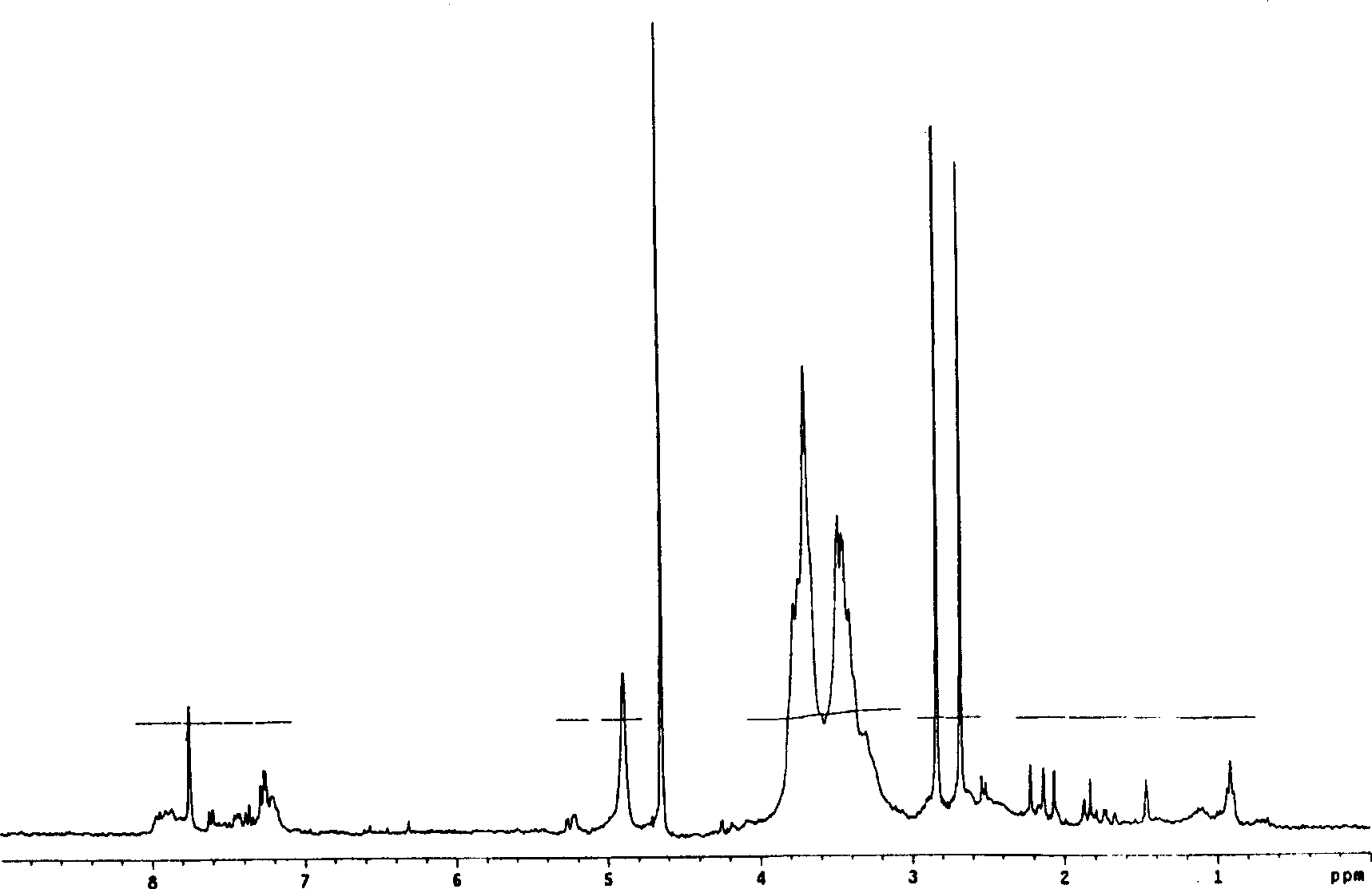
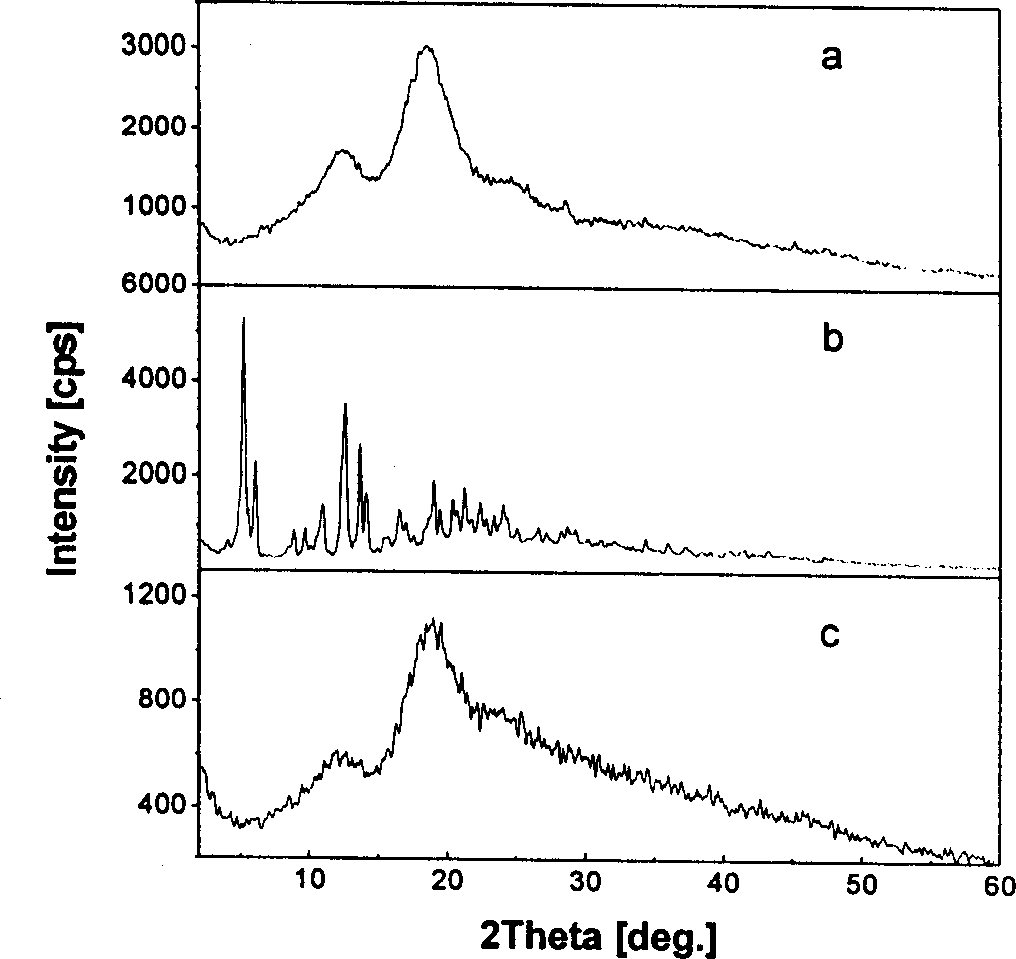
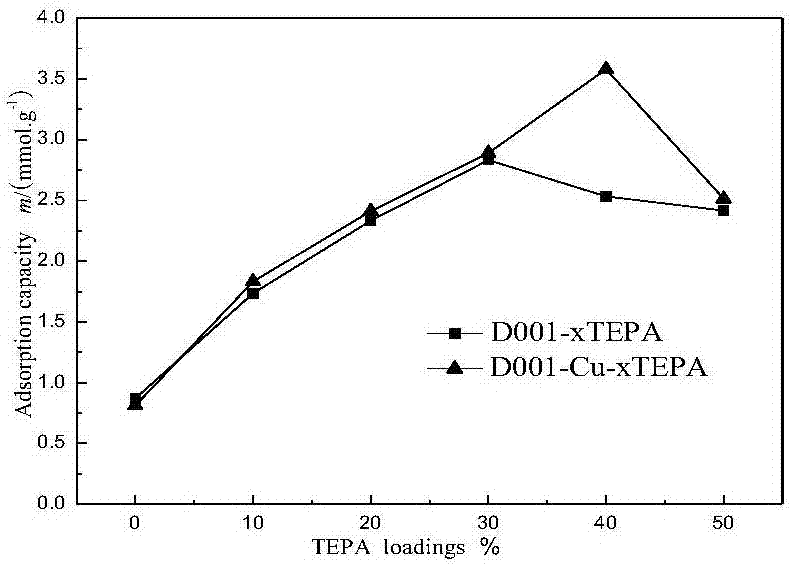
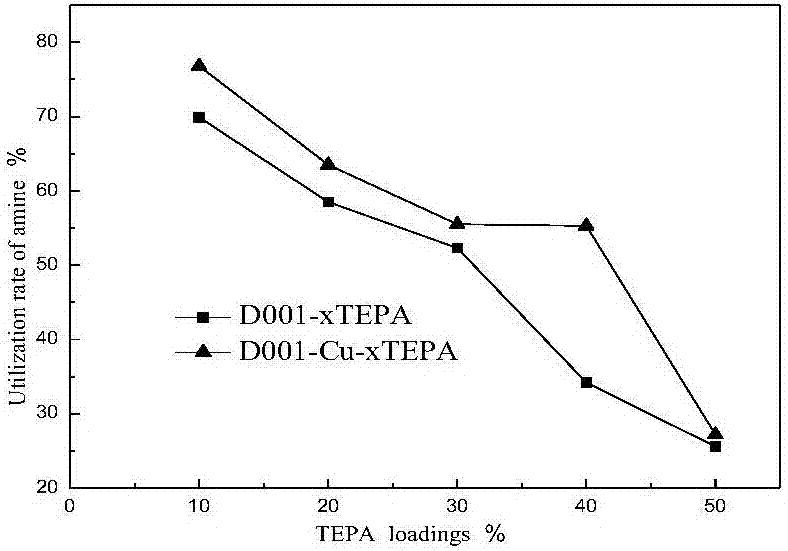
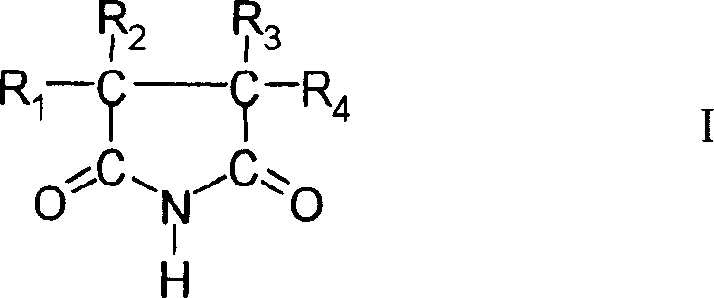
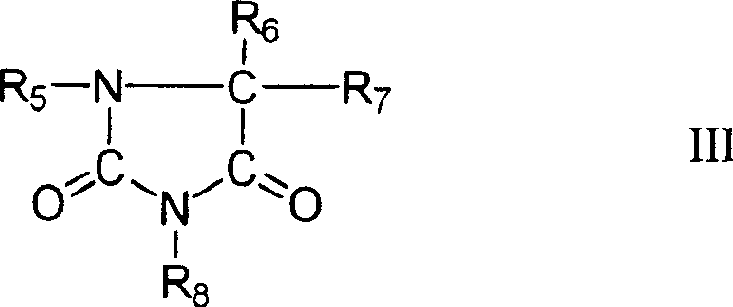
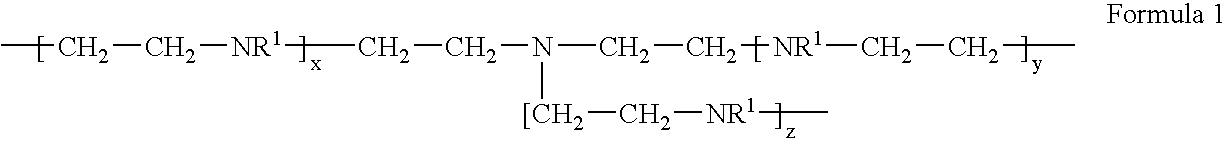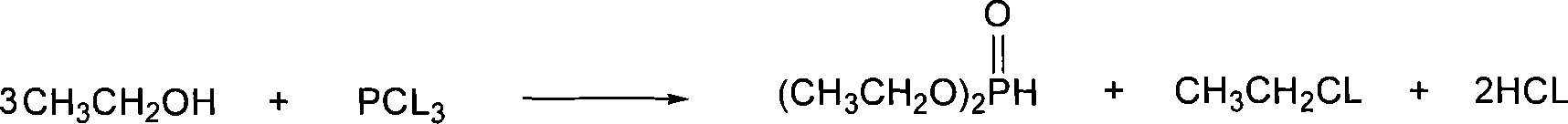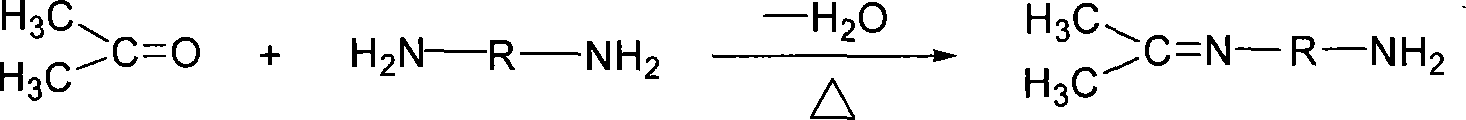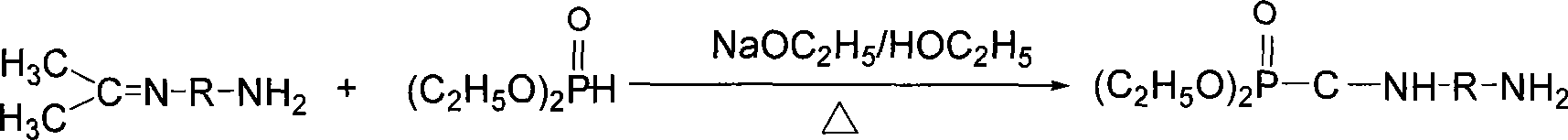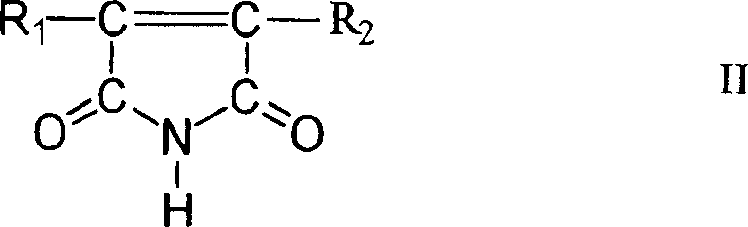Patents
Literature
143 results about "Pentamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
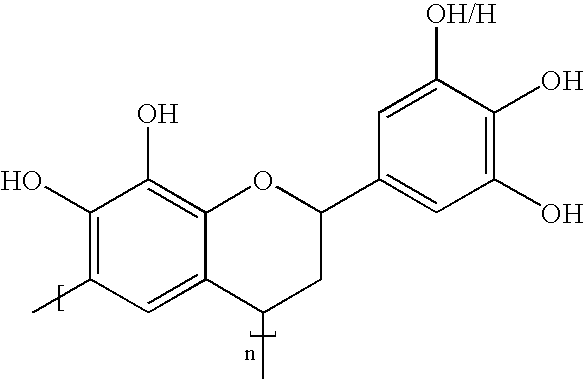
Pentamine is a ganglionic blocker.
