Ventilating material mouth mask with functions of oxygen supply and dehumidifying
The invention discloses a ventilating material mouth mask with functions of oxygen supply and dehumidifying, and a functional layer of the mouth mask can supply oxygen and achieve dehumidifying , so as to improve the quality of air in the mouth mask. The functional layer is located between an outermost layer and an innermost layer, or at the innermost layer, or at a unique layer, or in a storage bag, or is pasted at the innermost side of the mouth mask. The functional layer comprises a metallic peroxide, a metallic superoxide, a metallic oxide, and a non-metallic oxide, wherein the metallic peroxide, the metallic superoxide, the metallic oxide and the non-metallic oxide respectively have functions of reducing humidity and generating oxygen. The metallic peroxide is selected from a group composed of a magnesium peroxide, a potassium peroxide, a sodium peroxide, and a calcium peroxide. The metallic superoxide contains potassium superoxide or sodium superoxide. The metallic oxide is selected from a group composed of magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, and sodium oxide. The non-metallic oxide is silicon dioxide.
Owner:曹荣华 +2
Low-temperature sintered MnZn ferrite material and preparation and sintering method thereof
The invention provides a low-temperature sintered MnZn ferrite material and a preparation and sintering method thereof. The ferrite material is prepared from the following main components according torespective standard substances: 49.5 to 56.5 mol percent of Fe2O3, 6.5 to 16 mol percent of ZnO, and 29.5 to 41 mol percent of MnO; auxiliary additives comprise calcium oxide, sodium peroxide, potassium peroxide, molybdenum sesquioxide, silicon dioxide and zinc metaborate; the total amount of the auxiliary additives is 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of the total amount of the main components; the ferrite material is subjected to ball grinding, granulation, secondary ball grinding and spraying to obtain ferrite material powder; after being pressed for molding, the ferrite material powder is sintered at 1,180 + / - 30 DEG C for 3 to 5.5 hours, thereby obtaining a sintered magnetic core. The sintering temperature of the low-temperature sintered MnZn ferrite material provided by the invention is substantially reduced, so that the low-temperature sintered MnZn ferrite material can be sintered at about 1,180 DEG C; the sintering heat preservation time length is shortened to 3 to 5 hours; low-power-consumption and low-power ferrite with high performance is obtained, which is low in sintering temperature, short in heat preservation time and low in magnetic core production energy consumption.
Owner:成都圻坊生物科技有限公司
Rooting agent containing hydroxyethyl cellulose and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106376605AImprove growth vigorImprove survival rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsHydroxyethyl celluloseFORMALDEHYDE SOLUTION
The invention provides a rooting agent containing hydroxyethyl cellulose. The rooting agent comprises the following raw materials: hydroxyethyl cellulose, sodium tripolyphosphate, a wild chrysanthemum flower extract product, polylactic acid resin, compound sodium nitrophenolate, willow branch powder, starch, amylase, potassium peroxide, a magnesium fertilizer and chelating iron. The invention also provides a preparation method of the rooting agent containing hydroxyethyl cellulose. The method comprises a step of preparation of an ureaformaldehyde solution. The method for preparing the ureaformaldehyde solution comprises the following steps: adding urea and water in a dissolving tank, and adding sodium hydroxide after dissolving so that the pH value of a urea solution is 8.5-9. By using the prepared rooting agent, growth vitality of the roots of pomegranate planted in saline land can be greatly increased. The survival rate and rooting rate of the pomegranate planted in saline land can be greatly increased.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Oxygen-producing respiratory protection device
InactiveCN101107046AHigh performance dataLow costFire rescueRespiratory apparatusGratingLithium hydroxide
