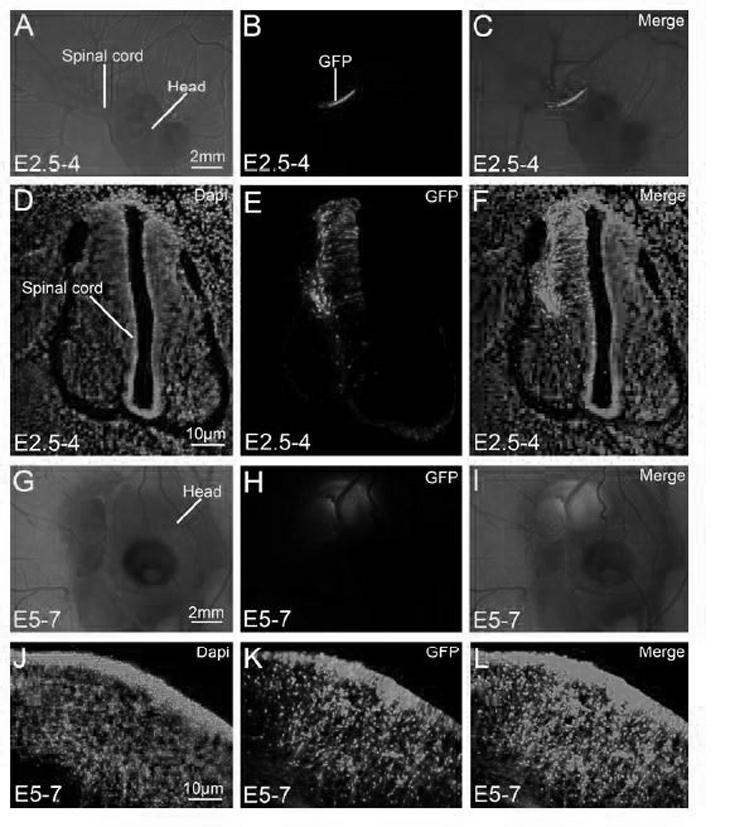
Method for chicken embryo cultivation and in vivo electroporation of gene
A chicken embryo culture and transgene technology, which is applied in the fields of developmental biology and transgene, chicken embryo culture and in situ electrical transgene of chicken embryo, can solve the problems of difficult culture operation, inconvenient gene transfection, easy pollution, etc., to improve The survival rate of chicken embryos, the effect of improving the survival rate of culture and preventing water evaporation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Early stage culture of embodiment 1 chicken embryo
[0035] This embodiment specifically adopts the following experimental methods:
[0036] Purchase fresh fertilized eggs from the breeder factory, bring them back to the laboratory on the same day, and choose different chicken embryo culture methods for early culture of chicken embryos:
[0037] Method 1: Keep the egg shell intact, cultivate in a constant temperature incubator at a temperature of 37°C, and transfer eggs at intervals of 2 hours;
[0038] Method 2: After chicken embryos are cultured for 2 days, the eggshells are opened and cultured in a constant temperature incubator at a temperature of 37°C, and the interval between egg transfers is 2 hours;
[0039] Method 3: After the chicken embryos are cultured for 2 days, the eggshells are opened and cultured in a constant temperature incubator at a temperature of 37°C. Put a beaker of water in the incubator, and the egg transfer interval is 2 hours;
[0040] Meth...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2 The dehulling culture of chicken embryo
[0050] This embodiment specifically adopts the following experimental methods:
[0051] Purchase fresh fertilized eggs from the breeder factory, bring them back to the laboratory on the same day, keep the egg shells intact, and cultivate them in a constant temperature incubator at a temperature of 37°C, with an interval of 2 hours between egg transfers. On the third day of cultivation, they will be intact without breaking the vitelline membrane. Transfer the embryos out of the eggshell and move them into different containers in a constant temperature and humidity incubator with a culture temperature of 37°C and a relative humidity of 60%:
[0052] Method 1: 90mm caliber Petri dish;
[0053] Method 2: 60mm caliber Petri dish;
[0054] Method 3: Add appropriate amount of sterile water to a 150mm petri dish, and cover the petri dish;
[0055] Method 4: 70mm caliber round concave bottom porcelain bowl;
[0056] Meth...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Early Chicken Embryo Culture and In Vivo Electrotransfer Method
[0066] This embodiment specifically adopts the following experimental methods:
[0067] (1) Chicken embryo culture: buy fresh fertilized eggs from the breeder factory, bring them back to the laboratory on the same day, wash them with warm water, dry them, mark the time on the egg shells, put the fertilized eggs horizontally into the incubator, and set the incubator Set the temperature at 37.8°C, humidity at 60%, and turn the eggs at an interval of 2 hours. Take the eggs out of the incubator on the second day of cultivation, and place them horizontally in a petri dish covered with napkins without turning them. Use a hacksaw blade to lightly saw two lines 1cm apart on the side and directly above the blunt end, punch two holes with a 10ml syringe needle, and use a syringe with a needle to pierce the needle into the opening near the side, absorb 3-4ml egg white, Then use ophthalmic surgical scissor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com