Micromolecular marker for diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion and application thereof
A pleural effusion and small molecule technology, which is applied in the field of small molecule markers for the diagnosis of cancerous pleural effusion, can solve the problems of limited application, low specificity, and high cost, and achieve strong specificity, high sensitivity, and identification The effect of high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
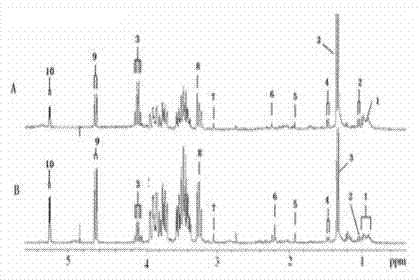
[0020] Example 1 NMR Analysis of Small Molecular Markers in Pleural Effusion
[0021] 1. Experimental objects: 26 benign pleural effusions and 26 cancerous pleural effusions were taken as NMR analysis samples.
[0022] 2. Experimental method: Take 1 ml of the above 22 benign pleural effusions and 26 cancerous pleural effusions and mix them with 20 ml of acetone, vortex for 30 seconds, let it stand for 5 minutes to precipitate protein, and centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes. Molecular compounds remained in the supernatant, and the supernatant was evaporated to dryness, and the residue was redissolved in 500 μl of heavy water, wherein the heavy water contained TSP (deuterated trimethylsilyl sodium propionate) as the internal standard of chemical shift ( δ = 0), and then the sample solution was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken and transferred into an NMR sample tube. The sample test was carried out on a Bruker DPX-300 nuclear magnetic r...
Embodiment 2
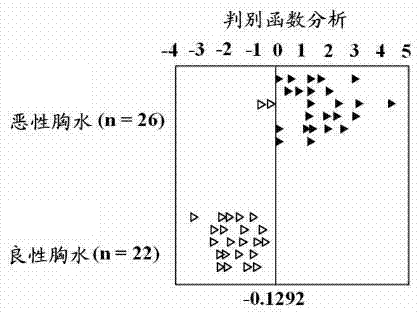
[0029] Example 2 Discriminant function analysis of small molecule markers in benign and cancerous pleural effusions
[0030] In order to further optimize the small molecular markers for identifying benign and cancerous pleural effusions, the present invention uses discriminant function analysis (DFA) to perform further statistical analysis on the small molecular markers in benign and cancerous pleural effusions. The discriminant function analysis method is divided into two processes: (1) discrimination: to identify potentially influential small molecule markers; (2) classification: to use classification criteria to maximize the correct classification and emphasize the differences between groups, After obtaining the discriminant function equation, cross-validation was carried out on the cancerous pleural effusion group.
[0031]In univariate analysis, patients with cancerous pleural effusions had significantly higher levels of valine, lactate, and alanine than those with benign...
Embodiment 3
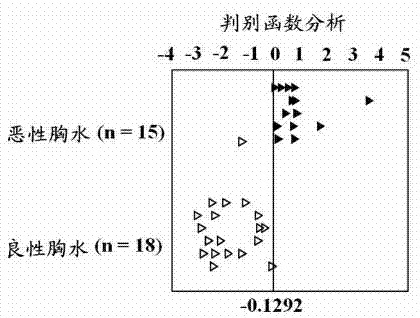
[0035] Example 3 Verification experiment of small molecular markers for identifying benign and cancerous pleural effusions
[0036] In order to verify the reliability of the discriminant function described in Example 2 above and the accuracy of the identification of small molecule markers, the present invention established a verification group, a verification group (including 15 benign pleural effusion and 18 cancerous pleural effusion samples) The sample classes in are unknown prior to discriminant function analysis. According to the nuclear magnetic resonance method described in Example 1, the hydrogen spectrum signals of 5 compounds of lactate, acetoacetate, trimethylamine oxide, betaine and α-glucose in benign pleural effusion and cancerous pleural effusion were detected, and The calculation equation of the discriminant function analysis described in Example 2:=-0.2688+[0.1058 × Int. (lactate)] - [0.4263 × Int. (acetoacetate)] - [2.6758 × Int. (oxidation Trimethylamine / be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com