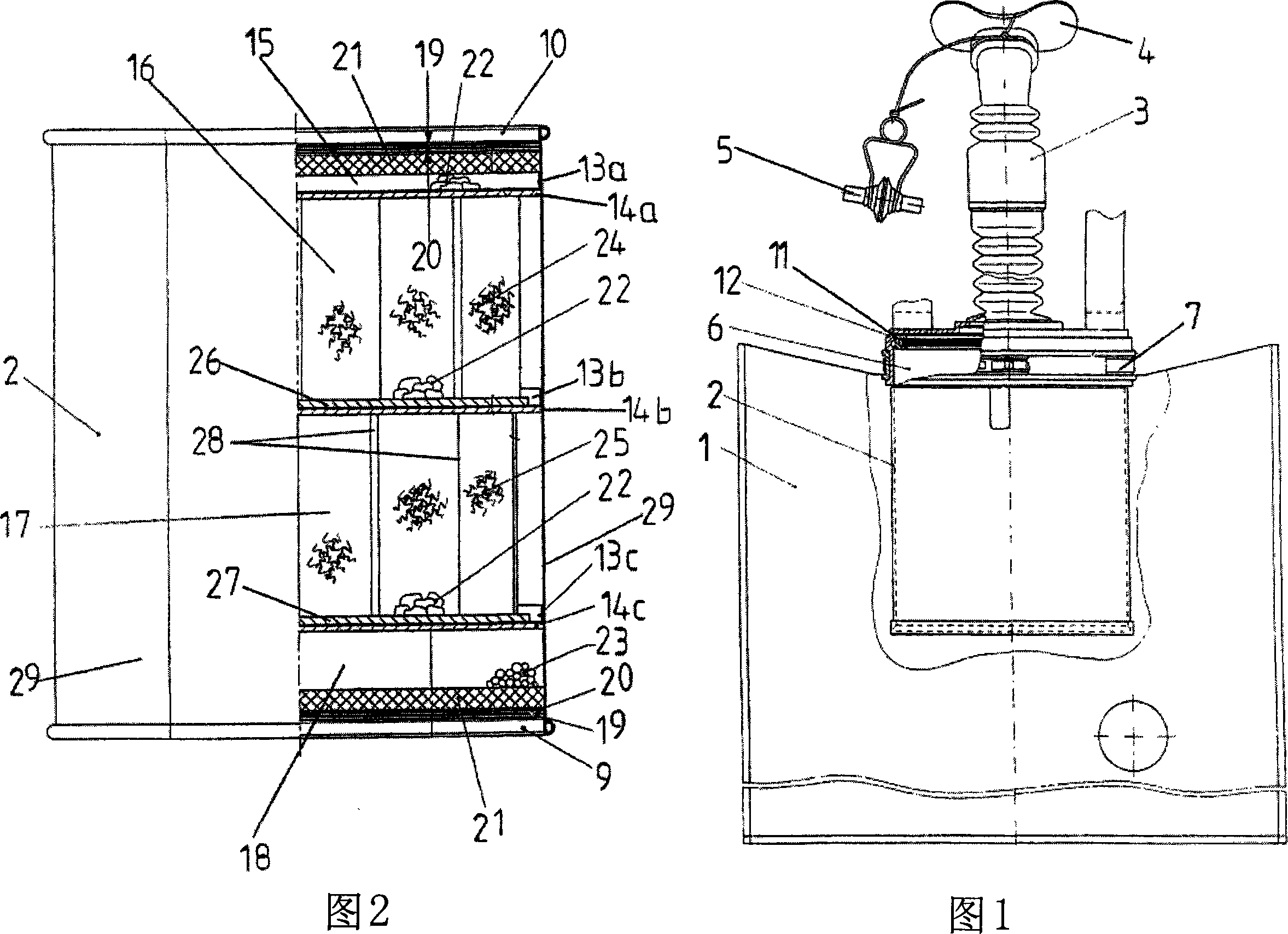
The invention relates to a respiratory protection device wherein the chemical cartridge through which inhaled air flows in order to produce oxygen is subdivided into a plurality of air treatment compartments (15 to 18) by means of retaining gratings. The outer air treatment compartments (15, 18) are provided with fine copper braid shock-absorbing means (21a, b) that rest flat against the respective cover. The center air treatment compartments (16, 17) are provided with a concertina-folded damping element (24, 25) from a multilayer fine braid having fold edges that extend in parallel and at a distance to the outer wall of the chemical cartridge (2). The one - zigzagged - edge of said damping element is fastened to a wire grating (26, 27). The damping elements of adjacent air treatment compartments are not aligned. The air treatment compartments accommodate potassium peroxide granules (22) for producing oxygen. An air treatment compartment (18) can be filled with lithium hydroxide tablets (23) for binding excess carbon dioxide. The inventive device is immediately operative at high mechanical stress even when it was not actively used for a long time and has a high output.
Owner:MSA EURO
Method combining oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water
InactiveCN102642951BEfficient Adsorption RemovalImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPotassium persulfateChlorine dioxide
The invention provides a method combining an oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water. The oxidizing composite reagent is added into the water and stirred, and then the activated carbon is utilized to adsorb the arsenic. The oxidizing composite reagent is formed by compositing potassium ferrate, chlorine dioxide, sodium peroxide, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, or is formed by compositing potassium peroxide, sodium peroxide, sodium monopersulfate, iron chloride and hydroxylaminehydrochloride, or is formed by compositing calcium peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, calcium monopersulfate, calcium persulfate, cerium chloride, ferric chloride, cerous sulfate and humus, or is formed by compositing cobalt chloride, ammonium monopersulfate, ammonium persulfate, cerous sulfate, sodium peroxide and hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The method can not only remove the arsenic in drinking water, underground water and surface water rapidly, efficiently, conveniently and safely, but also effectively reduce concentration of the arsenic in sewage containing arsenic and effluent of sewage secondary sedimentation tanks, and simultaneously can have good recovery effect on lakes and inland seawater polluted by the arsenic.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Sulfur dioxide scrubbing system and process for producing potassium products
ActiveUS20170190575A1Gas treatmentThiosulfates/dithionites/polythionitesPotassium peroxideOxidation state
The invention relates to a process for preparing potassium thiosulfate, potassium sulfite or potassium bisulfite comprising the following steps:Step (1a): providing a potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate solution for neutralizing acid forming components such as dissolving SO2 or H2S;Step (1b): providing an SO2 contacting solution, containing at least some potassium sulfite or potassium bisulfite or potassium thiosulfate;Step (2): providing SO2 gas;Step (3): reacting these to absorb the SO2 gas and to form an intermediate reaction mixture comprising potassium sulfite, or potassium bisulfite or a mixture thereof, and optionally recovering the potassium sulfite, or potassium bisulfite or a mixture thereof, and / or optionally using steps 4 and 5;Step (4): adding sulfur or sulfide containing compound containing sulfur having the oxidation state of 0, −2 or of between 0 and −2 to the reaction mixture and optionally potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate, and reacting the mixture under suitable conditions to form potassium thiosulfate; andStep (5): recovering the potassium thiosulfate, and optionally concentrating the potassium thiosulfate.
