Method for selectively separating iron from hydrochloric acid solution containing ferrous chloride
A technology of ferrous chloride and hydrochloric acid solution, applied in directions such as process efficiency improvement, can solve problems such as high cost of raw materials, complicated iron removal process, etc., achieves reduction of production cost, is beneficial to environmental protection and operator's health, and oxidation speed quick effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
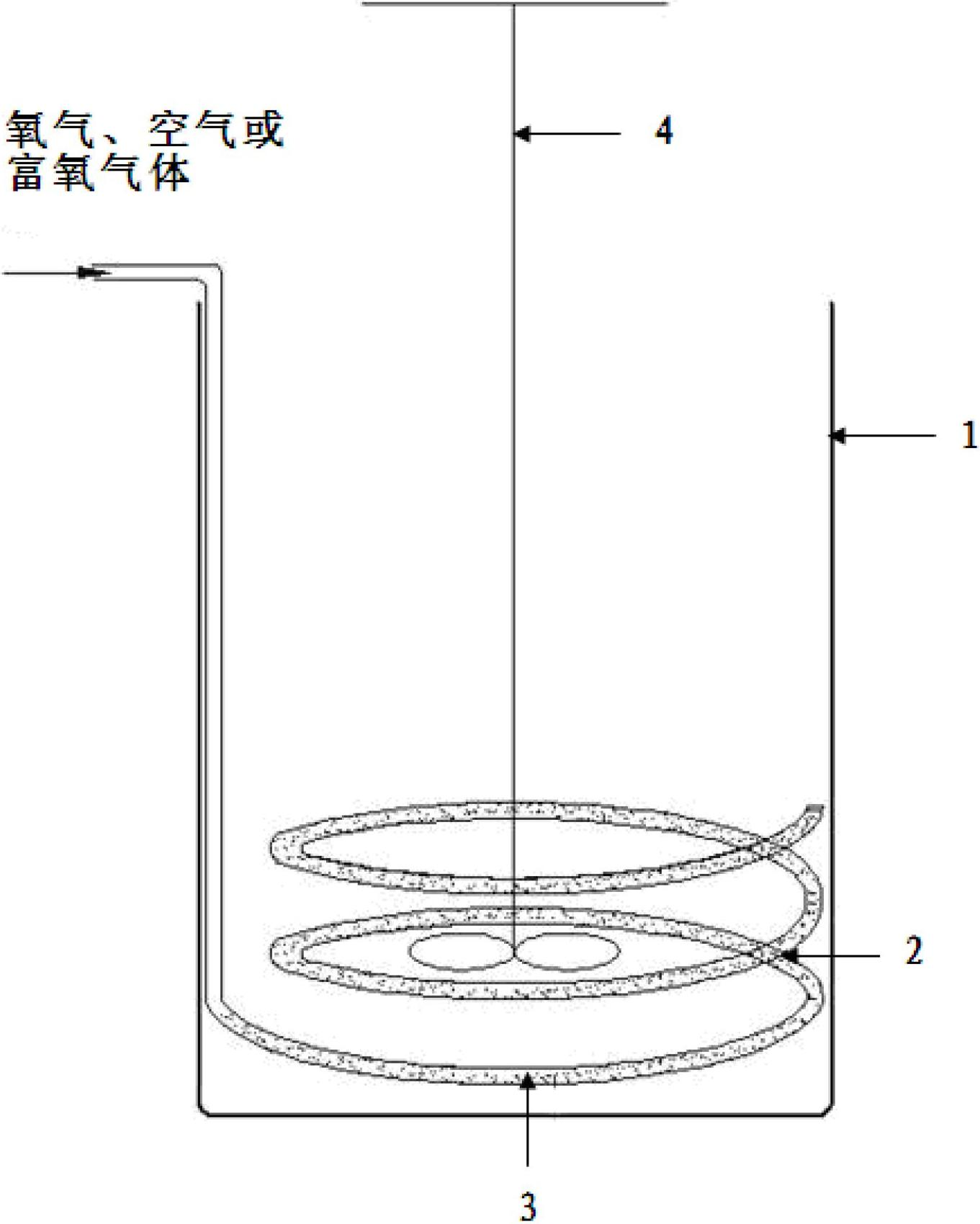
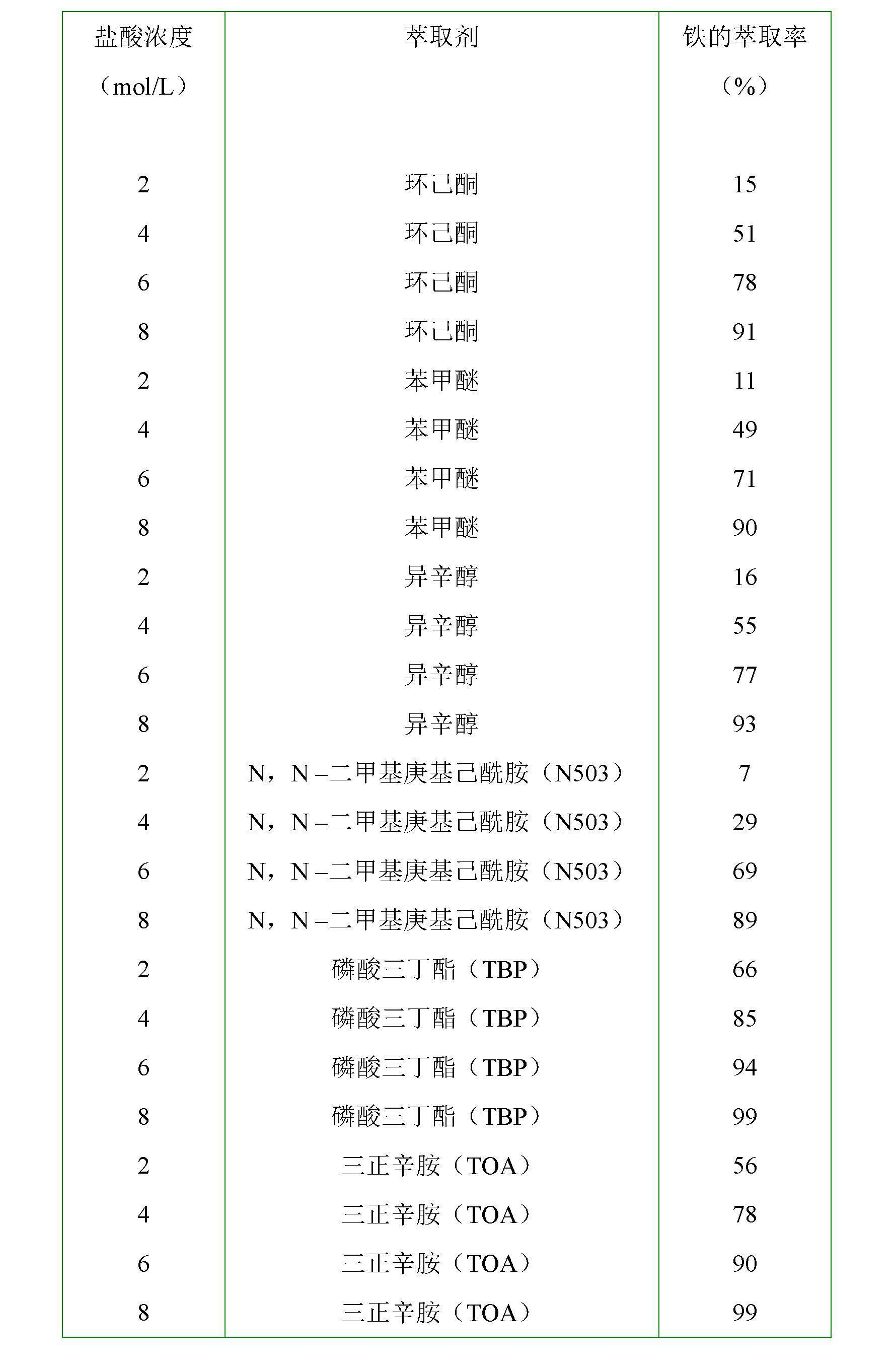
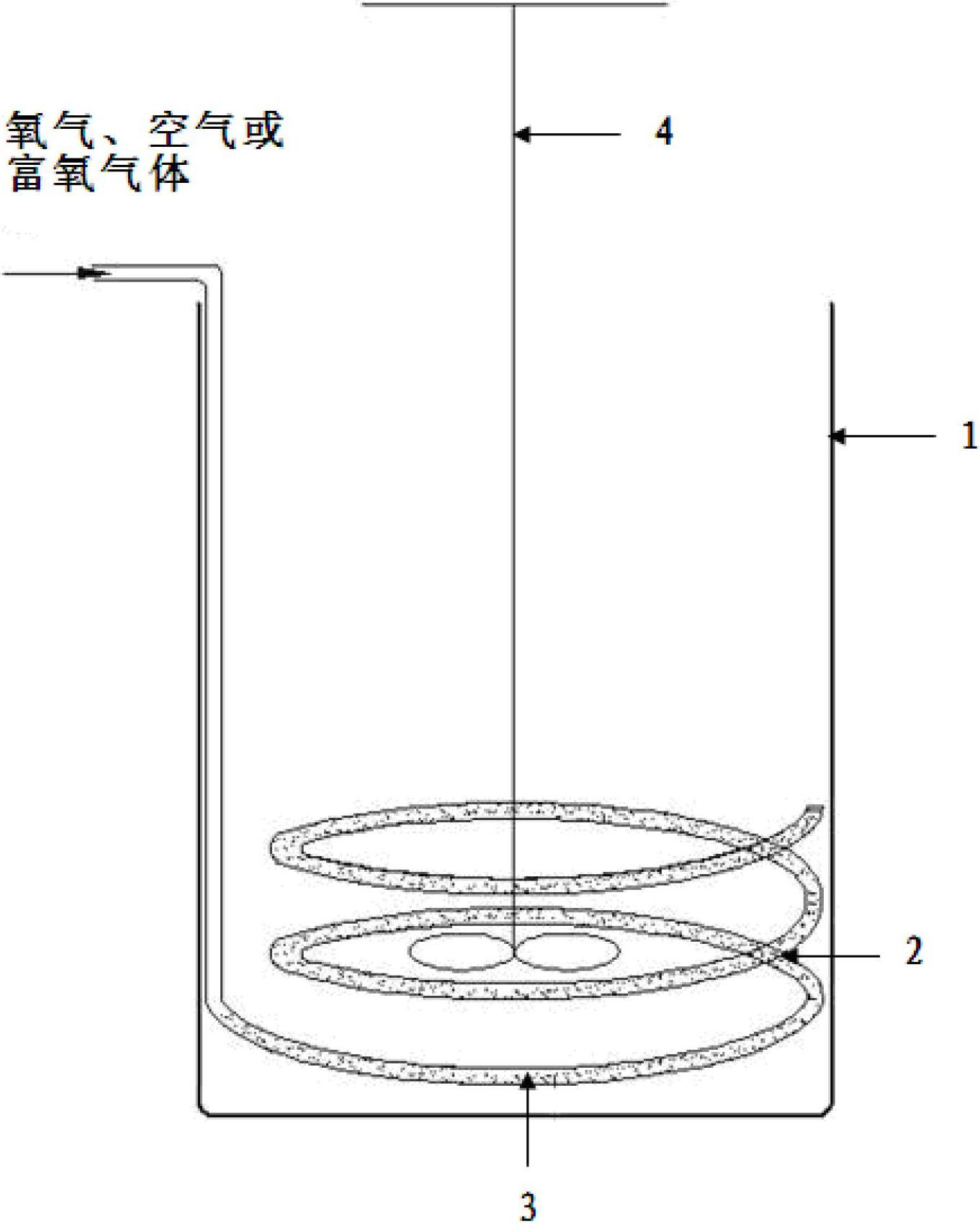
[0029] In this embodiment, the hydrochloric acid solution containing ferrous chloride is steel material hydrochloric acid pickling waste liquid, after adding HCl, in the hydrochloric acid solution, FeCl 2 240 g / L, HCl 160 g / L (4.38M), using this hydrochloric acid solution as the water phase. The organic phase is composed of methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) and kerosene, and the volume concentration of methyl isobutyl ketone in the organic phase is 60%. Add 0.5L of aqueous phase and 0.5L of organic phase to figure 1 A mixed solution is formed in the extraction tank shown (the