Cytosis polymer microfluidic chip and preparation method thereof
A microfluidic chip, polymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, manufacturing tools, welding equipment, etc., can solve problems such as uneven stress, air bubbles, and reduced production efficiency, and achieve improved application functions and performance, chip design. The effect of flexibility and cost control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
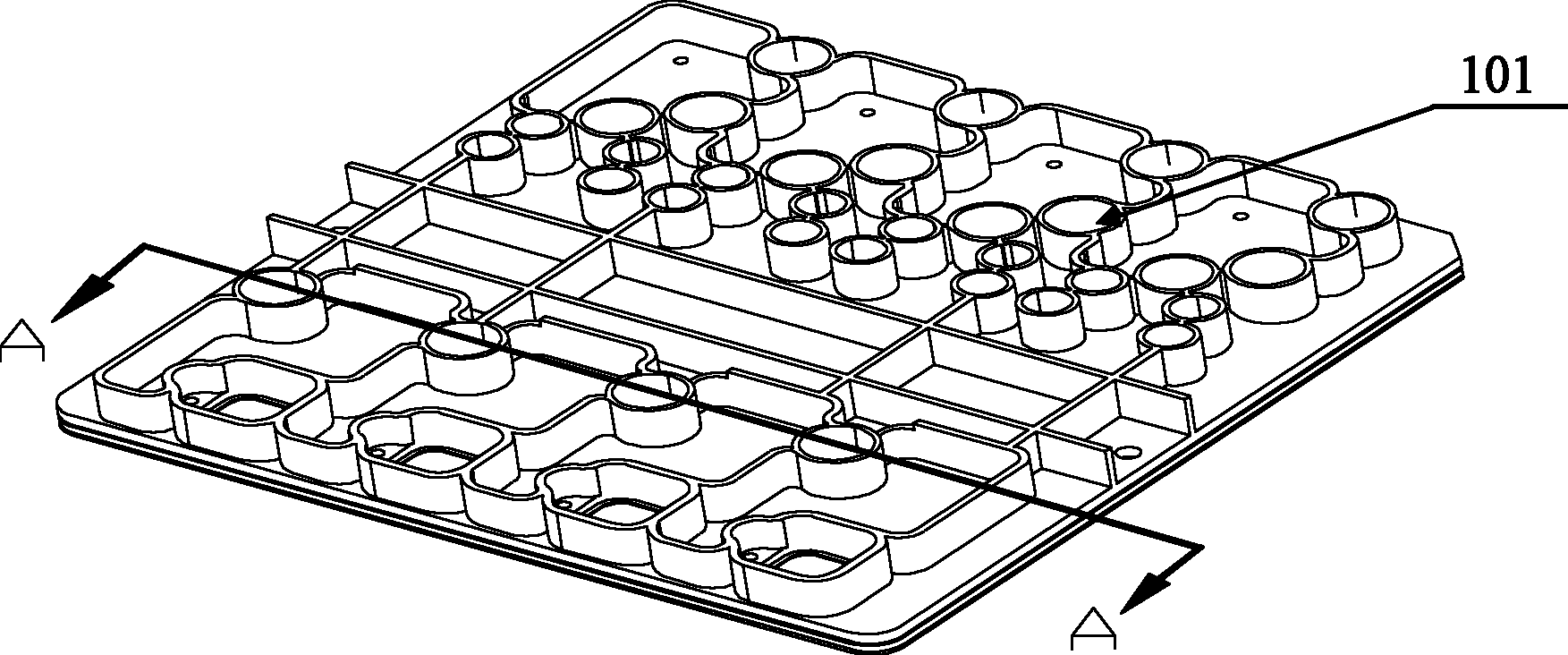
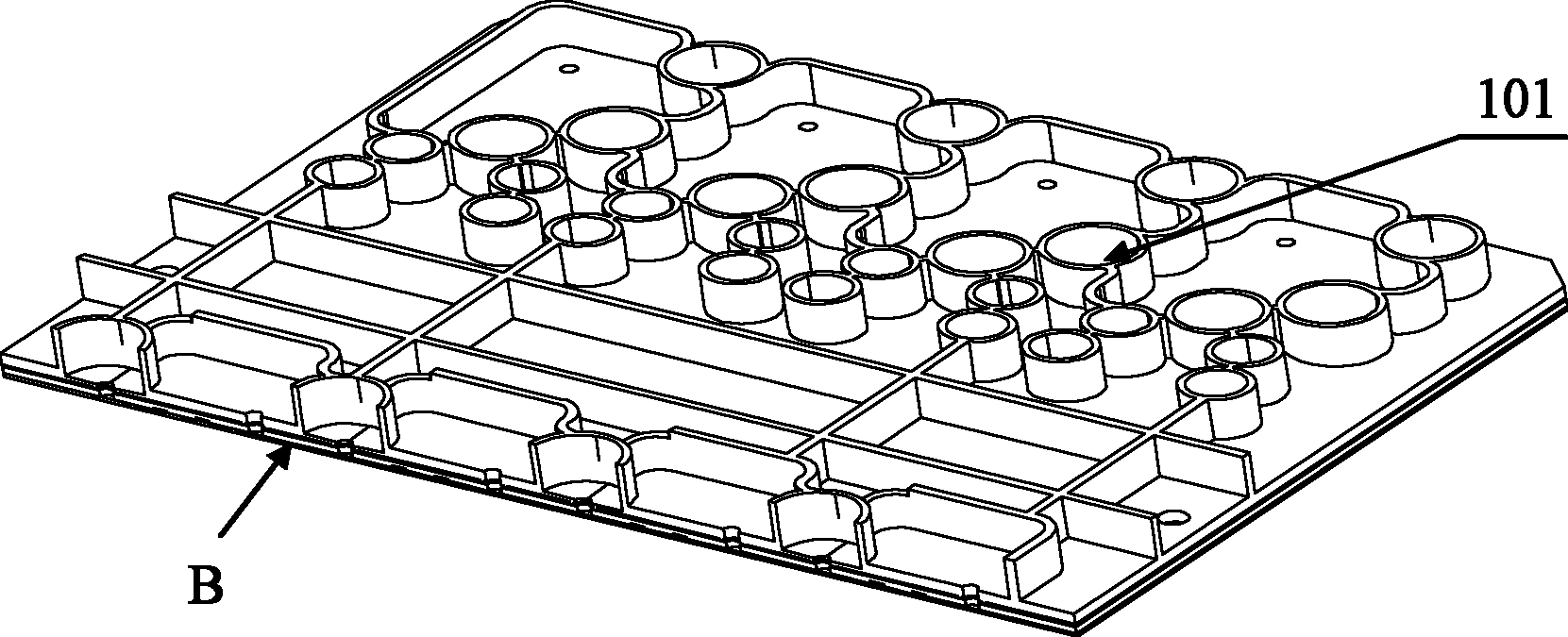
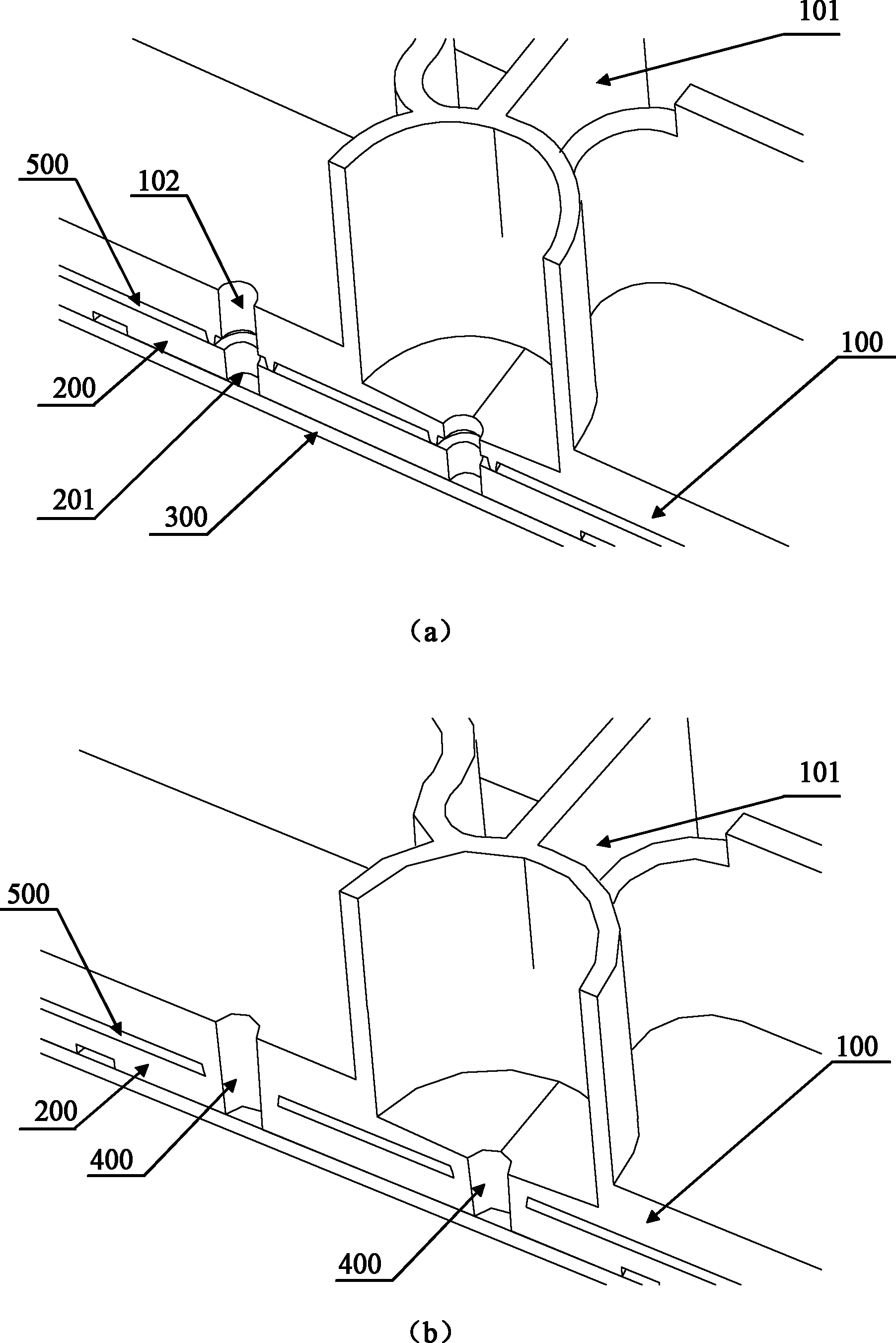
[0047] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 As shown in (a) and (b), the overall structure of the membrane movable polymer microfluidic chip of this embodiment includes: a first substrate 100, a diaphragm 300, and several structural components 101 on one side of the first substrate 100 , A number of first through holes 102 on the first substrate 100. The structural components 101 are various channels, containers, and external mechanisms in the chip. The chip also includes a second substrate 200, one side of the second substrate 200 is attached to the other side of the first substrate 100. In order to facilitate the sticking