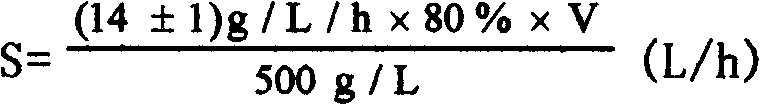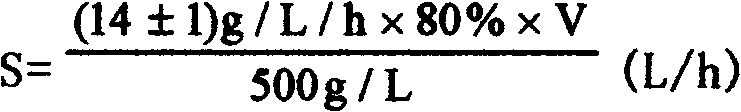Control method for producing gluconate by microbial method
A technology of gluconate and control method, which is applied in the control field of microbial production of gluconate, which can solve the problems of lack and failure to observe the growth period of gluconic acid microorganisms, and achieve the effect of precise control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] The first step, seed culture: Add 2.5Kg of glucose, 75g of corn steep liquor, 6.4g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 2g of urea, and 2ml of antifoaming agent into a 15L culture tank. To 38°C, add 250ml eggplant bottle bacterial suspension, control dissolved oxygen (DO) ≥ 30, cultivate for 15h to obtain seed liquid.
[0014] The second step, fermentation: add 4.2KG of glucose, 2.8g of magnesium sulfate, 0.28g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.4g of urea, and 1ml of defoamer to a 50L fermenter. At 38°C, inoculate the cultured seed solution with a 10% inoculation amount. Control dissolved oxygen (DO) ≥ 30, temperature 38 ℃, use 20% calcium carbonate to adjust pH to 5.5, start fermentation.
[0015] The third step, feeding:
[0016] (1). Ingredients: 14Kg of glucose solution, 36g of corn steep liquor, 5.6g of magnesium sulfate, 2.8g of urea, 1ml of defoamer were added to a 30L feeding tank, and the volume was adjusted to 20L, sterilized at 120°C for 15 minutes, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The first step, seed culture: Add 2.5Kg of glucose, 75g of corn steep liquor, 6.4g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 2g of urea, and 2ml of antifoaming agent into a 15L culture tank. To 38°C, add 250ml eggplant bottle bacterial suspension, control dissolved oxygen (DO) ≥ 30, cultivate for 15h to obtain seed liquid.
[0025] The second step, fermentation: add 4.2KG of glucose, 2.8g of magnesium sulfate, 0.28g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.4g of urea, and 1ml of defoamer to a 50L fermenter. At 38°C, inoculate the cultured seed solution with a 10% inoculation amount. Control dissolved oxygen (DO) ≥ 30, temperature 38 ℃, use 32% sodium hydroxide to adjust pH to 5.5, start fermentation.
[0026] The third step, feeding:
[0027] (1). Ingredients: 14Kg of glucose solution, 36g of corn steep liquor, 5.6g of magnesium sulfate, 2.8g of urea, 1ml of defoamer were added to a 30L feeding tank, and the volume was adjusted to 20L, sterilized at 120°C for 15 minutes, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com