Process for production of polylactic acid
A manufacturing method, polylactic acid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical/physicochemical processes, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of low heat resistance and low rigidity, and achieve low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0181] (Example 1: Production of poly-L-lactic acid)
[0182] 600kg of L-lactide (manufactured by Musashino Chemical Research Institute Co., Ltd.), 30g of tin octoate (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.), and 1500g of lauryl alcohol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) were charged into 1000L pretreatment Tank, at 40°C, 1.33×10 3 Dry under Pa (10mmHg) for 30 minutes. Next, the decompression was released and replaced with nitrogen gas with a purity of 99.999% by mass. This decompression operation and nitrogen replacement operation were repeated three times as pretreatment. The water content of the pretreated L-lactide was 20 ppm.
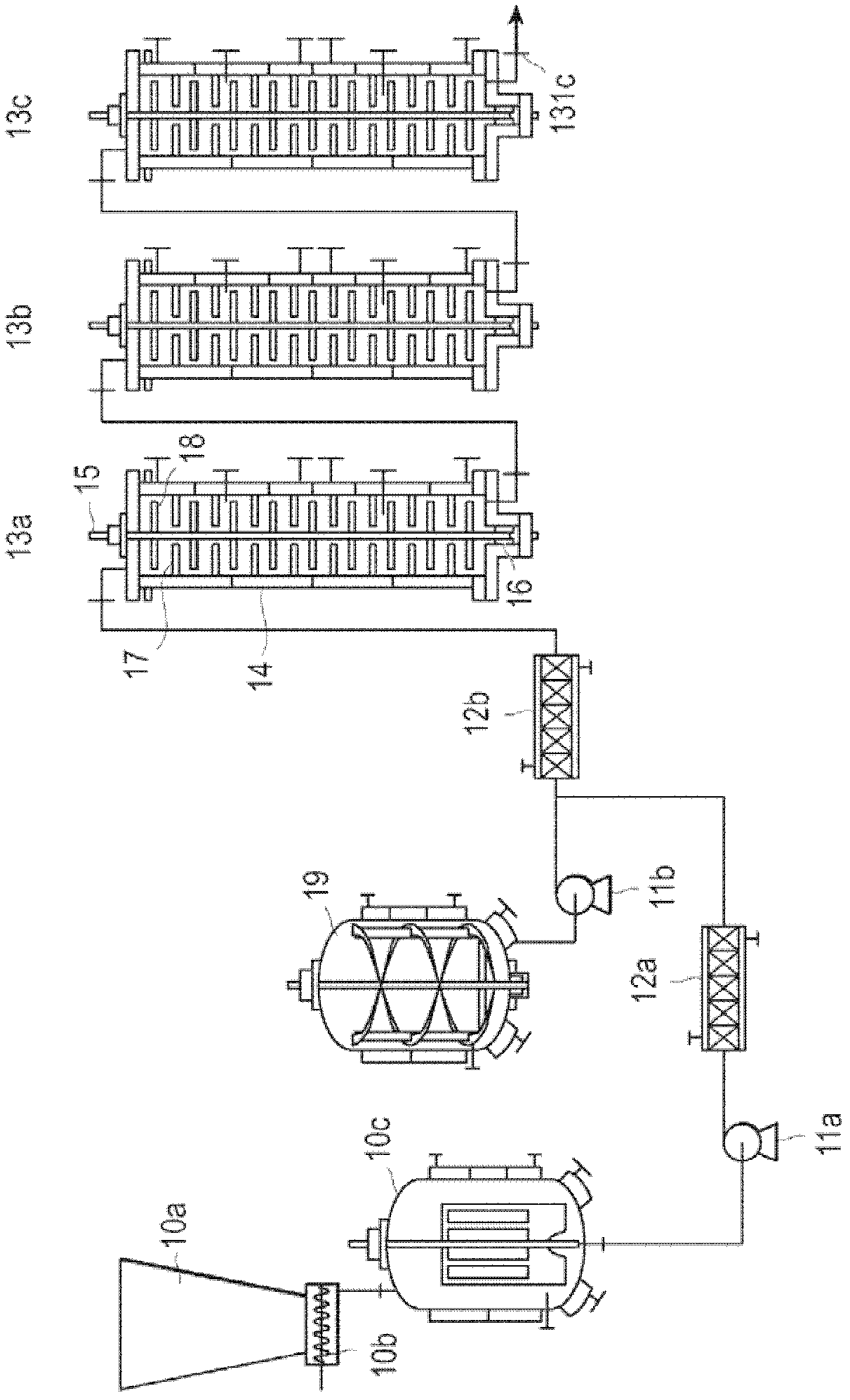
[0183] Then, the feeder is used to cover the nitrogen gas with a purity of 99.999% by mass at a speed of 11.8kg / h, such as Figure 7 The lactide melting tank with a capacity of 15 L equipped with MaxBlend (registered trademark) blades shown above supplies the above-mentioned L-lactide. While melting L-lactide, i...
