Biodegradable scaffold
A biodegradable material technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as stent narrowing, stent collapse, and displacement, and achieve the effects of controllable heating temperature, concentrated heating points, and reduced retraction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
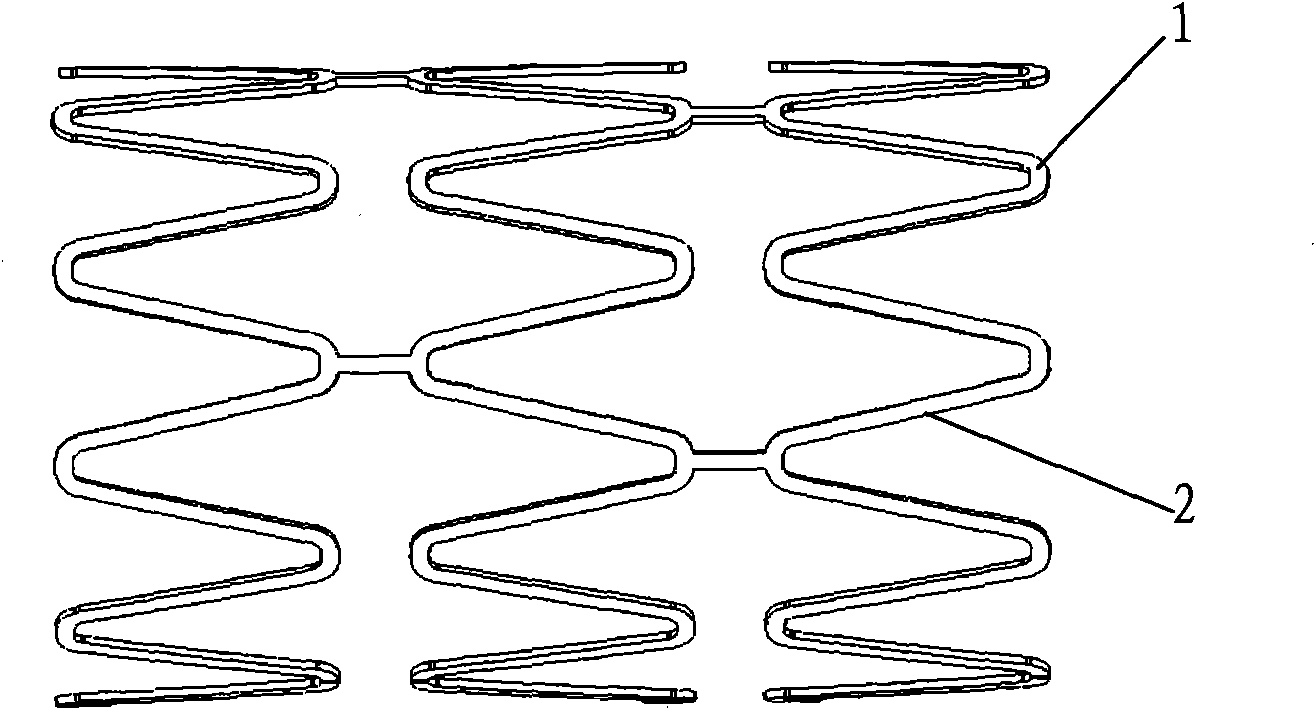
[0039] In the embodiment of the present application, several magnetic particles 3 are distributed in the stent main body 1 .
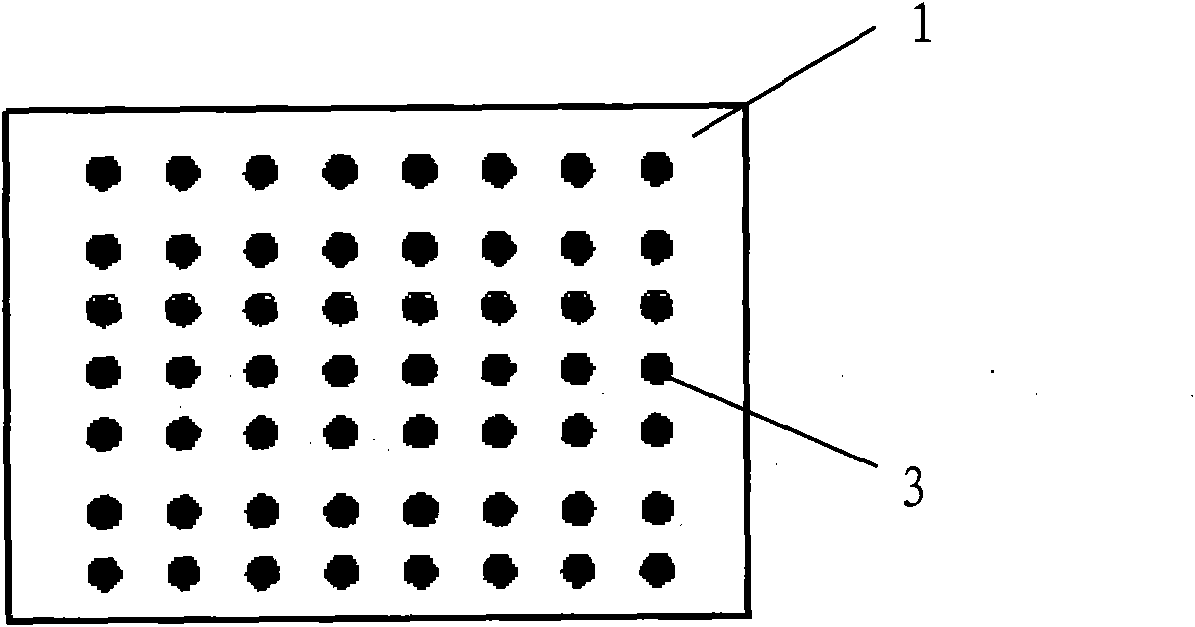
[0040] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a cross-sectional view of the stent rod provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application. In the figure, several magnetic particles 3 are evenly distributed in the stent body 1, and its main material is a material that can generate heat under the action of an alternating magnetic field, including but Not limited to γ-Fe 2 o 3 , Fe 3 o 4 , Ni, Co, Fe, FeCo, NiFe, CoFeO, NiFeO, MnFeO in one or more. In addition, in the embodiment of the present application, the diameter of the magnetic particle 3 is at the nanoscale, preferably 10-100 nm in diameter, and the mass ratio of the magnetic particle 3 to the degradable material in the stent main body 1 is 1:10-1:100.