Owner:TESSENDERLO KERLEY INC
Method for ageing to improve vinosity of rice wine
InactiveCN108504528APromote oxidationImprove esterification abilityAlcoholic beverage preparationOxidation-Reduction AgentPotassium peroxide
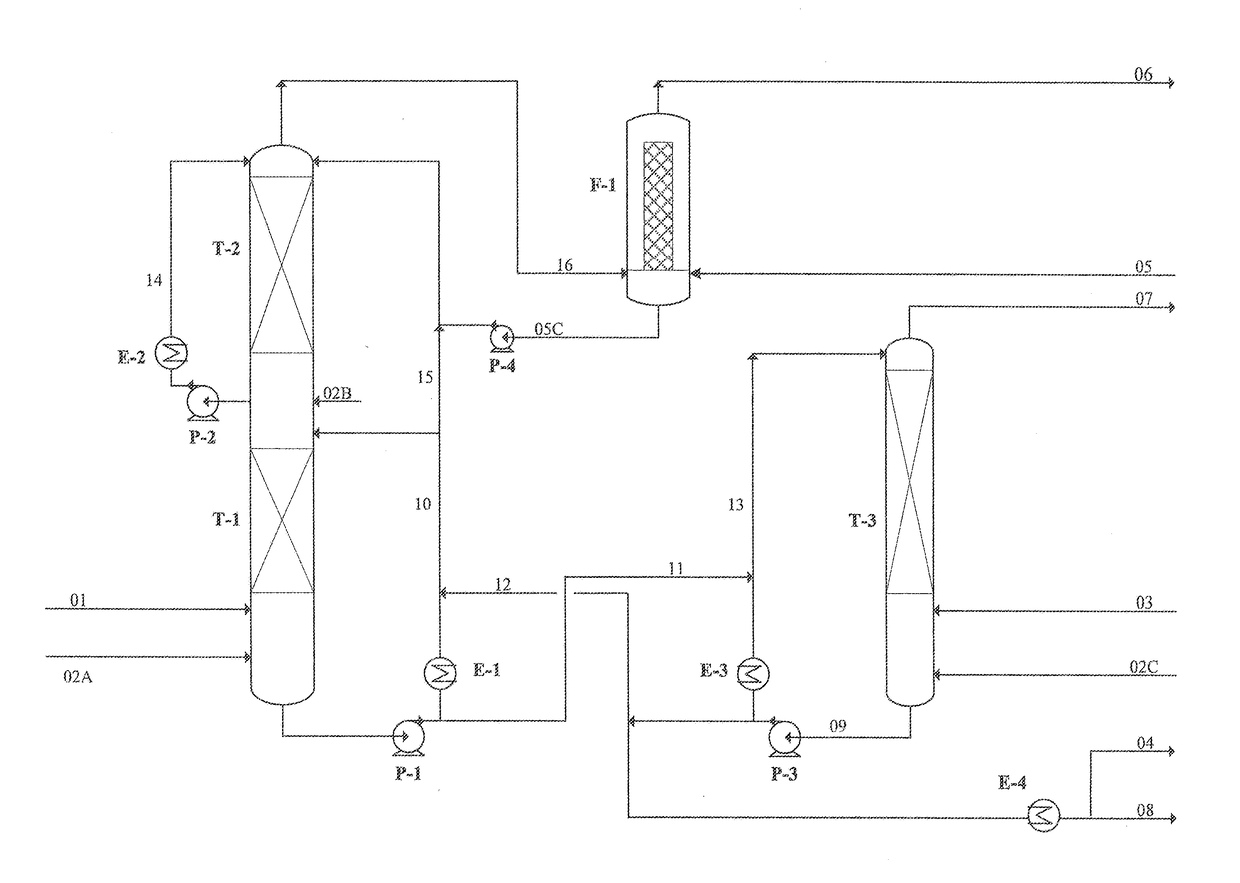
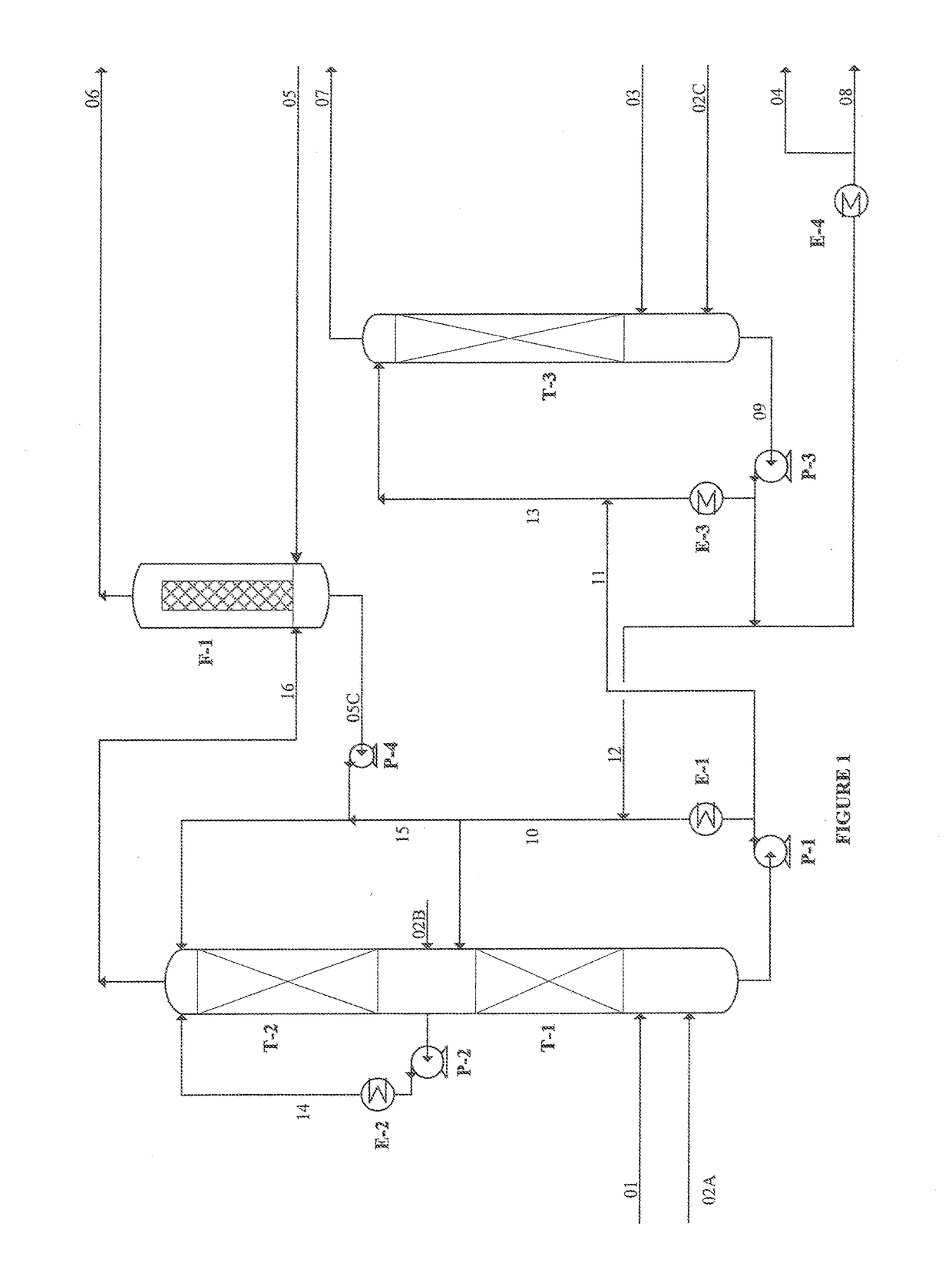
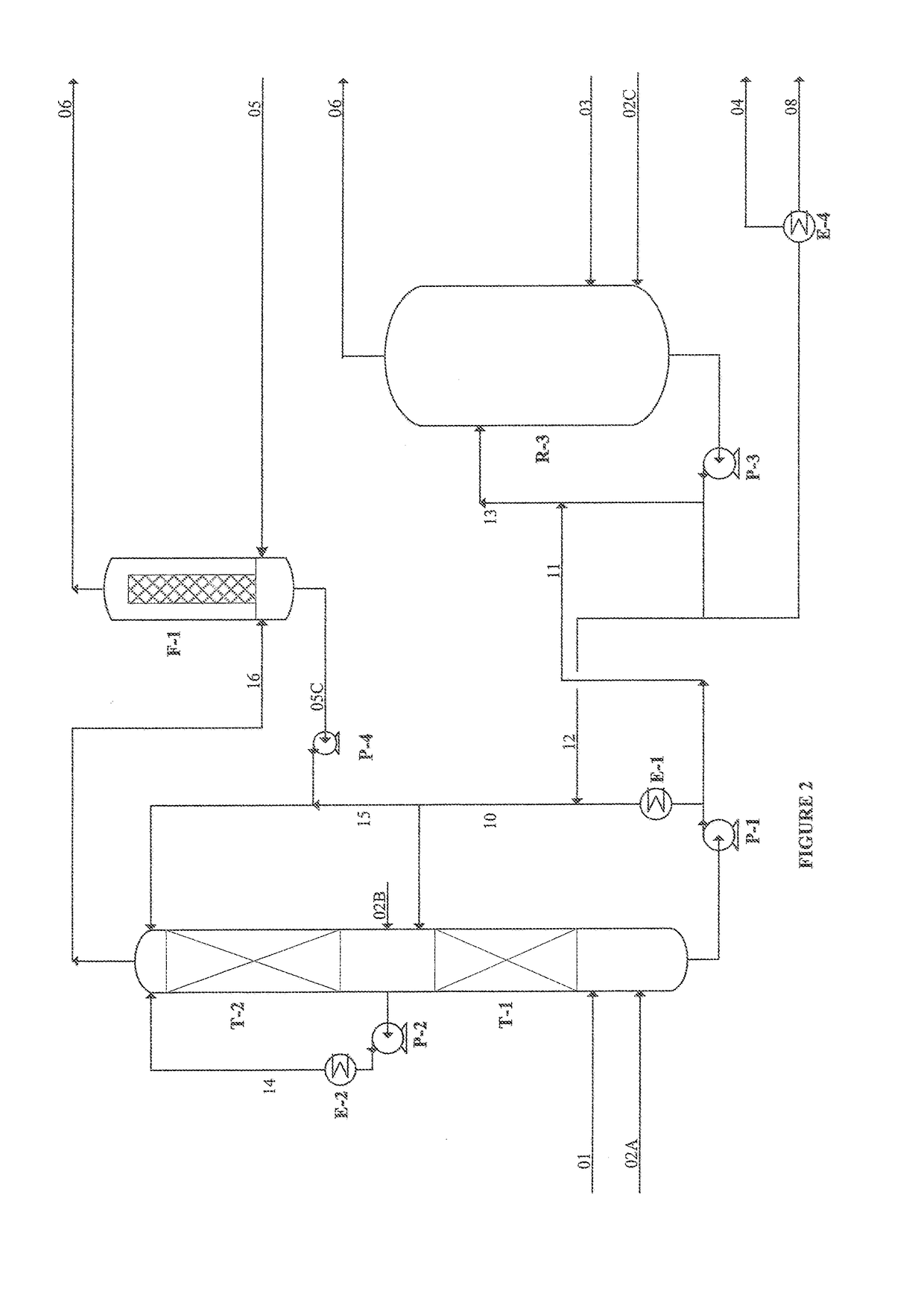
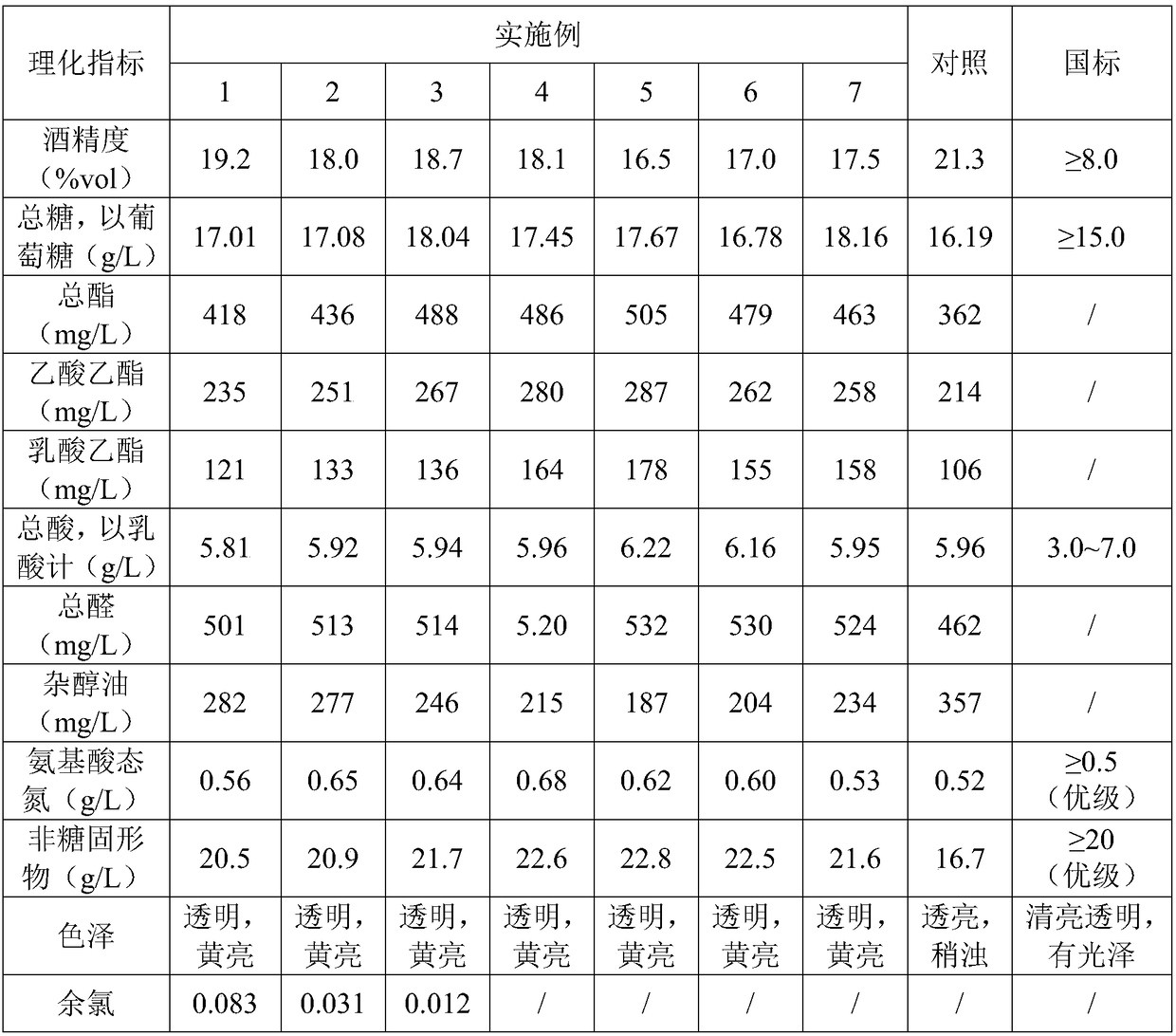
The invention discloses a method for ageing to improve vinosity of rice wine, relating to the technical field of rice wine ageing. The method comprises the following process steps: sending green wineinto an ageing device, adding a hypochlorous acid solution to to-be-treated rice wine by taking hypochlorous acid and potassium peroxide as oxidizing agents, performing redox reaction under the illumination condition, and sealing treated rice wine at room temperature for storage for 2 months. According to the invention, hypochlorous acid and potassium peroxide are taken as oxidizing agents, and under the synergistic effect of ultraviolet light and a catalyst, redox reaction and esterification reaction are promoted to be performed in an accelerated way, ageing rate is high and efficiency is high.