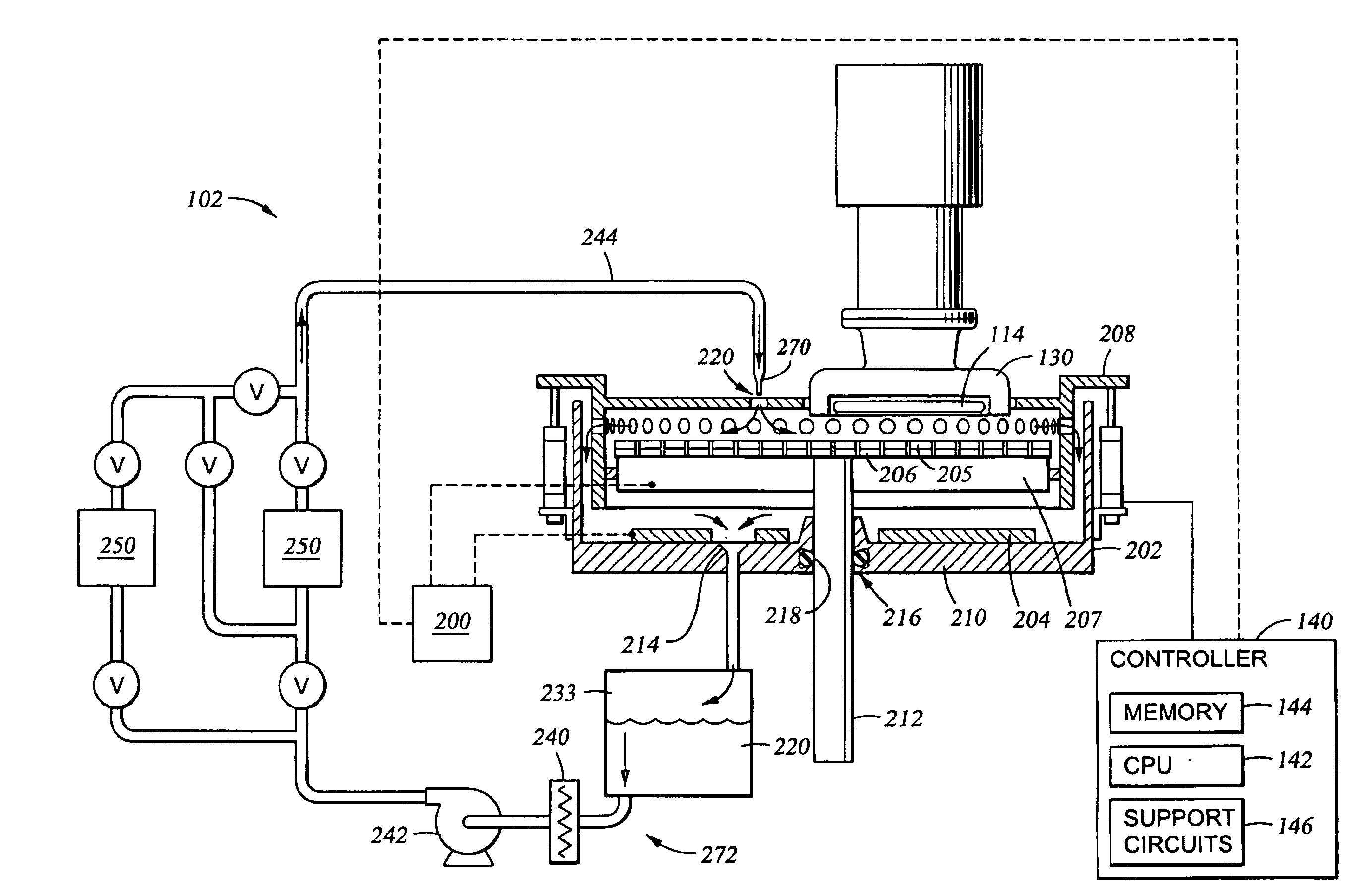
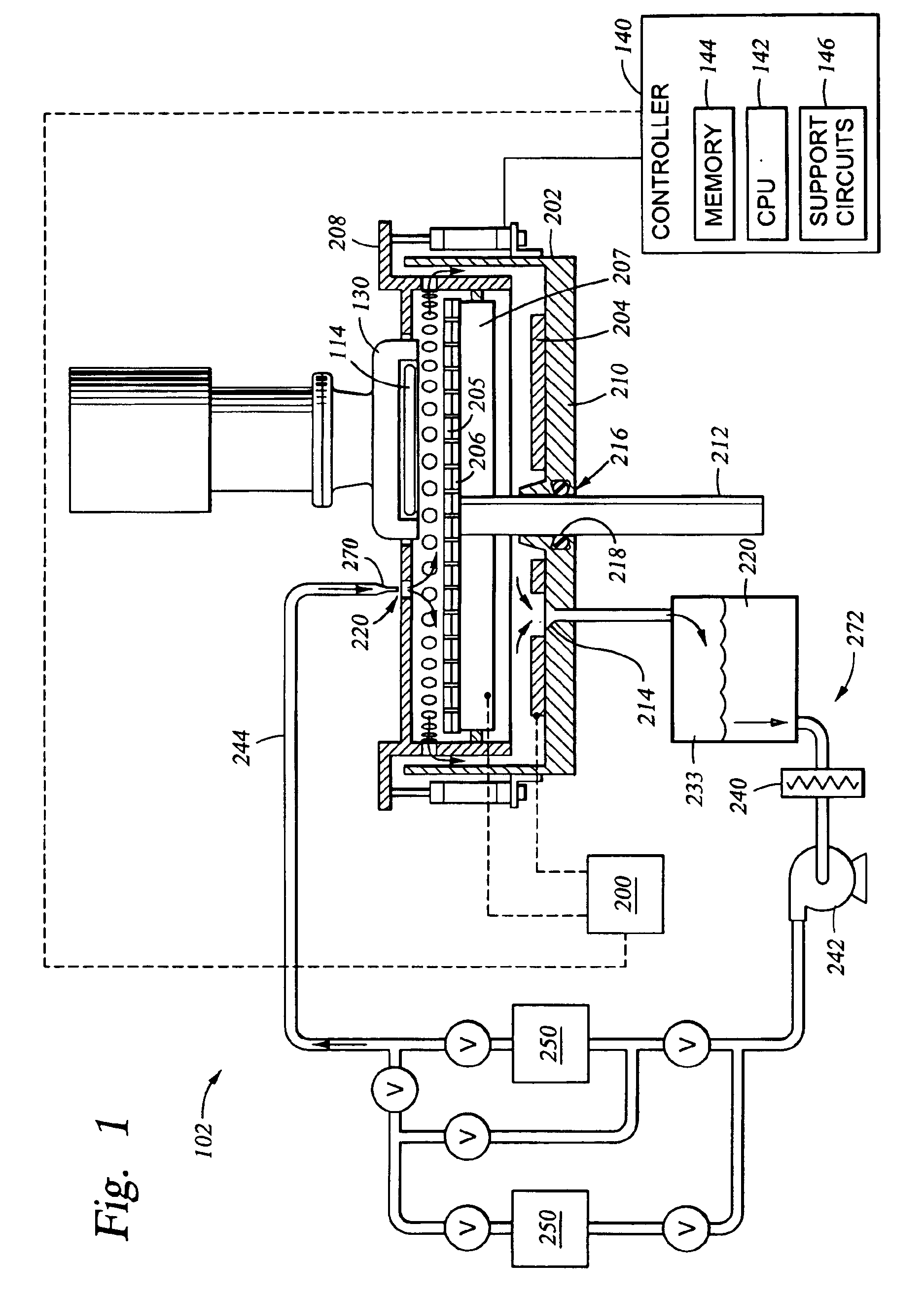
Electrolyte composition and treatment for electrolytic chemical mechanical polishing
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Graphene aerogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses graphene aerogel and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing graphene oxide dispersion liquid with an amine water-soluble compound to obtain graphene oxide mixed liquid, wherein the amine water-soluble compound is selected from one or more of diethylamine, ethidene diamine, propane diamine, butane diamine, diethylene triamine, triethylene tetramine, tetraethylene pentamine, allylamine polymer and N,N'-bis(2-aminoethyl)-1,3-propane diamine; (2) irradiating the graphene oxide mixed liquid by high-energy rays under the anaerobic condition to obtain amino-modified graphene aerogel; (3) performing freeze-drying or supercritical CO2 drying to obtain the graphene aerogel. The graphene aerogel adopts a porous and macroporous structure, is relatively uniform in structure, and can be used for adsorbing an organic solvent; moreover, the preparation method is simple and environment-friendly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gel foam selective water blockoff agent and use thereof
InactiveCN101481604AImprove stabilityLong water blocking periodDrilling compositionFoaming agentHexamethylenetetramine
The invention relates to gel-foam selective plugging agent and the application thereof, belonging to the technical field of oilfield chemistry. The plugging agent comprises the components: 30-50% of acrylamide, 20-40% of hexamethylenetetramine, 5-15% of phenol, 5-15% of tetraethylene pentamine and 5-15% of foaming agent. The aqueous solution with the mass ratio of 0.5-2% can be prepared in site and is injected into a well after being evenly dissolved, so that the plugging agent is used for plugging water in the oil well at the temperature of 90-150 DEG C. The plugging agent uses organic cross linker for cross bonding polymer to form gel foam under the condition of high temperature, so as to be resistant to the high temperature of 90-150 DEG C and have long period of validity in plugging water.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Double-capsule self-repairing epoxy coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105833811ASimple preparation processIncrease productivityMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationChemistrySilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a double-capsule self-repairing epoxy coating and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method mainly uses Pickering emulsion droplet template method and conducts an interface polymerization of interface isophorone diisocyanate and tetraethylenepentamine in water-oil of epoxy interface to prepare epoxy microcapsule and tetraethylenepentamine microcapsule; and the two microcapsules are added to epoxy resin microcapsules for the formation of double-capsule self-repairing epoxy coating. The Pickering emulsion droplet template method ensures the stability of the emulsion, prevents emulsion droplet blending, improves package amount and efficiency of the microcapsule core material; Pickering emulsion improves the repair efficiency of the double-capsule self-repairing epoxy coating; the introduction of nano silica particles and nano clay in the capsule walls of the epoxy microcapsule and tetraethylenepentamine microcapsule improves the mechanical strength and thermal stability of the microcapsule wall, but also improves the brittleness of the microcapsule and the releasing efficiency of the microcapsule core material, so as to ensure the repair performance of the double-capsule self-repair coating.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Polymeric chelant and coagulant to treat metal-containing wastewater
The present invention is directed to the use of a combination of a polymeric chelant and coagulant to treat metal containing wastewater. More particularly, the invention is directed at removing copper from CMP wastewater. The composition includes a combination of (a) a polymeric chelant derived from a polyamine selected from the group consisting of diethylenetriamine (DETA), triethylenetetraamine (TETA), tertraethylenepentaamine (TEPA), poly[vinylamine], and branched or linear poly[ethylenimine] (PEI); and (b) a water soluble or dispersible copolymer of a tannin and a cationic monomer selected from the group consisting of methyl chloride or dimethyl sulfate quaternary salt of dimethyl aminoethyl acrylate, diethylaminoethyl acrylate, dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, diethylaminoethyl methacrylate, dimethylaminopropyl methacrylamide, dimethylaminopropyl acrylamide, and diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Use of aldehyde scavengers in interior building products