molar ratio of the extractant in the organic phase to the iron ion in the aqueous phase = 2.5:1), and the air passes through the air outlet hole with a diameter of 1 mm on the annular air duct 2 placed in the tank body 1 3 Enter the mixed solution, the air flow rate is 2000ml / min, the reaction is carried out at 25°C, and the reaction time is 50min (the amount of air introduced is: the ferrous chloride in th...
Embodiment 2
[0033] In this example, the water phase is the same as in Example 1, the organic phase is composed of tributyl phosphate (TBP) and cyclohexane, and the volume concentration of tributyl phosphate in the organic phase is 35%. Add 0.33L of aqueous phase and 1.67L of organic phase to figure 1 A mixed solution is formed in the extraction tank shown (the molar ratio of the extractant in the organic phase to the iron ion in the aqueous phase = 3.4:1), oxygen (purity 99%) passes through the aperture on the annular air guide tube 2 placed in the tank body 1 The air outlet 3 with a diameter of 1 mm enters the mixed liquid, the oxygen flow rate is 400ml / min, the reaction is carried out at 25°C, and the reaction time is 50min (the amount of oxygen introduced is: the chlorine in the mixed solution formed by the aqueous phase and the organic phase Ferrous chloride is completely oxidized to 3.4 times the theoretical amount of oxygen required for ferric chloride), after the reaction time expi...
Embodiment 3
[0037] In this example, the aqueous phase is the same as in Example 1, the organic phase is composed of N,N-dimethylheptylhexanamide (N503) and toluene, and the volume of N,N-dimethylheptylhexanamide in the organic phase The concentration is 30%. Add 0.28L of aqueous phase and 1.72L of organic phase to figure 1 A mixed liquid is formed in the extraction tank shown (the molar ratio of the extractant in the organic phase to the iron ion in the aqueous phase = 2.9:1), and the oxygen-enriched gas with an oxygen volume concentration of 30% passes through the annular air duct 2 placed in the tank body 1 The air outlet 3 with a diameter of 2mm on the top enters the mixed liquid, the flow rate of the oxygen-enriched gas is 1700ml / min, the reaction is carried out at 35°C, and the reaction time is 50min (the amount of the oxygen-enriched gas introduced is: the water phase and the organic phase The ferrous chloride in the mixed solution formed is completely oxidized to 6 times of the th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com