of the diaphragm and prevent defects or bubbles in the sticking area after sticking, the other surface of the second substrate 200 is a flat surface. The second substrate 200 is provided with a second through hole 201 corresponding to the first through hole 102 of the first substrate 100. The first through hole 102 and the second through hole 201 form an...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing the membrane movable polymer microfluidic chip in embodiment 1, which includes the steps of preparing a first substrate 100 and a second substrate 200, and the surface of the first substrate facing away from the structural component is a welding surface, The surface of the second substrate 200 that is attached to the first substrate 100 is a soldering surface, and at least one fuse is provided on the soldering surface of the first substrate 100 or the second substrate 200; the first substrate 100 and the second substrate 200 are attached The welding surface of the fusion line is melted to weld the first substrate 100 and the second substrate 200 together; after welding, the diaphragm 300 is attached to the surface (non-welded surface) of the second substrate 200.
[0052] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, an ultrasonic indenter is used to melt the fuse to weld the first substrate 100 and the second substrate ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Such as Image 6 As shown, the preparation method of the membrane movable polymer microfluidic chip of this embodiment is basically the same as the method of embodiment 2, that is, the first substrate 100 and the second substrate 200 are prepared, and the surface of the first substrate facing away from the structural components is the welding surface , The surface of the second substrate 200 that is attached to the first substrate 100 is a welding surface, and at least one fuse is set on the welding surface of the first substrate 100 or the second substrate 200; the first substrate 100 and the second substrate are attached The welding surface of 200 is melted to weld the first substrate 100 and the second substrate 200 together; after welding, the diaphragm 300 is attached to the surface (non-welded surface) of the second substrate 200.
[0059] The difference is that a laser is used to melt the fuse to weld the first substrate 100 and the second substrate 200. Therefore, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com