InactiveUS20130023612A1Accelerate buildingNon-fibrous pulp additionAbsorbent padsScavengerPolyvinyl alcohol
A coating for application to the surface of an interior building product comprises: a resin formulation such as a melamine formaldehyde resin characterized by its ability to strengthen the interior building product when applied as a coating to the building product; and an aldehyde scavenger selected from the group consisting of; tetraethylene pentamine, propionamide, caprolactam, ammonium hydroxide, sodium bisulfate, sodium metabisulfite, ammonium primary phosphate, ammonium secondary phosphate, a combination of ammonium primary phosphate and ammonium secondary phosphate, a combination of ammonium primary phosphate, ammonium secondary phosphate and a sulfite, a polyvinyl alcohol; adipic dihydrazide and a combination of a polyvinyl alcohol and adipic dihydrazide.
Owner:USG INTERIORS INC
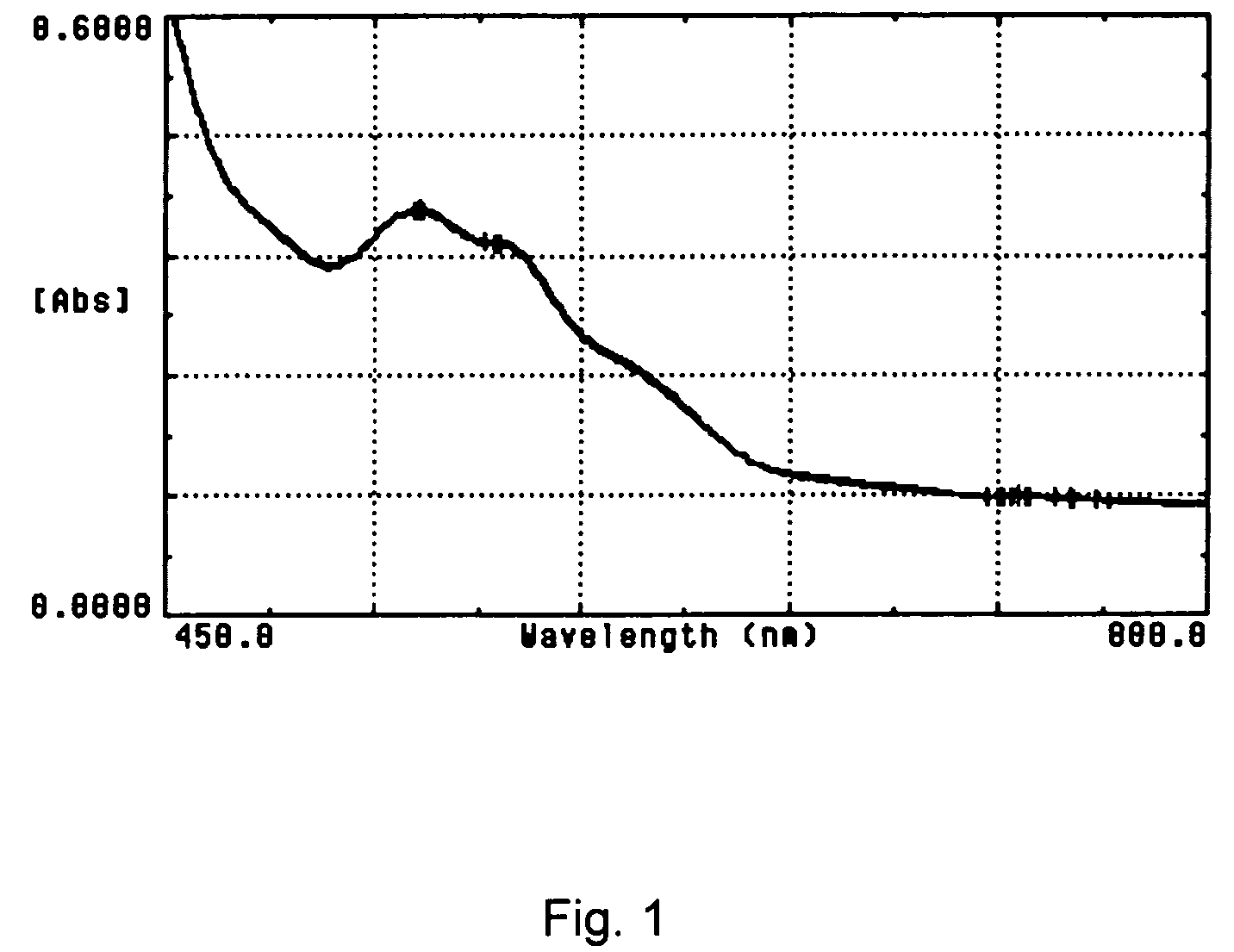
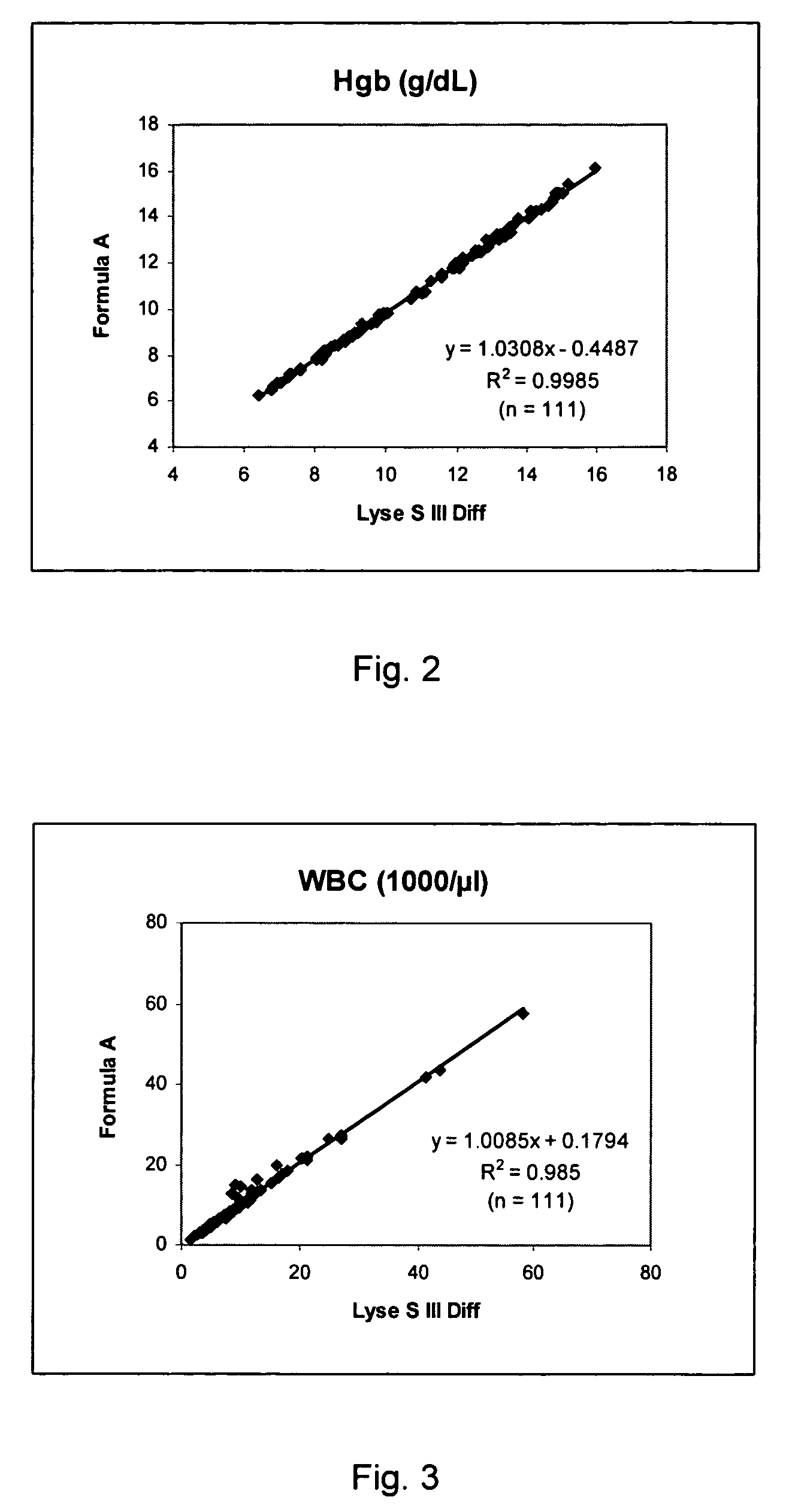
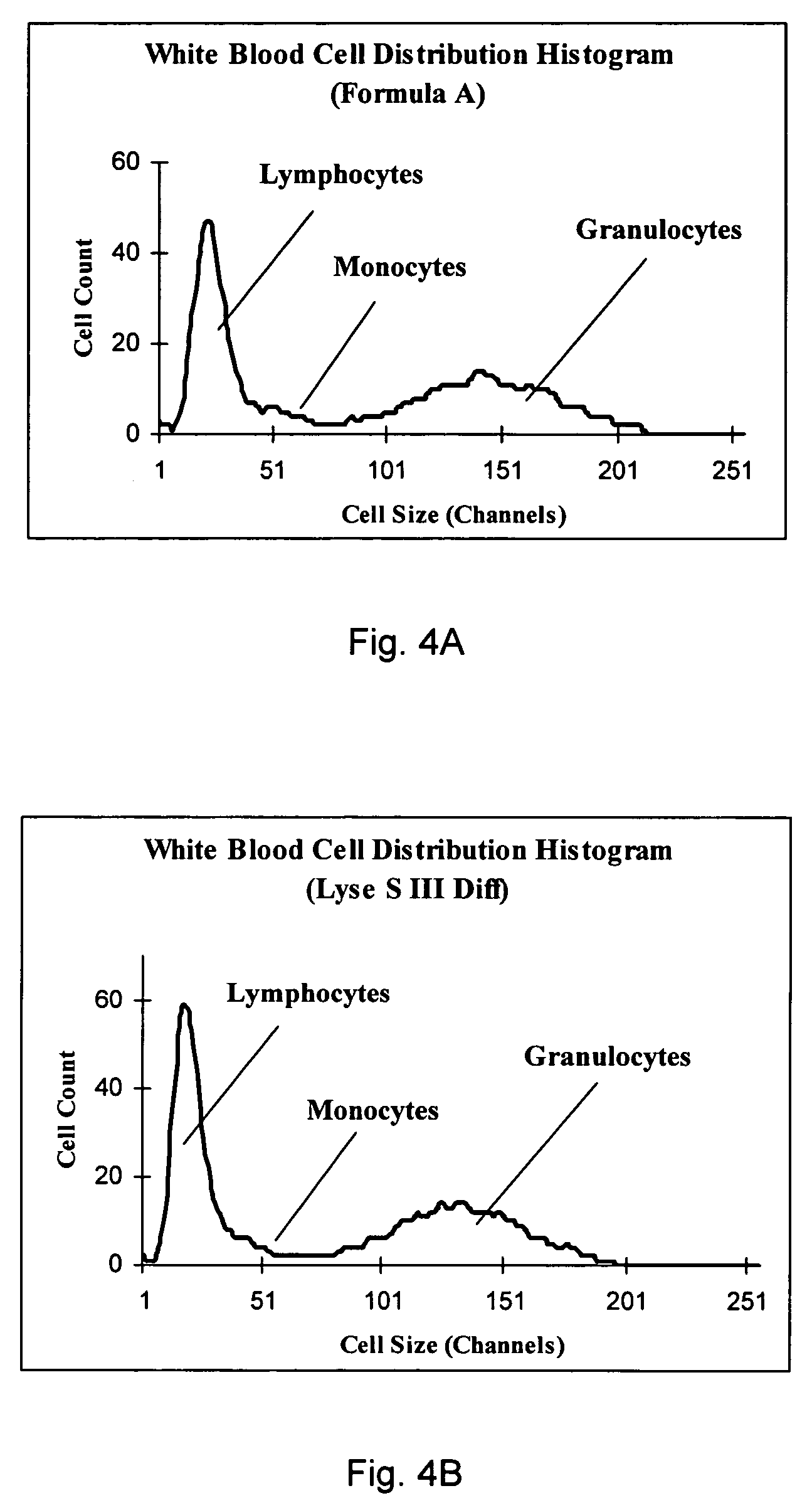
Cyanide-free lytic reagent composition and method of use for hemoglobin and white blood cell measurement
A cyanide-free lytic reagent composition and method of use for measuring the total hemoglobin concentration and white blood cells in a blood sample are disclosed. The lytic reagent composition includes a quaternary ammonium surfactant to lyse red blood cells and release hemoglobin and a ligand to form a stable chromogen with the hemoglobin. The lytic reagent composition has a pH in a range of 3 to 10. The lytic reagent composition can also include a second quaternary ammonium surfactant. The ligand can be malic acid, malonic acid, ethylene diamine, N,N-diethylethylene diamine, N,N′-diethylethylene diamine, diethylene triamine, tetraethylene pentamine, 1,6-hexanediamine, 1,3-pentanediamine, 2-methylpentamethylenediamine, 1,2-diaminocyclohexane, 4-aminoacetophenone, bis-hexamethylenetriamine, pyridazine, or 3,6-dihyroxypyridazine.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Cyanide-free monovalent copper eletroplating solutions
A substantially cyanide-free plating solution for depositing copper from the monovalent ionic state, which includes a source of copper ions, a reducing agent capable of reducing divalent copper ions to monovalent copper ions, an alkali material in an amount sufficient to maintain the pH of the solution in the range of about 7 to about 10, and a complexing agent of an imide, such as succinimide, 3-methyl-3-ethyl succinimide, 3-methyl succinimide, 3-ethyl succinimide, 3,3,4,4-tetramethyl succinimide, or 3,3,4-trimethyl succinimide, or a hydantoin, such as dimethyl hydantoin. The substantially cyanide-free plating solutions may also include at least one of a conductivity salt, an additive to promote brightness, or an alloying metal. The reducing agent may be an alkali sulfite, alkali bisulfite, hydroxylamine, or hydrazine. The copper is typically provided in the form of CuC1, CuC12, CuSO4, or Cu20 in an amount sufficient to provide a copper ion concentration of from about 2 to about 30 grams per liter of solution, and the complexing agent is present in an amount sufficient to provide a molar ratio of copper ions to complexing agent of from about 1:1 to about 1:5, preferably about 1:4. The alkali material is typically NaOH, KOH, NH4OH, or Na2CO3, and the conductivity salt is typically NaC1, KC1, Na2SO4, K4P2O7, Na3PO4, C6H5Na3O7, C6H11NaO7, NH4C1, or KNaC4H4O6. Useful additives include organic amines or oxyalkyl polyamines, such as triethylene tetramine, tetraethylene pentamine, and polyoxypropyl-triamine. Methods for preparing such a solution for plating copper onto a substrate, and of plating copper onto a substrate with such a solution are also disclosed.
Owner:LEARONAL
Metal surface conditioning agent and metal surface treatment technology
ActiveCN104131277ANo pollutionEasy to operateMetallic material coating processesEthylenediaminePhytic acid