Owner:枣阳市灵鹿酒业有限公司
Glue roller squeegee oil for large size ceramic tile otter board printing
InactiveCN101397217AApplicable printing requirementsAdjustable specific gravityPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention belongs to the squeegee oil category of ceramic industry, in particular to rubber roll squeegee oil for large-scale ceramic tile screen printing. The rubber roll squeegee oil is a mixture which consists of the following components by weight: 45 to 60 parts of glycerol, 30 to 45 parts of polyether polyol, 7 to 18 parts of polymer and 0.2 to 5 parts of initiator; and the characters are as follows: the rubber roll squeegee oil is colorless or slightly yellow translucent body; the viscosity is 110 to 130Mpa question mark S; the density at 20 DEG C is 1.040 to1.060; the pH value is 6 to 8, and the freezing point is minus 30 DEG C. The high polymer refers to acrylic acid, acrylamide or polyethylene glycol. The initiator refers to sodium peroxide, amine peroxide or potassium peroxide. The rubber roll squeegee oil can be applicable to the printing needs of ceramic walls and floor tiles with various specification and large format; the specific gravity and the thickness can be adjusted. The rubber roll squeegee oil has good suspension and dispersion properties, no delamination during the placement, performances of keeping moisture, lubrication, penetrating screen, cooling screen, anti-static, and the like and strong applicability. Printing glaze slurry which is prepared by the rubber roll squeegee oil has good liquidity, low viscosity and convenient application, the bonding force of a color agent on a green body is increased, and a printed pattern is bright and clear.
Owner:淄博宜龙实业有限公司
Magnesium alloy surface chromium-free composite passivation solution
InactiveCN104342678AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove efficiencyMetallic material coating processesChromium freePhosphate
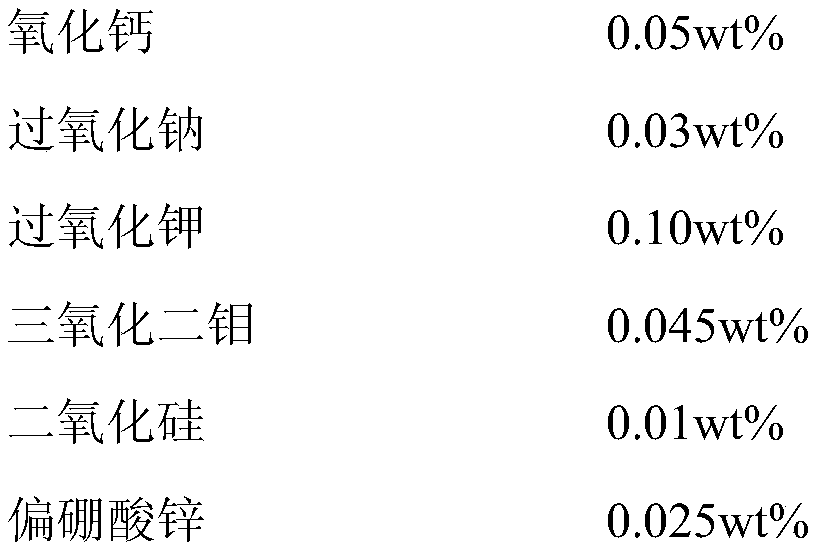
The present invention discloses a magnesium alloy surface chromium-free composite passivation solution, which comprises 12-14 g / L of sodium molybdate, 6-8 g / L of manganese dihydrogen phosphate, 4-6 g / L of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 14-16 g / L of zinc oxide, 26-28 g / L of 85% phosphoric acid, 6-8 g / L of sodium nitrate, 2-4 g / L of calcium chlorate, 2-4 g / L of boric acid, 1-3 g / L of strontium chloride, 2-4 g / L of potassium peroxide, 0.3-0.5 g / L of OP-10, and the balance of deionized water.
Owner:WUXI SHITANGWAN IND PARK DEV CONSTR
High-strength flame-retardant cable material for power cables and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength flame-retardant cable material for power cables and a preparation method thereof. The cable material comprises, by weight, 60-100 parts of heat-vulcanized silicone rubber, 20-100 parts of silicon dioxide, 20-30 parts of white carbon black, 10-15 parts of potassium peroxide, 20-30 parts of magnesium chloride, 6-8 parts of composite ceramic powder, 25-35 parts of water-granulated slag micro powder, 4-6 parts of glass fiber, 8-16 parts of sodium orthosilicate, 30-40 parts of zinc stearate and 20-30 parts of reinforcing agent. While good mechanical performance and insulativity are kept, the overall strength and flame retardancy of the cable material are improved, and the application range of the cable material is widened.
Owner:ANHUI TIANYUAN CABLE
Rooting agent containing kava extract and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a rooting agent containing a kava extract. The rooting agent provided by the invention is characterized by comprising the following preparation raw materials: the kava extract, sodium pyrophosphate, a licorice extract, plantain seed gum, polylactic acid resin, sodium 5-nitroguaiacolate, a white sugar solution, cellulose, potassium peroxide, ferrous sulfate, magnesium humate, ferrous sulfate and a sustained-release matrix. The invention also provides a preparation method for the rooting agent containing the kava extract. The preparation method is characterized by comprising a step of drying; and in the step of drying, a shaped cylindrical rooting agent is dried, wherein the water content of the rooting agent is no more than 3%. By utilizing the rooting agent prepared by using the method provided by the invention for cutting of apple cuttings in saline-alkali soil, the expanding speed of a plant root system can be increased; and by utilizing the rooting agent prepared by using the method provided by the invention for cutting plantation of the apple cuttings in the saline-alkali soil, the rooting rate and the cutting survival rate of the apple cuttings can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
A method for preparing black titanium dioxide by hydrothermal synthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing black titanium dioxide by using a hydrothermal synthesis method. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) adding sodium peroxide or potassium peroxide into titanium hydride or titanium nitride powder, mixing the materials uniformly, adding water, and stirring the materials uniformly; (2) soaking the polytetrafluoroethylene lining of a reaction kettle into aqua regia at the room temperature for 1 hour, boiling the polytetrafluoroethylene lining with distilled water for three times, putting a powder mixed solution prepared in the step (1) into the polytetrafluoroethylene lining, putting the polytetrafluoroethylene lining into a matched steel casing, and tightening the steel casing; (3) putting the reaction kettle into a constant-temperature reactor, and reacting at the temperature of 150-250 DEG C for 3-7 hours; (4) after the reaction, centrifuging a product obtained in the step (3), discarding supernatant, taking precipitate out, and washing the precipitate with deionized water; and (5) drying the precipitate obtained in the step (4) to obtain the black titanium dioxide powder.
