Pneumatic internal combustion hybrid engine
A technology of hybrid power and engine, applied in the field of pneumatic internal combustion hybrid power engine, to avoid the effect of low pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] First of all, it should be noted that the internal combustion engine in the present invention is not limited to a gasoline engine and a diesel engine, but may also be a natural gas engine and the like. Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
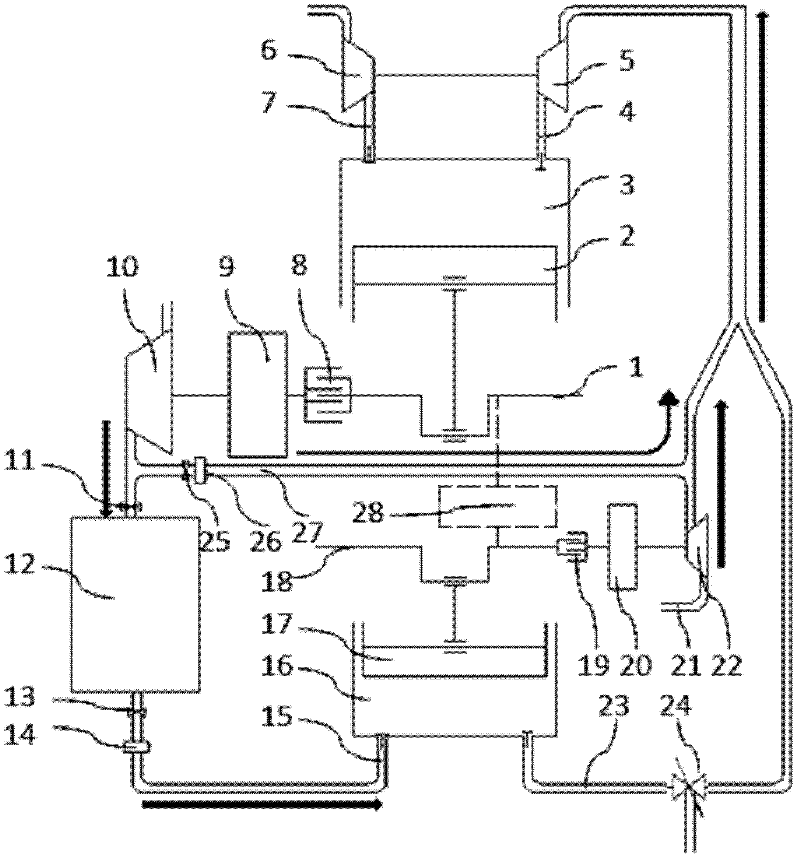
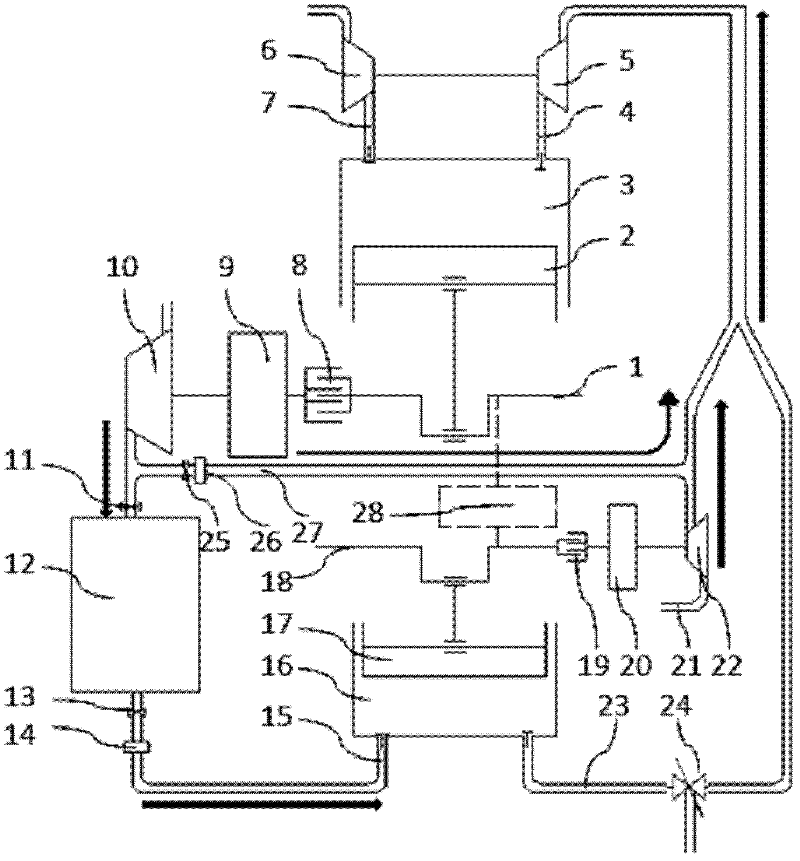
[0018] The structure of the pneumatic internal combustion hybrid engine of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0019] The air motor has an air motor cylinder 16, and the air motor cylinder 16 is provided with an intake valve, an exhaust valve and an air motor crankshaft 18. The intake valve is connected to the pressure regulating mechanism B 14 , the shut-off valve B 13 , the high-pressure gas tank 12 and other mechanisms successively through the intake pipe 15 . The pneumatic crankshaft 18 is connected through the clutch B19, the speed regulating mechanism B20 and the air compressor C22. The air motor exhaust valve is connected with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com