The invention relates to a metal surface conditioning agent, which is composed of novel organic acidity, zinc nitrate, sodium molybdate, nicdel nitrate, sodium hydrogenfluoride, phytic acid, a nonionic surfactant and water; the novel organic acidity is the organic acidity obtained by respectively reacting ethene diamine or diethylenetriamine or triethylene tetramine or tetraethylenepentamine with citric acid. A metal surface treatment technology comprises the following steps: preparing the novel organic acidity, and using the novel organic acidity for complex formulation with zinc nitrate, sodium molybdate, nicdel nitrate, sodium hydrogenfluoride, phytic acid, the nonionic surfactant and water to obtain the metal surface conditioning agent. The concrete processing flow comprises the following steps: removing oil, washing, washing, pickling, neutralizing, conditioning surface, treating surface, performing post-treatment on surface or washing, performing air drying. The surface treatment technology can replace the current phosphatization technology, and has the technology advantages of environmental protection and simple operation, and is better than the phosphatization technology from the aspect of technology index.
Owner:DALIAN JIESHI CLEANING PRODS
Epoxy resin modified VAE composite waterproof material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103555091AImprove water resistanceIncrease crosslink densityFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsPropanoic acidPhosphoric acid
An epoxy resin modified VAE composite waterproof material and a preparation method thereof. The composite waterproof material is composed of a component A and a component B. A preparation method of the component A is as below: adding a vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion into a material canister, then adding an epoxy resin emulsion and a defoaming agent, stirring, then adding aluminum hydroxide, phosphoric acid tris(2-chloroethyl) ester, talcum powder, a polytetrafluoroethylene fine powder, tetra [beta-(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxy phenyl) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester, 2-(2H-benzo triazoles-2-yl)-6-dodecyl-4-methylphenol and water, and stirring to obtain the component A. A preparation method of the component B is as below: under the protection of nitrogen, adding tetraethylenepentamine into a reactor, dropwise adding ethylene glycol diglycidylether and butyl glycidol ether for a thermal reaction, then adding water to dilute and stirring to obtain the B component. The component A and the component B are stirred according to a part ratio of 100: 5-8 and applied; and after curing, a flame retardant antifouling self-cleaning composite waterproof material with a semi-interpenetrating network macro-molecular structure is obtained.
Owner:太原英可奥笔墨科技有限公司
Method for synthesizing imidazoline intermediate and cationic derivative thereof
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an imidazoline intermediate and a cationic derivative thereof. The method comprises the following process steps of: putting fatty acid, polyamine and water into a reaction kettle in a mole ratio of 1:1.1-2:1-5, heating to the temperature of between 100 and 180 DEG C to distill over the water added before and the water generated in the reaction, removing redundant polyamine and water under a pressure of between -0.04 and -0.1MPa and performing a reaction at a temperature of between 180 and 240 DEG C for 3 to 8 hours to synthesize the imidazoline intermediate; and reducing the temperature of the imidazoline intermediate to be below 80 DEG C, adding a solvent of which the mass is 30 to 100 percent of the imidazoline intermediate into the imidazoline intermediate, then adding 1 to 2mol of sulfate into the mixture and performing heat preservation reaction at the temperature of between 50 and 80 DEG C for 2 to 4 hours to synthesize cationic imidazoline. The fatty acid is oleic acid, linoleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid, lauric acid, coconut oil acid, capric acid and octanoic acid; the polyamine is ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine, triethylene tetramine and tetraethylene pentamine; the solvent is isopropanol, absolute ethyl alcohol or 95 percent ethanol; and the sulfate is dithyl sulfate and dimethyl sulfate.