Owner:重庆深盟新材料科技有限公司
Rooting agent containing rice vinegar and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106386910AReduce morbidityImprove survival rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsVitis viniferaSphaceloma
The invention provides a rooting agent containing rice vinegar. The rooting agent is prepared from the following raw materials: rice vinegar, EDTA, ureaformaldehyde powder, 1.5 to 1.8 parts of clove oil, sa-hao seed gum, ginger extract, aloe extract, polylactic acid resin, potassium peroxide, manganese dioxide, hydromel, lignosulfonic acid, aluminum magnesium silicate and a basic material. The invention also provides a preparation method for the rooting agent containing rice vinegar. The method comprise a step of preparation of a binding agent. The binding agent is prepared by heating the hydromel to 60 to 62 DEG C, adding the sa-hao seed gum into the hydromel and carrying out uniform mixing under stirring. As the rooting agent prepared in the invention is used for planting grapes on saline land, the incidence rate of Sphaceloma ampelinum is greatly decreased, and the incidence rate of anthrachose is lowered.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Oxygen preparing process for portable respirator
InactiveCN1468801AGood effectImprove performanceFire extinguisherOxygen preparationCalcium hydroxideAluminium hydroxide
In the oxygen preparing process for portable respirator, the materials including sodium peroxide 10-20 wt%, aluminum hydroxide 15-25 wt%, manganese dioxide 5-7 wt% and aluminum powder 2.5-3.5 wt% as well as potassium hydroxide the rest are used. The present invention has excellent effect of producing oxygen and moisture, can produce oxygen reliably in the temperature over minus 10 deg.c, and may be used widely in various respirators.
Owner:黄峻
Zinc-coated steel plate surface passivation technology
InactiveCN104342691AImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesCalcium silicateAcid washing
The invention discloses a zinc-coated steel plate surface passivation technology. Each liter of a passivating liquid used in the technology is composed of the following components: 22 to 24 grams of sodium silicate, 6 to 8 grams of calcium silicate, 6.5 to 7.5 grams of sodium borate, 8 to 10 grams of potassium peroxide, 5 to 7 grams of sodium citrate, 22-22 mL of HNO3 (68%), 24 to 26 mL of H2SO4 (70%), 3 to 5 grams of dodecyl magnesium sulfate, and the balance being water. The passivation technology comprises the following steps: (1) acid washing: washing a zinc-coating steel plate for 4 to 8 seconds by a nitric acid solution with a concentration of 3 to 5%, and then washing by water; (2) passivating: filling a passivation tank with the prepared passivating liquid, diluting the passivating liquid by water, wherein the ratio of the passivating liquid to water is 1:9-11, adjusting the diluted passivating liquid to 1.5 to 2.5, controlling the temperature at a range of 55 to 65 DEG C, soaking the acid-washed zinc-coated steel plate into the diluted passivating liquid, and carrying out passivation for 180 to 220 seconds.
Owner:WUXI SHITANGWAN IND PARK DEV CONSTR
Biological membrane filler for phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment as well as preparation method and application of biological membrane filler
ActiveCN113087133AEfficient removalHigh film-hanging efficiencyWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentIron sulfateSludge
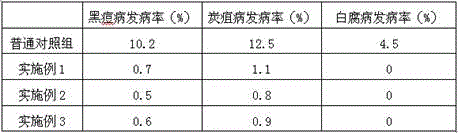
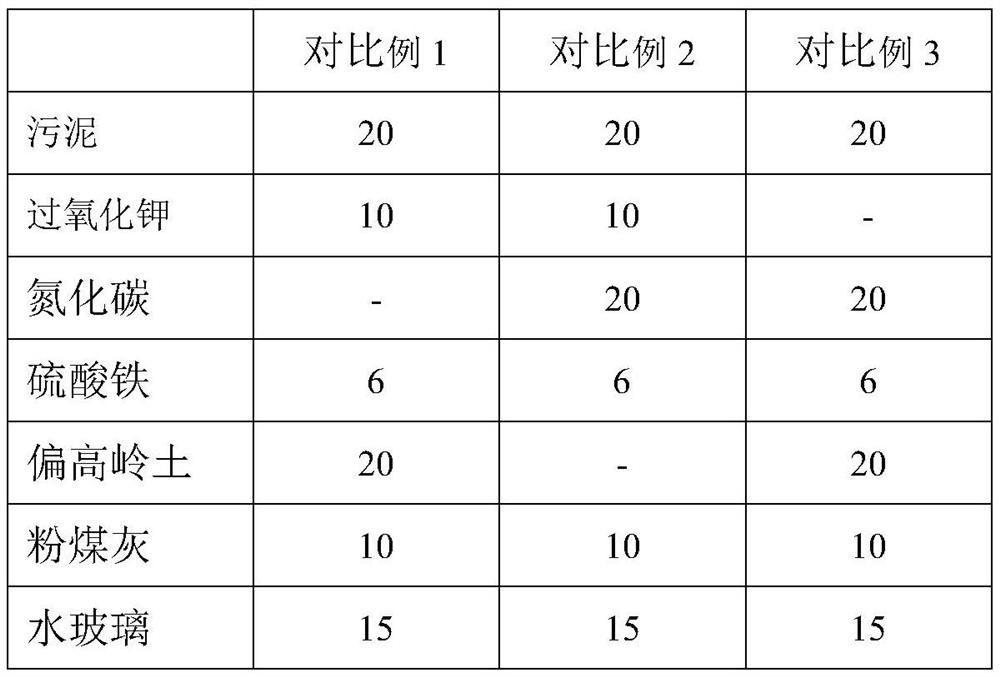
The invention discloses a biological membrane filler for phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment as well as a preparation method and application of the biological membrane filler. The biological membrane filler for phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment is prepared from the following components: sludge, metakaolin, potassium peroxide, carbon nitride, ferric sulfate, fly ash, sodium silicate and water. According to the invention, the biological membrane filler for phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment is developed, the biological membrane filler which has excellent impact strength and provides nutrient substances for phosphorus removal bacteria is prepared from the components such as the sludge, the metakaolin, the potassium peroxide, the carbon nitride and the sodium silicate , so that the membrane culturing efficiency of a biological membrane is high, phosphorus in wastewater is effectively removed, and the biological membrane filler has a stable and efficient treatment effect on high phosphorus content or excessive trace phosphorus in the wastewater.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Treating agent for clearing methane bacterium inhibitor and method for treating generic solid wastes