[0041] In order to improve the biocompatibility and dispersibility of the magnetic particle 3, in the embodiment of the present application, pref...
Embodiment 2
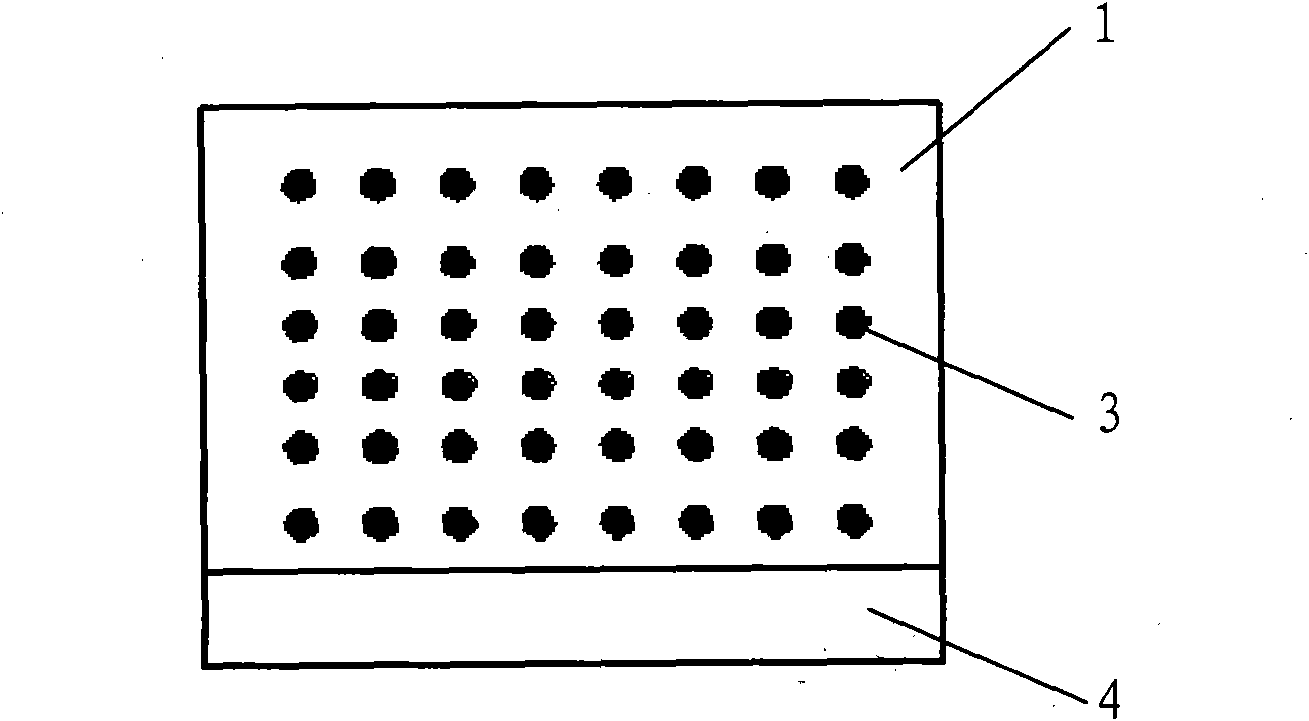
[0043] Such as image 3 As shown, it is a cross-sectional view of a stent rod provided by the embodiment of the present application. On the basis of Embodiment 1, the biodegradable stent also includes: an inner coating of a biodegradable material coated on the inner periphery of the stent body 1 4.
[0044] The degradable material of the inner coating 4 is the same as that of the stent body 1 in Example 1, including but not limited to polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, copolymers of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid, polycaprolactone, polydiox One or more of hexacyclic ketone, polyanhydride, and tyrosine polycarbonate.
[0045] In the embodiment of this application, preferably, as Figure 4As shown, several magnetic particles 3 are also distributed in the inner coating 4 , and several magnetic particles 3 are evenly distributed in the inner coating 4 .
[0046] In other embodiments of this application, such as Figure 5 As shown, the biodegradable stent also includes:...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Figure 6 A cross-sectional view of a support rod provided in Embodiment 3 of the present application.
[0049] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the biodegradable stent includes: a stent body 1 made of a degradable material and an inner coating 4 of a biodegradable material coated on the inner periphery of the stent body, and several magnetic magnets are distributed in the inner coating 4 particle 3.
[0050] In the embodiment of the present application, the degradable materials in the stent body 1 and the inner coating 4 are the same as those in the previous embodiments, and the magnetic particles 3 are also the same as in the previous embodiments.
[0051] In other embodiments of this application, such as Figure 7 As shown, the biodegradable stent also includes: a biodegradable material outer coating 5 coated on the periphery of the stent body 1, and drugs can also be added to the outer coating 5, and after the stent is implanted in the human body, it can continuously ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com