Owner:苗俊良
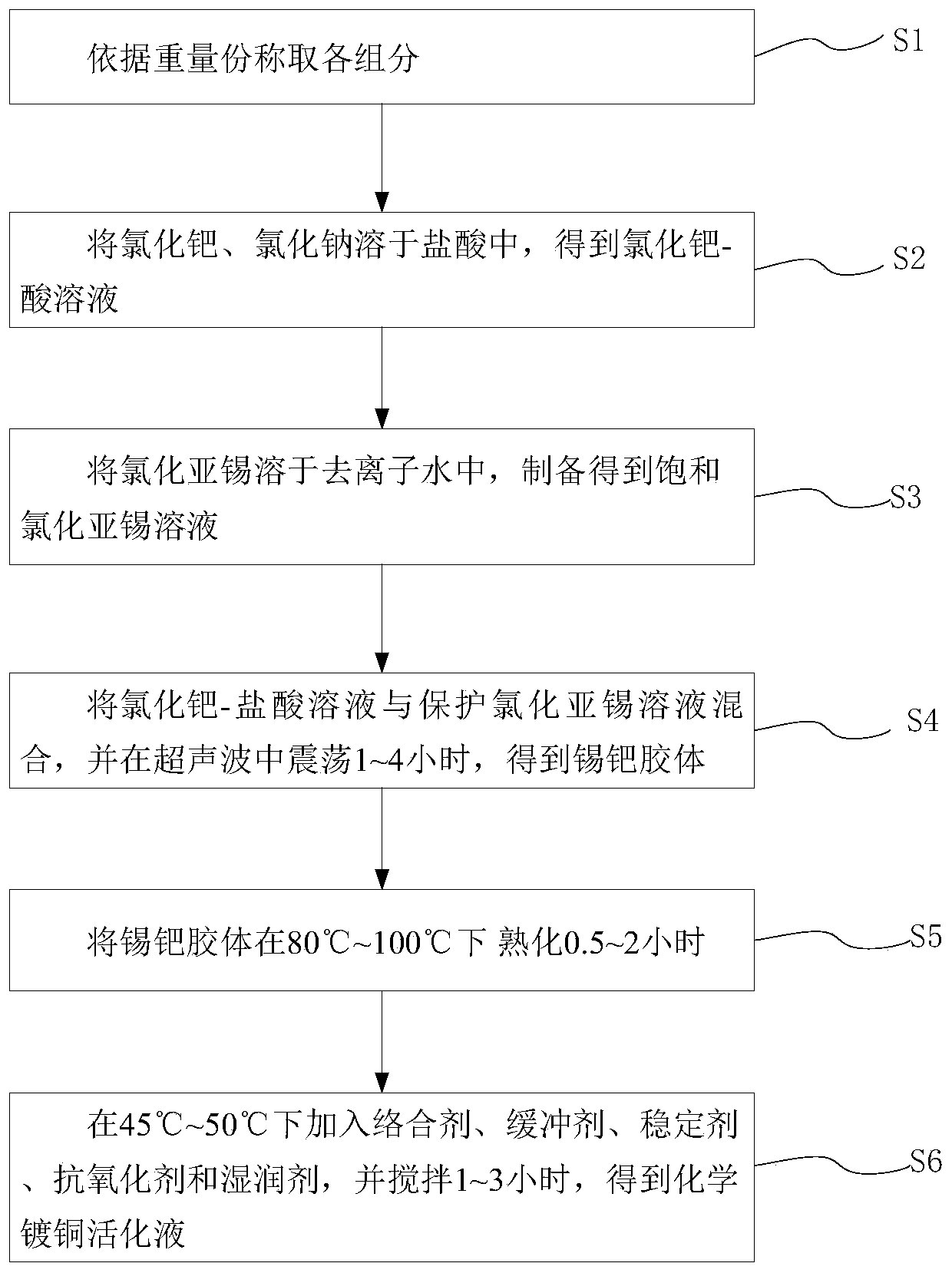
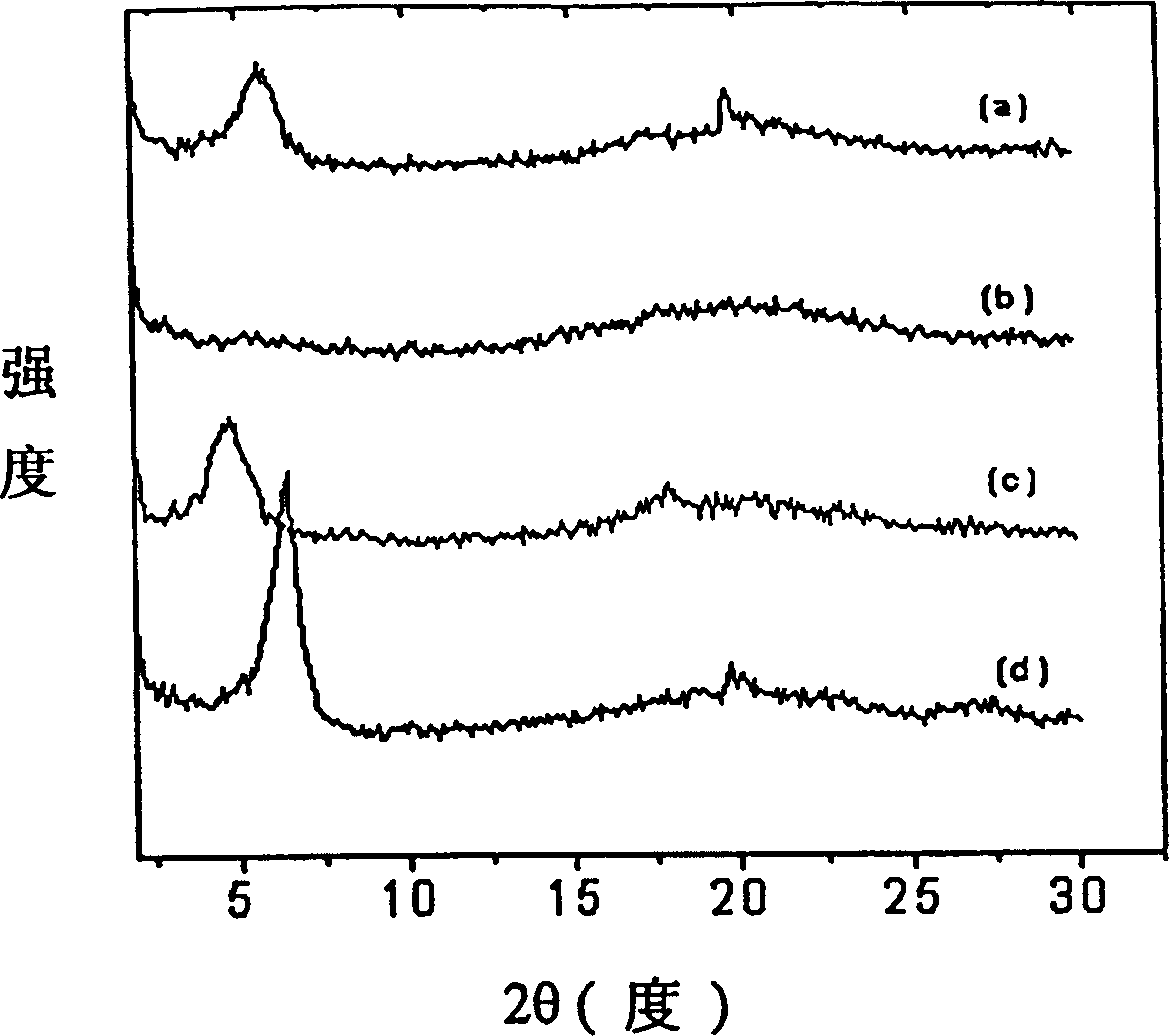
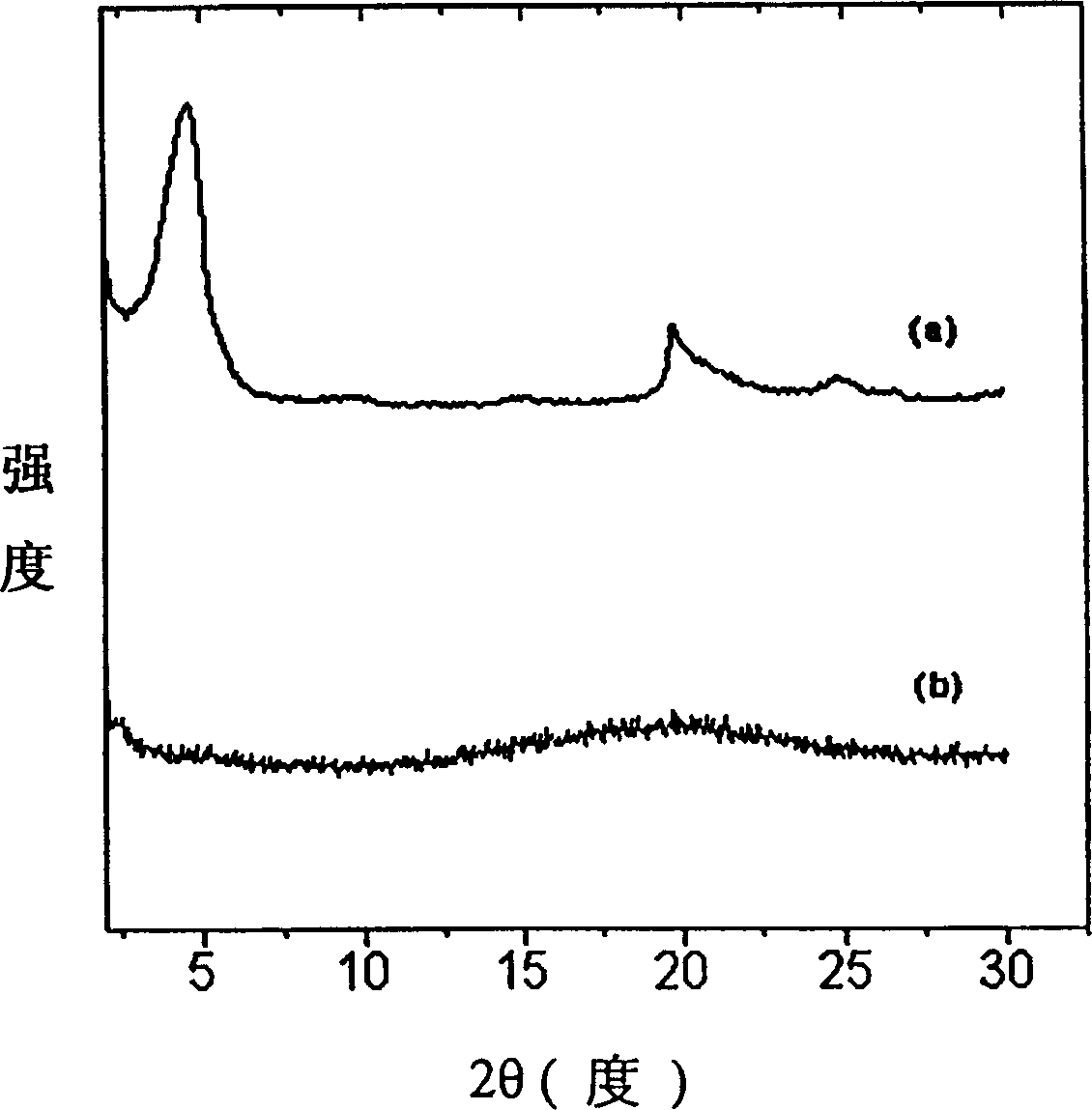
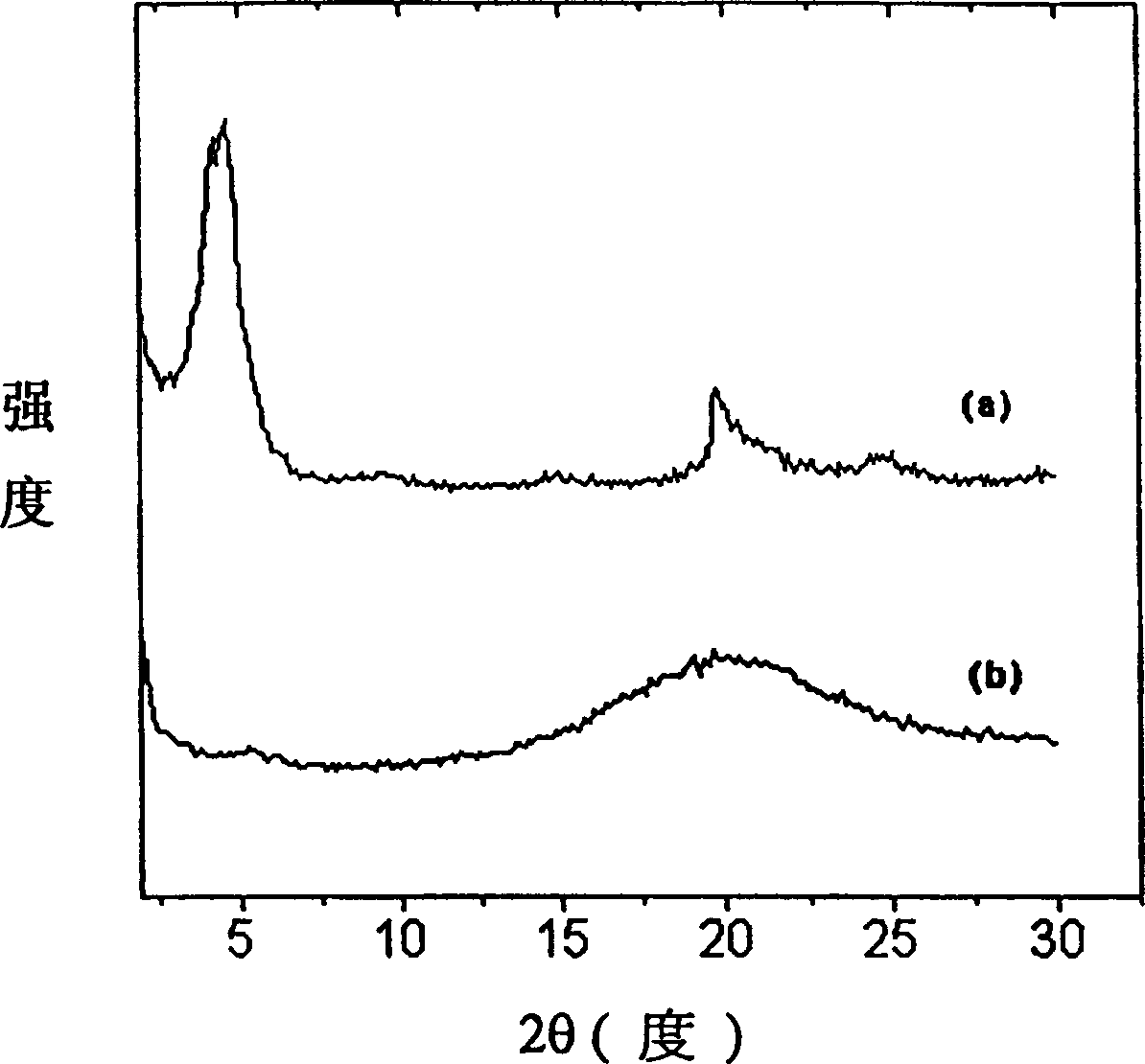
Electroless copper plating activating solution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110670050AImprove stabilityStrong complexationLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPropanoic acidDiethylenetriamine
The invention provides an electroless copper plating activating solution and a preparation method thereof. The electroless copper plating activating solution is prepared from, by weight part, 1-10 parts of palladium chloride, 100-400 parts of stannous chloride, 50-200 parts of sodium chloride, 10-100 parts of sodium chloride, 0.1-50 parts of a complexing agent, 1-200 parts of a buffering agent, 0.1-10 parts of a stabilizing agent, 0.05-10 parts of an antioxidant and 0.1-10 parts of a wetting agent. The complexing agent is one or more of ethidene diamine, trimethyl amine, triethylanmine, diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. The buffering agent is one or more of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, glycine, propionic acid, malic acid and 2-(cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic acid. The electroless copper plating activating solution is high in stability and can adapt to intense circulating stirring in a horizontal electroless copper plating process.
