Queen bee intestinal enzyme and its preparation method and application
An intestinal and queen bee technology, applied in the field of queen bee intestinal enzymes and preparation thereof, can solve the problems of difficult screening of biologically active polypeptides, unsuitable for royal jelly proteolysis, lack of polypeptides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
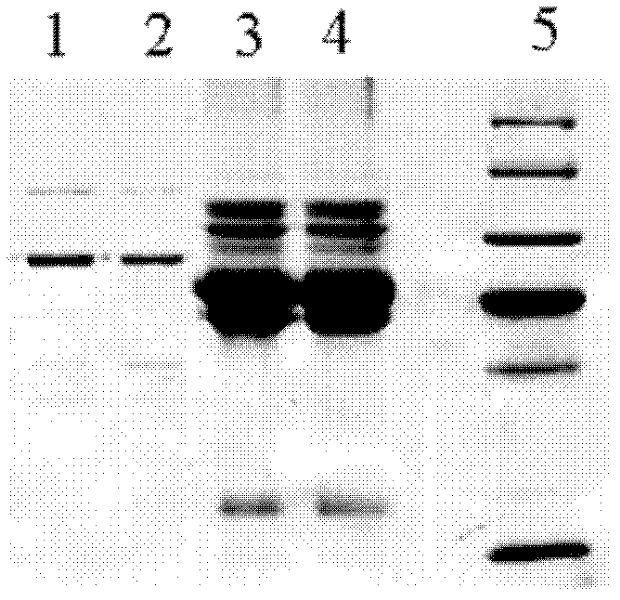
[0065] Fresh queen bee larvae aged 2 to 3 days were taken, washed with isotonic ice-cold 0.9% saline, filtered, dissected one by one and collected all intestinal tracts of the worms. Add 50mmol / L phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7 at a mass volume ratio (g / ml) of 1:1 to dilute the intestinal tract of the worm, and use an electric homogenizer to grind it into a homogenate under ice-bath conditions. Centrifuge at 20,000×g for 20 min at 4°C. After centrifugation, the suspension is divided into three layers, namely, the upper layer of floating matter (lipid components), the middle layer of suspended solution, the lower layer of sedimentation, and the middle layer is recovered. The middle layer was centrifuged again at 20000×g at 4°C for 20 min, and the middle layer was taken to obtain a yellow transparent intestinal enzyme solution, which was stored in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0066] Take part of the intestinal enzyme solution, and use the BCA method to detect the prote...
Embodiment 2
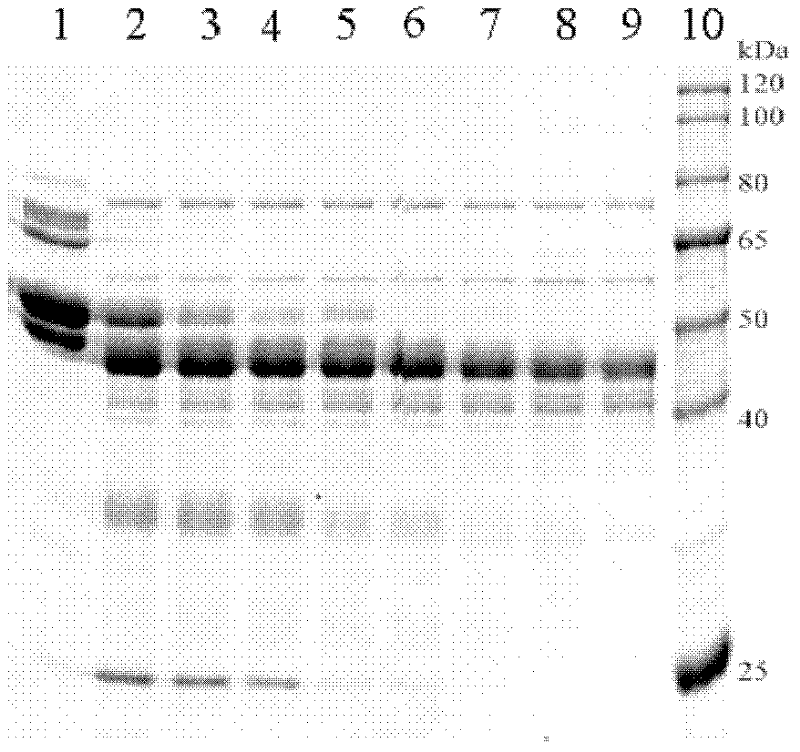
[0068] Fresh queen bee larvae aged 2 to 3 days were taken, washed with isotonic ice-cold 0.9% saline, filtered, dissected one by one and collected all intestinal tracts of the worms. Add 50mmol / L phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7 at a mass volume ratio (g / ml) of 1:1 to dilute the intestinal tract