Embodiment 2
[0184] (Example 2: Synthesis of Stereocomplex Polylactic Acid Block Copolymer)
[0185]
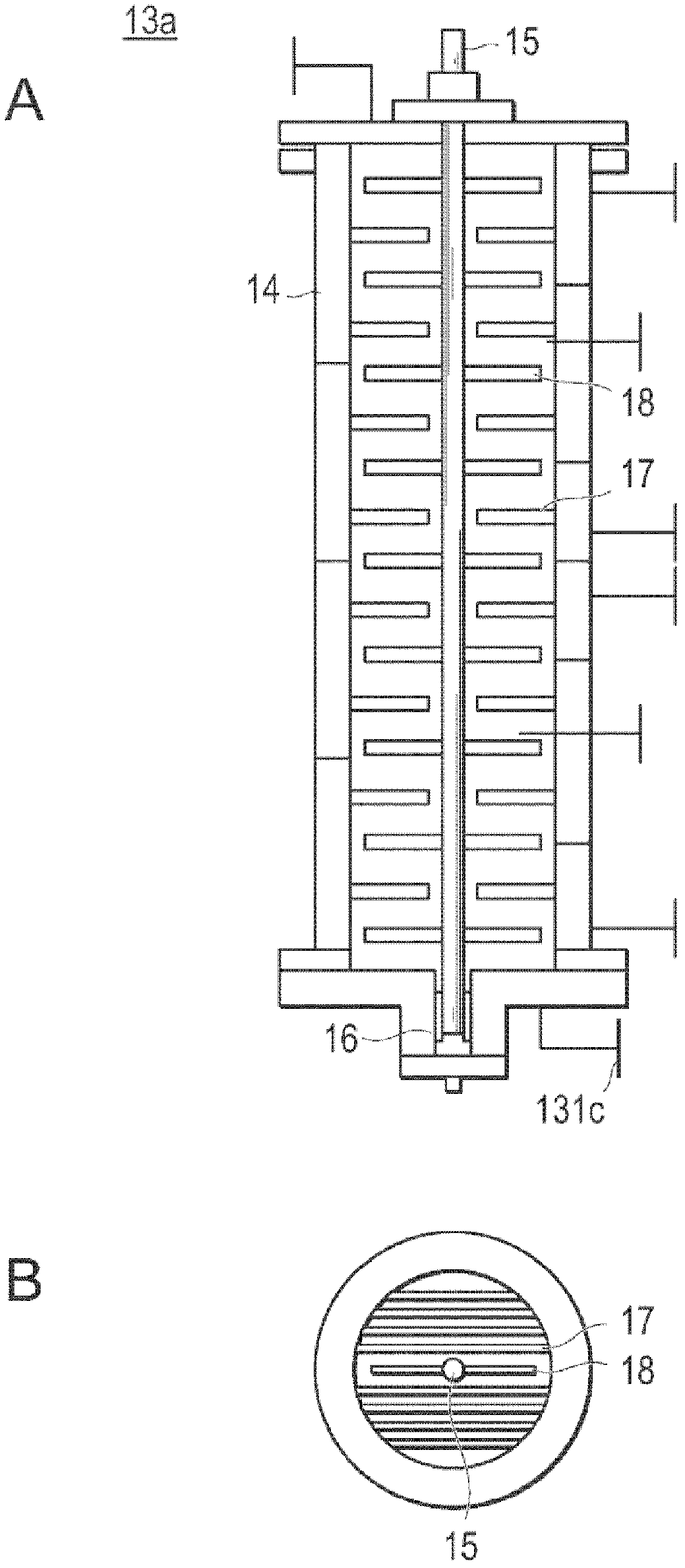
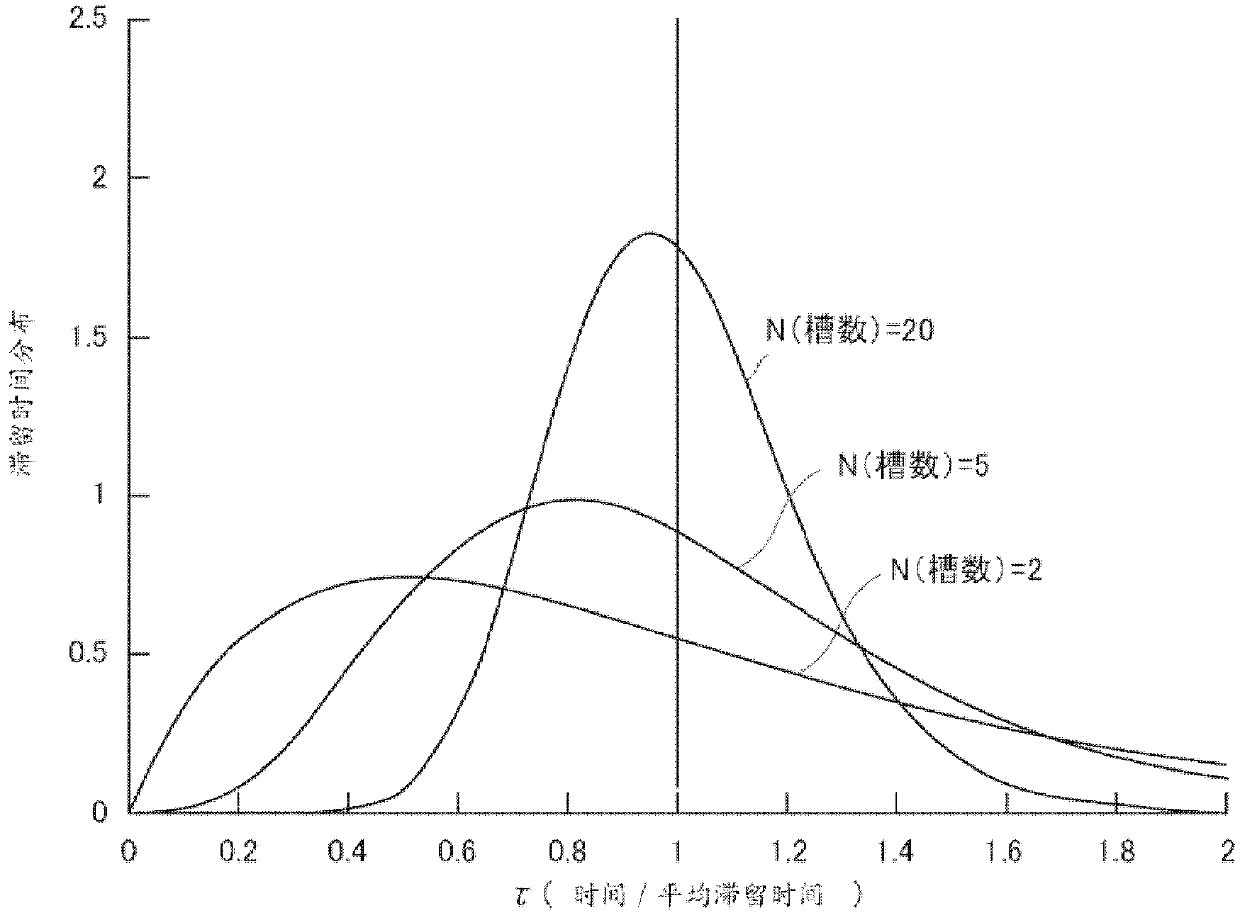
[0186] In place of L-lactide, D-lactide (manufactured by Musashino Chemical Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was used, except that the amount of lauryl alcohol used was 5400 g, and poly-D was produced by the same method as in Example 1. - Lactic acid. use as figure 2 The shape shown is a 16.8 L capacity reactor with plug flow. The ξ(τ) of each of the first reactor, the second reactor, and the third reactor was 0.28, and the ξ(τ) of the entire reaction system was 0.16. After reaching a steady state, the poly-D-lactic acid obtained from the third reactor was stored in a polymer melting vessel previously replaced with nitrogen with a purity of 99.999% by mass, and a heat medium at 200° C. was circulated in the jacket. The lactide conversion rate of the obtained poly-D-lactic acid was 95.9%, Mw was 56,850, Mn was 36,850, and the molecular weight distribution was 1.54. Moreover, the yellow...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com