Owner:SHENZHEN CYPRESS IND DEV CO LTD
Nano composite material of epoxy resin/clay for copper foil base plate
InactiveCN1415659AContain Dimensional StabilityImprove heat resistanceMetal layered productsEpoxyCross-link
A nano epoxy resin / clay composition for the copper foil substrate is composed of a high-molecular matrix containing epoxy resin and a laminated clay material. It is prepared through preparing the modified clay by intercalating clay with the mixture of benzalkonium chloride and dicyanoamine or tetraethylidenje pentamine and cross-linking with oligomer of epoxy resin. Its advantages are low hydroscopicity and high size stability and refractory nature.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
Water soluble anticancer medicine taxol composite and its prepn
InactiveCN1440748AImprove low solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsWater solublePentamine
The present invention relates to soluble anticancer medicine taxol composite and its preparation. The present invention is prepared directly with tetravinyl pentamine bridged dicyclodextrin and taxol in the compounding ratio of 0.5. The soluble anticancer medicine taxol composite of the present invention has taxol slubilizing and slow releasing effect and thus prolonged medicine effect. The present invention provides a new way for the clinical application of taxol as anticancer medicine.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Curing agent of phosphate bonding agent self-hardening sand and preparation and using methods of curing agent of phosphate bonding agent self-hardening sand
ActiveCN105855456ARealize self-hardeningImprove pollutionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresPhosphateSilanes
The invention provides a curing agent of phosphate bonding agent self-hardening sand. The curing agent of the phosphate bonding agent self-hardening sand can be applied to modeling and core making. Phosphate is a phosphate bonding agent which takes aluminium dihydrogen phosphate as a main ingredient. The curing agent comprises two components including a component I and a component II, wherein the component I is phenylamine; the component II consists of urea, water, ammonium chloride, silane and tetraethylenepentamine; and the hardening speed of a sand sample is adjusted by adjusting the addition of the two components. A using method of the curing agent comprises the following specific process steps: mixing the curing agent and crude sand at first; then adding the phosphate bonding agent and mixing uniformly to discharge sand; and pouring the mixture into a mold, compacting and preparing the sample, wherein the sand sample can be self-hardened at room temperature. The tensile strength of the prepared sand sample is greater than or equal to 1.0 MPa after 24 hours, and moreover, the sand sample is good in anti-moisture-absorption performance and collapsibility. The curing agent is simple in preparation process and stable in chemical property, and has good application prospect. The self-hardening process involved in the invention facilitates solving the technical problem of poor anti-moisture-absorption performance of the traditional hot and hard phosphate sand core and the technical problems of difficulty in quantifying in the self-hardening process and easiness in generation of dust during sand mixing.
Owner:辽宁谱瑞科技有限公司
Solid amine carbon dioxide adsorption material, preparation method and application
The invention relates to a solid amine carbon dioxide adsorption material, a preparation method and application. According to the preparation method, liquid organic amine is loaded to ion exchange resin through a collocation method. The preparation method includes the steps that 1, the ion exchange resin is soaked in a copper chloride solution to make copper ions combined to the resin in exchange; 2, TEPA is dissolved in methyl alcohol, the resin combined with the copper ions is soaked in the solution, and ultrasonic treatment is conducted for 3 h; 3, vacuumizing is conducted to remove the methyl alcohol solvent, drying is conducted, and the solid amine adsorbent is obtained. The material is placed in a fixed bed, a CO2 adsorption test is conducted, and adsorption conditions are optimized; when the TEPA loading amount is 40%, the adsorption temperature is 65 DEG C, and the air inflow is 40 mL / min, a maximum CO2 adsorption amount of 4 mmol / g is achieved. Besides, the preparation method is simple, the regeneration energy consumption is low, the organic amine is dispersed uniformly, and the stability of repeated use is high.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A displacement chemical gold plating solution
InactiveCN102286736AExcellent adhesionAvoid corrosionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPotassiumDiethylenetriamine
The invention discloses a displacement type electroless gold plating solution, which comprises monopotassium citrate monohydrate bis(malononitrile alloy (I)), a conductive compound, a buffering agent, a shielding complexing agent, a nickel oxidation remover and water. The nickel oxidation remover is one or more of diethylenetriamine, pentamethyldiethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine, hexamethyltriethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. The present invention provides the source of gold ions with potassium citrate monohydrate (malononitrile alloy (I)) as the displacement type chemical gold plating solution, thus does not need to use potassium gold cyanide as the gold source compound, and is an environmentally friendly displacement chemical Gold plating solution. Since the substrate metal is easily corroded in the electroless plating solution of the displacement type to produce more nickel oxides, the nickel oxide remover is used to remove the nickel oxides on the surface of the substrate metal. Experimental results show that the uniformity of the plating film formed by using the displacement type chemical gold plating solution provided by the invention is good, the grain boundary has no corrosion condition, and the solder wettability is good.
Owner:SHENZHEN FARCIEN APPLIED MATERIALS
Multiple quaternary ammonium salts clay interlaminar modifier and preparation method thereof
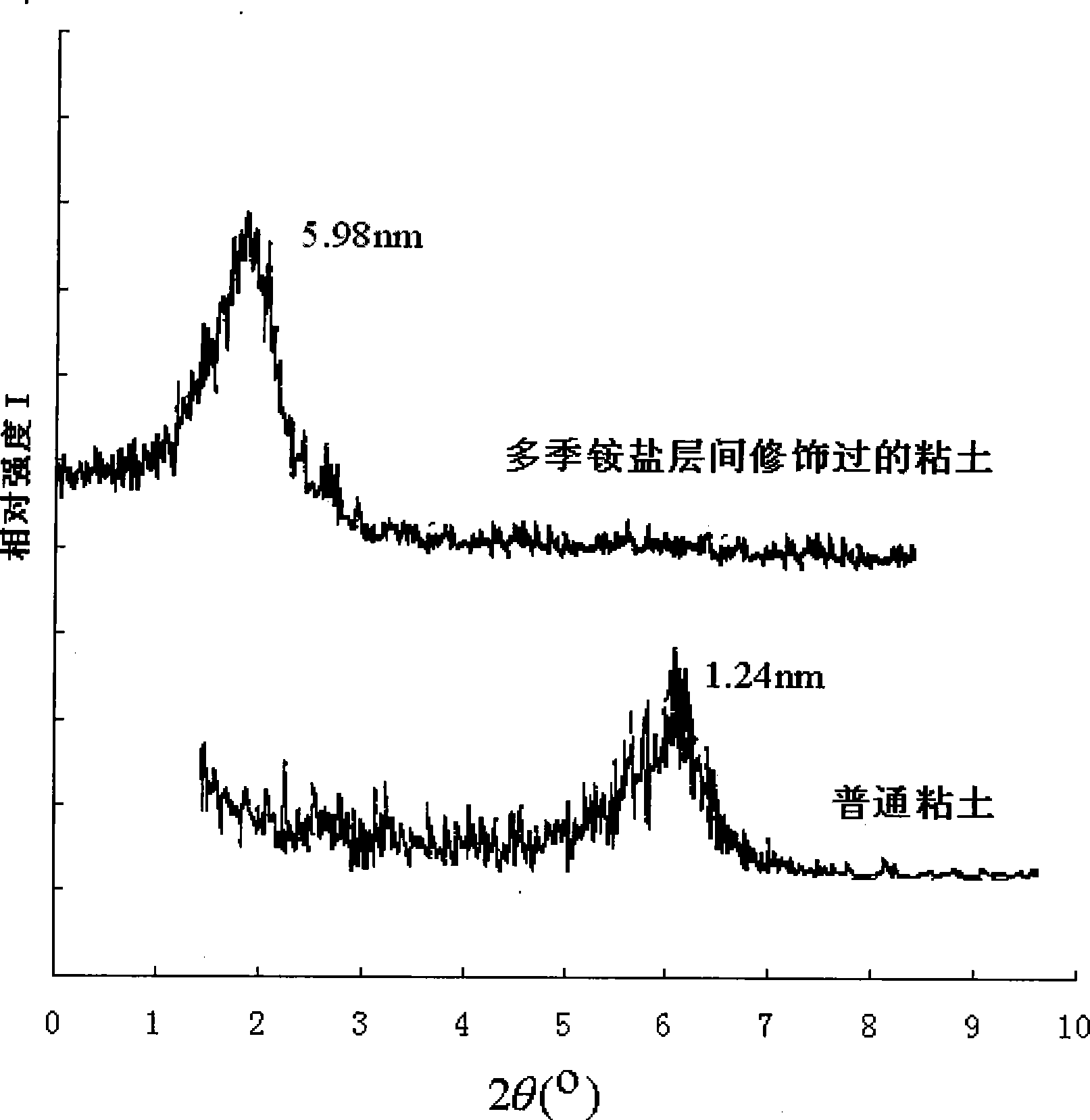
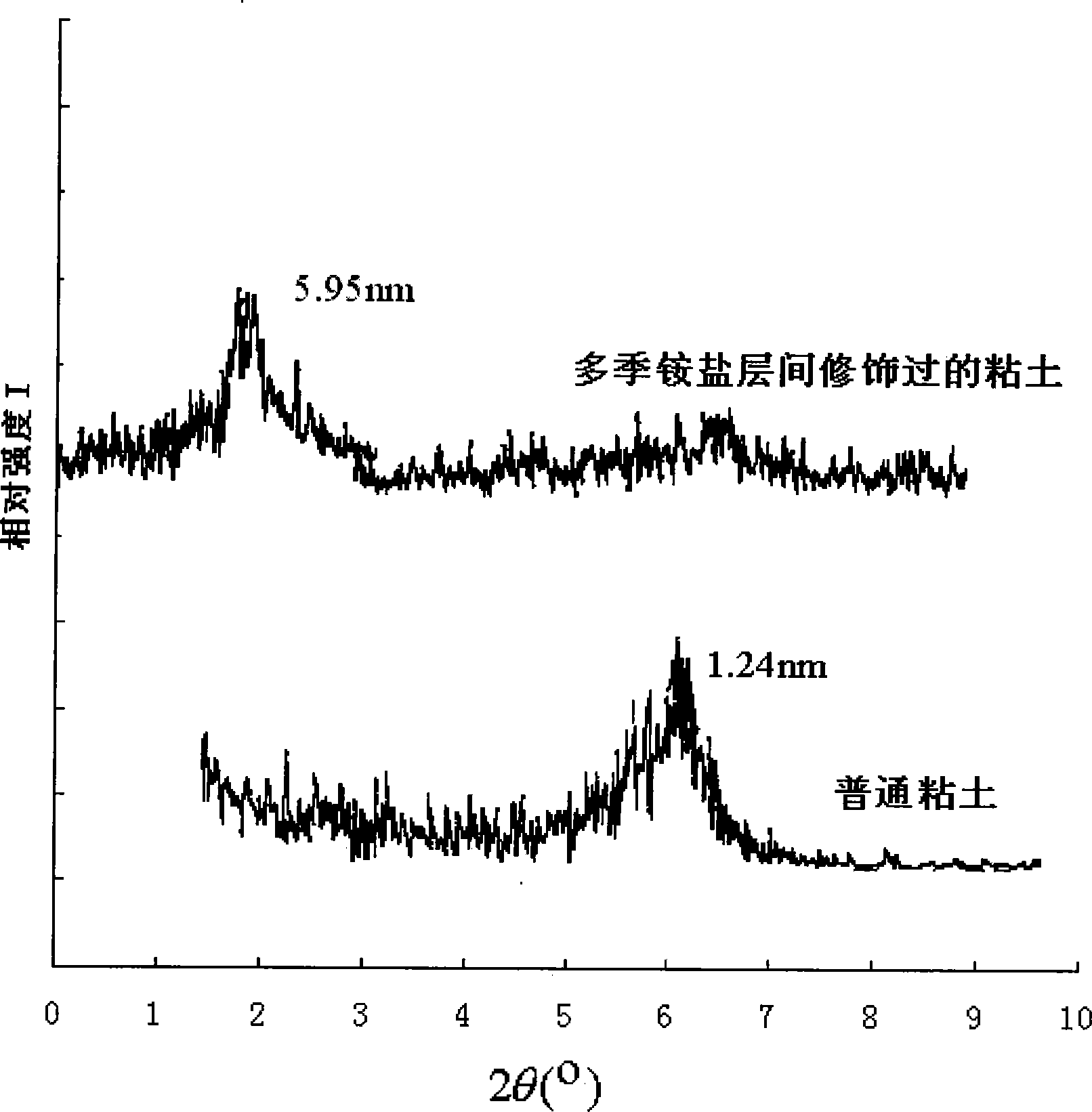
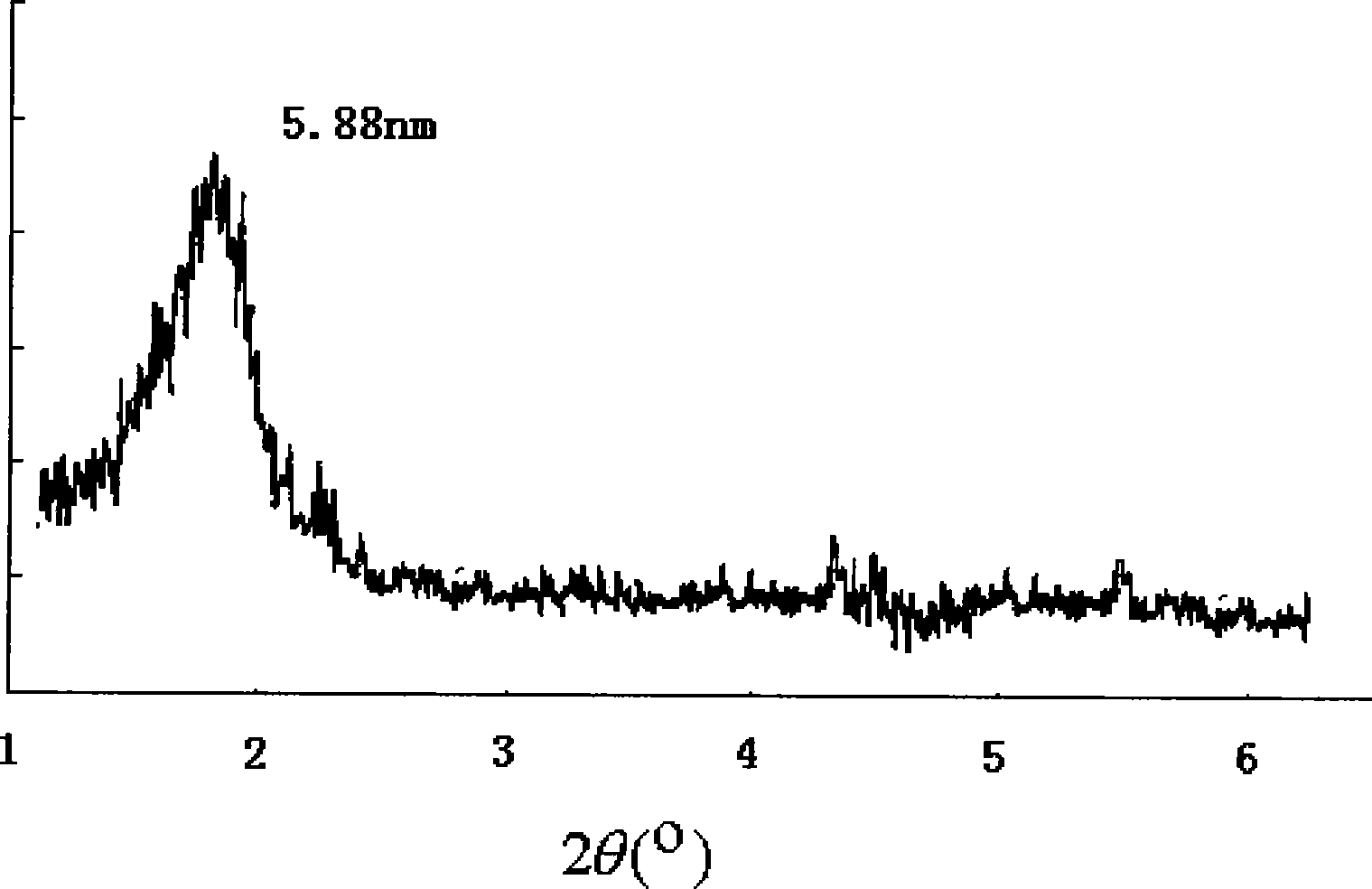
The invention discloses multiple quaternary ammoniums salts type clay-intercalated modification agent and a process for preparation. The steps of the process for preparation comprise 1) dissolving unsaturated fatty acid into dimethylbenzene and mixing with catalyst, heating up to 180-220 DEG C, then adding with diethylenetriamine to react and obtaining bisamide, 2), mixing the bisamide with ethanol, heating up to 30-40 DEG C, adding with polyethylene polyamine and reacting at the temperature of 70-80 DEG C, wherein the unsaturated fatty acid is nutmeg oleic acid, kittul oleic acid, oleic acid, castor-oil plant oleic acid or erucic acid, the polyethylene polyamine is quadrol, triethylene tetramine, tetraethylene pentamine or 3-chlorine-2-hydroxypropyl trimethylammonium, the mol ratio of the unsaturated fatty acid, diethylenetriamine and polyethylene polyamine is 1.5-2:0.8-1:0.8-1. The multiple quaternary ammoniums salts type clay-intercalated modification agent provided by the invention increases solubility and suspension property of clay in water, and can enlarge the distance of the clay-intercalated from 1.24nm to 5.98nm.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Organic phosphorus active flame-proof epoxy resin curing agent amine group phosphonate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an organophosphorus active flame-proof epoxide resin solidifying agent amino phosphonate ester and the preparing method. The amino phosphonate ester comprises the following parts: 3:1:1:1 absolute ethyl alcohol, phsophorus trichloride, organic amine (the structural formula is H2N-R-NH2)and acetone. The organic amine is diethylenetriamine, triethylene tetraamine, tetraethylene pentamine or 4, 4-diaminodiphenylmethane. The method comprises the following steps: 1, synthesizing diethyl phosphate with alcohol and phsophorus trichloride; 2, generating ketoimine with acetone and the organic amine by adding the anhydrating agent; 3, generating amino phosphonate with diethyl phosphate and ketoimine. The oxygen index of the product is more than 20 and less than 34.6. The invention is provided with the simple method and the simple operation.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG INST OF PETROCHEM
Novel multi-stage micro/mesoporous solid-state amine sorbent
InactiveCN108079956AReduce the amount of adsorptionGas treatmentOther chemical processesDesorptionSorbent
A novel multi-stage micro / mesoporous solid-state amine sorbent is disclosed. HZSM-5 with MCM-41 are mixed in different mass ratios to obtain composite molecular sieve supports; the composite molecularsieve supports are loaded onto composite molecular sieves by an impregnation method by use of tetraethylene pentamine (TEPA) as a modifier to prepare a series of novel multi-stage micro / mesoporous structural solid-state amine sorbents. When the mass ratio of HZSM-5 to MCM-41 is 1:1, the TEPA loading is 30%, the adsorption temperature is 55DEG C, and the gas inlet flow rate is 30 mL / min, the equilibrium adsorption amount is as high as 3.57 mmol / g, and after 10 cycles of adsorption and desorption, the adsorption amount is decreased by only 8.1%. The adsorption process of the HZSM-5 / MCM-41-30% TEPA for CO2 includes a rapid breakthrough adsorption phase and a relatively-slow gradual equilibrium phase, and the penetration adsorption amount is close to 80% of the equilibrium adsorption amount.The adsorption process of the HZSM-5 / MCM-41-30% TEPA for the CO2 is in accordance with Avrami kinetic model, indicating that CO2 adsorption is a result of physical adsorption and chemical adsorption.