of the worm, and use an electric homogenizer to grind it into a homogenate under ice-bath conditions. Centrifuge at 18000×g for 30 min at 4°C. After centrifugation, the suspension is divided into three layers, namely, the upper layer of floating matter (lipid components), the middle layer of suspended solution, the lower layer of sedimentation, and the middle layer is recovered. The middle layer was centrifuged again at 18000×g at 4°C for 30 min, and the middle layer was taken to obtain a yellow transparent intestinal enzyme solution, which was stored in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0069] Take part of the intestinal enzyme solution, and use the BCA method to detect the protei...
Embodiment 3
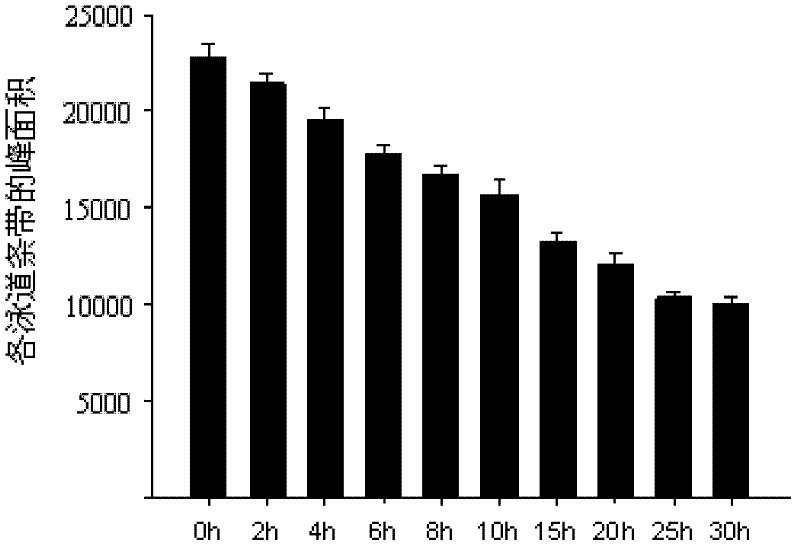
[0071] Fresh queen bee larvae aged 2 to 3 days were taken, washed with isotonic ice-cold 0.9% saline, filtered, dissected one by one and collected all intestinal tracts of the worms. Add 50mmol / L phosphate buffer with a pH value of 7.2 at a mass-volume ratio (g / ml) of 1:2 to the parasite intestine for dilution, and use an electric homogenizer to grind into a homogenate under ice-bath conditions. Centrifuge at 25,000×g for 24 minutes at 4°C. After centrifugation, the suspension is divided into three layers, namely, the upper layer of floating matter (lipid components), the middle layer of the suspended solution, the lower layer of sedimentation, and the recovery of the middle layer. The middle layer was centrifuged again at 25000×g at 4°C for 24 min, and the middle layer was taken to obtain a yellow transparent intestinal enzyme solution, which was stored in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0072] Take part of the intestinal enzyme solution, and use the BCA method to detect the protein ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com