ActiveCN106282244ALow costImprove survival rateWaste based fuelFermentationSodium bicarbonateStarch xanthate
The invention discloses a treating agent for clearing a methane bacterium inhibitor and a method for treating generic solid wastes. The treating agent is prepared from, by weight, 0.6-0.8 part of sodium bicarbonate, 1-3 parts of calcium oxide, 1-3 parts of ferrous sulfate, 0.4-0.6 part of potassium tripolyphosphate, 0.75-0.95 part of propylene glycol, 1.5-4.5 parts of sodium hydroxide, 6-8 parts of sodium chloride, 0.9-1.1 parts of potassium peroxide, 0.6-0.8 part of potassium ferrate, 0.5-0.7 part of potassium permanganate, 0.6-0.8 part of water-soluble starch xanthate and 0.4-0.8 part of ferric trichloride. The treating agent is low in cost, high in methane bacterium survival rate and quick in material metabolic degradation and can be used for innocent treatment of the generic solid wastes to realize recycling; according to experimental test results, operation efficiency of an anaerobic pool can be improved by 30%-40%.
Owner:深圳市固废环保科技有限公司
Passivation solution for magnesium alloys and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105951087ASolve pollutionImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesPhosphateCobalt
The invention discloses a passivation solution for magnesium alloys and a preparation method thereof. The passivation solution is prepared from sodium molybdate, ammonium vanadate, sodium silicate, cobalt nitrate, manganous dihydrogen phosphate, zinc oxide, oxalic acid, citric acid, potassium chlorate, potassium peroxide, ammonium fluoride, hydrofluoric acid and deionized water. The preparation method comprises the following steps of firstly, using an oxalic acid and citric acid solution to dissolve the zinc oxide; then adding other components; and using a hydrofluoric acid solution to adjust a pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) value. The passivation solution for the magnesium alloys provided by the invention adopts vanadate, molybdate, silicate and the like as raw materials, and does not contain heavy metal chromium polluting the environment, so that the problem that a passivation technology containing chromium pollutes the environment is fundamentally solved, and the passivation solution is beneficial to environmental protection; and in addition, according to the passivation solution for the magnesium alloys provided by the invention, metallic oxide and fluoride composite films can be generated on the surfaces of the magnesium alloys, and the corrosion resistance of the composite passivation films is excellent, and can be same as or even higher than the corrosion resistance of chromium passivation films.
Owner:WUXI EPIC TECH
Magnesium alloy surface chromium-free composite passivation solution preparation process
InactiveCN104342680AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove efficiencyMetallic material coating processesChromium freePhosphate
The present invention discloses a magnesium alloy surface chromium-free composite passivation solution preparation process, wherein the passivation solution comprises 12-14 g / L of sodium molybdate, 6-8 g / L of manganese dihydrogen phosphate, 4-6 g / L of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 14-16 g / L of zinc oxide, 26-28 g / L of 85% phosphoric acid, 6-8 g / L of sodium nitrate, 2-4 g / L of calcium chlorate, 2-4 g / L of boric acid, 1-3 g / L of strontium chloride, 2-4 g / L of potassium peroxide, 0.3-0.5 g / L of OP-10, and the balance of deionized water. The preparation process comprises: diluting phosphoric acid with deionized water, adding zinc oxide blended into a paste while stirring, sequentially adding sodium molybdate, manganese dihydrogen phosphate, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium nitrate, calcium chlorate, boric acid, strontium chloride, potassium peroxide, OP-10 and the remaining deionized water after the zinc oxide is completely dissolved, stirring for 20-30 min, and adjusting the pH value to 2-3.
Owner:WUXI SHITANGWAN IND PARK DEV CONSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com