Owner:韩会义
Preparation method of Cu-Ce-La-SSZ-13 molecular sieve catalyst
ActiveCN108128784AThe synthesis steps are simpleActive ingredients increasedMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationSulfurActive component
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Cu-Ce-La-SSZ-13 molecular sieve catalyst. The method is characterized in that a molecular sieve structure guide agent is formed jointly through addingCe(NO)3.6H2O and La(NO)3.6H2O after preliminary complexation of Cu<2+> and tetraethylene pentamine, and a Cu-Ce-La-SSZ-13 molecular sieve is synthesized through one step. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple; lanthanum as a third active component is introduced, so that the stability of the lanthanum in the molecular sieve and the oxidation capacity of the molecular sieve are improved. The Cu-Ce-La-SSZ-13 molecular sieve prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has excellent low-temperature catalytic activity, the SCR activity reaches above 90 percent at a temperature of 180 DEG C, and meanwhile, the water resistance and the sulfur resistance are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Organic boron crosslinking agent and guar gum fracturing fluid
InactiveCN109280547AReduce dosageFacilitate cross-linkingDrilling compositionCross-linkDiethylenetriamine
The invention discloses an organic boron crosslinking agent prepared by reacting boric acid with an organic polyamine compound in the absence of water, wherein the organic polyamine compound is selected from diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine, 1,4,7,10,13-pentaazatridecane, polyethylene-polyamines or polyethyleneimine. The invention also discloses a guar gum fracturing fluid, which includes,by weight, the following components:0.2%-0.6% of hydroxypropyl guar gum, 0.2%-0.6% of the organic boron crosslinking agent described in claim 1, 0.01%-0.2% of a pH regulating agent, 0-0.5% of a temperature stabilizer, 0.2%-2% of other additives, with the balance being water. The organic boron crosslinking agent of the invention has a large molecular volume and a plurality of cross-linking pointsformed with a low-concentration guar gum aqueous solution, and so, cross-linking properties and temperature resistance performance of a gelled fracturing fluid are improved, the using amount of the cross-linking agent is reduced, and the cost of a fracturing fluid system is reduced. The guar gum fracturing fluid of the invention has good cross-linking properties and good temperature resistance performance, the concentration of the hydroxypropyl guar gum can be adjusted according to the reservoir temperature, and the maximum usage temperature is 150 DEG C.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method and application of amino-functionalized mesoporous alumina-based bifunctional adsorbent
InactiveCN103071449AAchieve removalRealize functionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAluminium isopropoxideCopolymer
The invention relates to a preparation method of amino-functionalized mesoporous alumina-based bifunctional adsorbent, and the application of the bifunctional adsorbent. The method comprises the steps of: adding concentrated nitric acid or concentrated hydrochloric acid into the ethanol solution of a Pluronic triblock copolymer P123 or F127 at the room temperature, evenly stirring and adding aluminium isopropoxide into the mixed solution; carrying out constant temperature evaporation on the solution formed by stirring to obtain mesoporous alumina-P123 / F127 composite raw powder; adding the raw powder into the ethanol solution of tetraethylenepentamine, polyethyleneimine or triethanolamine; and sequentially carrying out mixing impregnation, centrifugal separation, ethanol washing and drying at the room temperature to obtain the adsorbent. The preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, template agent removal, amino-functionalization one-step completion and the like; and the amino-functionalized mesoporous alumina-based bifunctional adsorbent has good adsorptive property for Cr (VI) and CO2, especially has the removal rate of more than 90% for the Cr (VI) within 1min, and has the removal rate of 100% for the Cr (VI) solution with the concentration of less than 50mg / L.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A kind of oil-in-water emulsifier and its preparation method and use method
InactiveCN102286273ARealize rational utilizationPrevent inflowTransportation and packagingMixingRoom temperatureWarming process
The invention discloses a high temperature resistant oil-in-water emulsifier with high performance. The oil-in-water emulsifier is prepared through the following steps: adding 850-860kg of illegal cooking oil into a 2000L enamel reactor, then adding 510-520kg of tetraethylenepentamine and 25-30kg of 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, introducing steam by a jacket for heating and starting up stirring; in the process of raising the temperature, recovering water generated by reaction by a condensing reflux water division device, and beginning to boil a reaction material when the temperature is raised to 180-190 DEG C, continuously raising the temperature, keeping the temperature at 230-250 DEG C to heat for 40min, then stopping heating, and reducing the temperature by introducing coolingwater through the jacket; and cooling the reaction material to the room temperature, and then discharging and barreling. The reasonable utilization of wastes is realized, the illegal cooking oil harmful to human bodies is prevented from entering fast-food restaurants and wineshops, and an environment-friendly, healthy and safe solution is provided for solving the illegal cooking oil problem.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
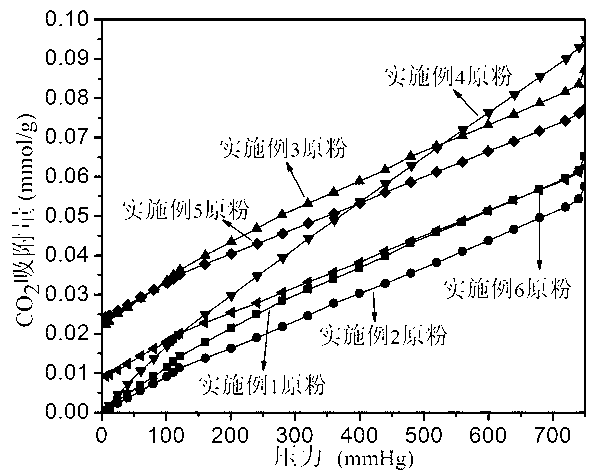
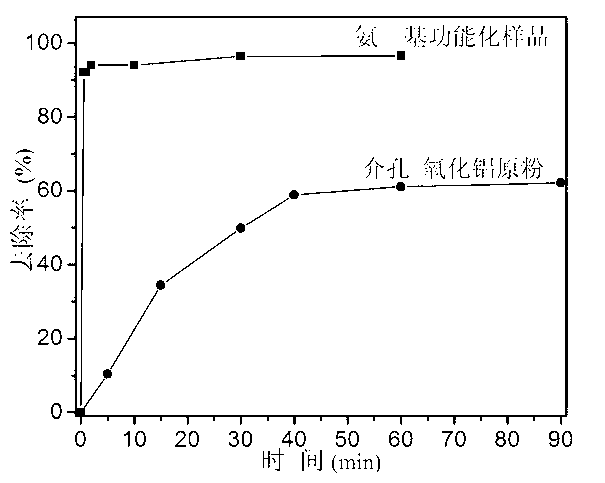
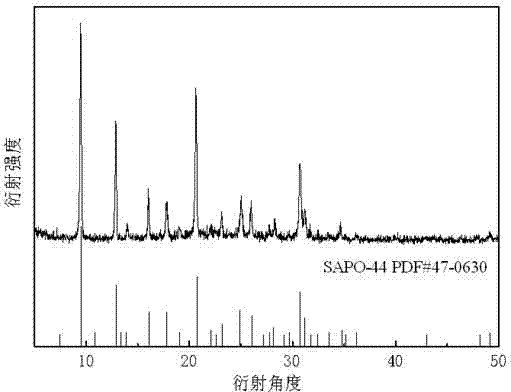
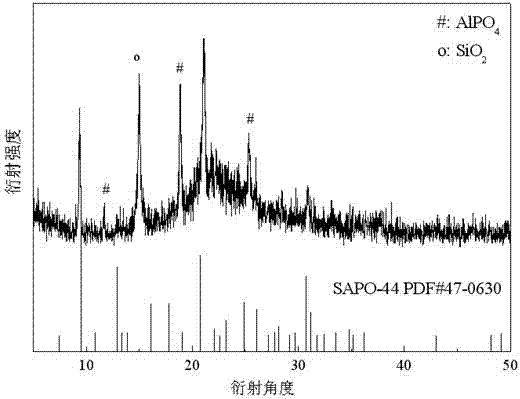
Preparation method of high-purity SAPO-44 microporous molecular sieve
ActiveCN104743574APromote formationHigh crystallinityMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular-sieve silicoaluminophosphatesMolecular sieveHexamethylenediamine
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for preparing fixed carrier compound membrane for CO2 separation by utilizing interfacial polymerization
InactiveCN1736569AHas an ultra-thin structureGood film formingProductsSemi-permeable membranesFiberSeparation factor
The invention discloses a method for preparation of CO2 carrier- fixed complex film with interfacial polymerization, belonging to the technique for preparation of film. The method contains the following steps: using a sheet film of polysulfone or polyethersulfone or a hollow fibre film as the basilemma, treating the surface of basilemma with a sodium dodecyl sulfonate water solution; soaking the treated basilemma in a diethylenetriamine, triethylene tetraamine, tetraethylene pentamine or polyethylene polyamine water solution in room temperature, and then adding to a trimesoyl- chloride skellysolve B solution or isophthaloyl- chloride skellysolve B solution or trimesoyl- chloride and isophthaloyl- chloride skellysolve B solution to generate interfacial polymerization; purifying the complex film with ionic hydration and drying naturally or drying naturally after a definite thermal treatment. The prepared complex film has a separation factor of 40- 200 to the mixture of CO2 / CH4, and a penetration ratio of 1- 6* 10- 5cm3(STP) / cm2.s.cmHg of CO2. The process is simple and it is easy to operate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Heat dissipation coating and preparation method
The invention provides a heat dissipation coating used for LED lights and a preparation method. The coating is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by weight parts: 40-45 parts of organic silicone resin, 18-22 parts of butyl acetate, 24-26 parts of ethyl acetate, 12-14 parts of nano-silica, 8-10 parts of nanometer titanium dioxide, 20-22 parts of aluminium nitride powder, 5-7 parts of emery powder, 1-2 parts of dibutyltin dilaurate, 2-3 parts of tributyl tin trichloride, 8-10 parts of vinyl acetate, 12-14 parts of nano bauxite, 3-5 parts of isopropyl tri(dioctyl pyrophosphate acyloxy) titanate, 1-2 parts of tetraethylenepentamine, 1-2 parts of salicylic acid, and 4-5 parts of a film forming agent. The emery powder provided in the invention is relatively high in melting point, thereby improving a high temperature resistance performance of the heat dissipation coating; the nanometer titanium dioxide has self-cleaning property, thereby helping to maintain a clean coating.
Owner:TIANCHANG JINLING ELECTRONICS
Cu-SSY-39 molecular sieve, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110467200ALow costAvoid pollutionDispersed particle separationCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveNitrogen
The invention relates to a Cu-SSZ-39 molecular sieve, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method for the Cu-SSZ-39 molecular sieve comprises the following steps: with a ZSM-5 molecular sieve as a silicon source and an aluminum source, mixing the ZSM-5 molecular sieve with a nitrogen-containing organic template agent, water, a copper source, tetraethylenepentamine andan alkali source, and then carrying out a reaction, crystallization and roasting successively to obtain the Cu-SSZ-39 molecular sieve. According to the method of the invention, the above raw materialsare subjected to the one-step hydrothermal reaction so as to prepare the Cu-SSZ-39 molecular sieve which has good NH3-SCR catalytic activity, nitrogen selectivity, hydrothermal stability and resistance to high space velocities; and the raw material ZSM-5 molecular sieve used in the preparation process is widely available and low in cost, so the prepared Cu-SSZ-39 molecular sieve has certain economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:合肥中科弘逸环保科技有限责任公司
Papermaking wastewater treatment agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105399194AEfficient removalEasy to transportWater treatment compoundsSpecific water treatment objectivesTert butylPolyacrylamide
The invention relates to a papermaking wastewater treatment agent and a preparation method thereof. The treatment agent comprises the following components in parts by mass: 90-115 parts of tetraethylene pentamine, 30-50 parts of sodium carbonate, 15-30 parts of diatomite, 4-12 part of powdered carbon, 0.001-0.005 part of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt, 0.0001-0.0005 part of polyacrylamide, 0.0003-0.0007 part of dimethyl ethanolamine, 0.08-0.35 part of tertiary butyl hydrogen, 0.3-0.9 part of mercaptobenzothiazole, 0.00005-0.00015 part of potassium peroxide, 0.002-0.004 part of calcium hydroxide, 0.00005-0.00015 part of dithiothreitol, 0.2-0.55 part of zinc sulfate, and 0.03-0.06 part of tetradecyltributylphosphonium chloride. The treatment agent provided by the invention can effectively remove harmful substances in papermaking wastewater.
Owner:JIANGSU GAIYA ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Cyanide-free monovalent copper eletroplating solutions
A substantially cyanide-free plating solution for depositing copper from the monovalent ionic state, which includes a source of copper ions, a reducing agent capable of reducing divalent copper ions to monovalent copper ions, an alkali material in an amount sufficient to maintain the pH of the solution in the range of about 7 to about 10, and a complexing agent of an imide, such as succinimide, 3-methyl-3-ethyl succinimide, 3-methyl succinimide, 3-ethyl succinimide, 3,3,4,4-tetramethyl succinimide, or 3,3,4-trimethyl succinimide, or a hydantoin, such as dimethyl hydantoin. The substantially cyanide-free plating solutions may also include at least one of a conductivity salt, an additive to promote brightness, or an alloying metal. The reducing agent may be an alkali sulfite, alkali bisulfite, hydroxylamine, or hydrazine. The copper is typically provided in the form of CuC1, CuC12, CuSO4, or Cu20 in an amount sufficient to provide a copper ion concentration of from about 2 to about 30 grams per liter of solution, and the complexing agent is present in an amount sufficient to provide a molar ratio of copper ions to complexing agent of from about 1:1 to about 1:5, preferably about 1:4. The alkali material is typically NaOH, KOH, NH4OH, or Na2CO3, and the conductivity salt is typically NaC1, KC1, Na2SO4, K4P2O7, Na3PO4, C6H5Na3O7, C6H11NaO7, NH4C1, or KNaC4H4O6. Useful additives include organic amines or oxyalkyl polyamines, such as triethylene tetramine, tetraethylene pentamine, and polyoxypropyl-triamine. Methods for preparing such a solution for plating copper onto a substrate, and of plating copper onto a substrate with such a solution are also disclosed.
Owner:LEARONAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com