Therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine
A hepatitis B and vaccine technology, applied in the direction of antibody medical ingredients, peptide preparation method, digestive system, etc., can solve the problem of reduced ability of transgenic mice to resist infection, and achieve the effect of eliminating virus and inhibiting HBV replication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
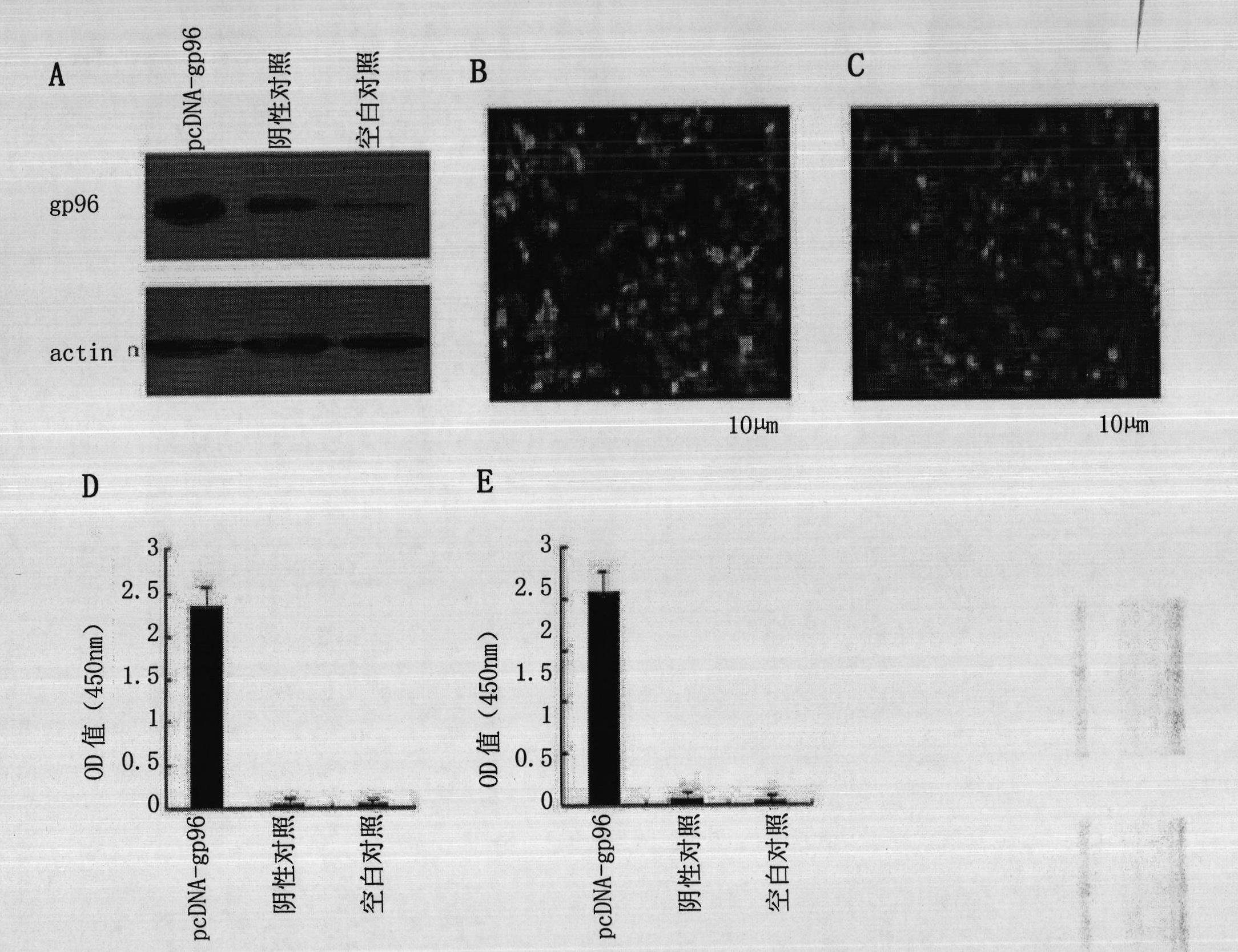
[0030] Example 1, Verification of the expression ability of HBsAg gene, HBcAg gene and gp96 gene
[0031] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0032] Prepare the DNA shown in Sequence 2 of the sequence listing and insert it between the EcoR I and Xho I restriction sites of the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1 (purchased from Invitrogen, product number V790-20) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pcDNA-gp96 .
[0033] The DNA shown in Sequence 2 of the sequence listing was prepared and inserted between the EcoR I and Xho I restriction sites of pEGFP-N1 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pEGFP-N1-gp96.
[0034] The DNA shown in Sequence 4 of the sequence listing was prepared and inserted between the EcoR I and Xho I restriction sites of the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pcDNA-HBcAg (pcDNA-HBc).
[0035] The DNA shown in sequence 6 of the sequence listing was prepared and inserted between the EcoR I and Xho I restriction sites of t...
Embodiment 2
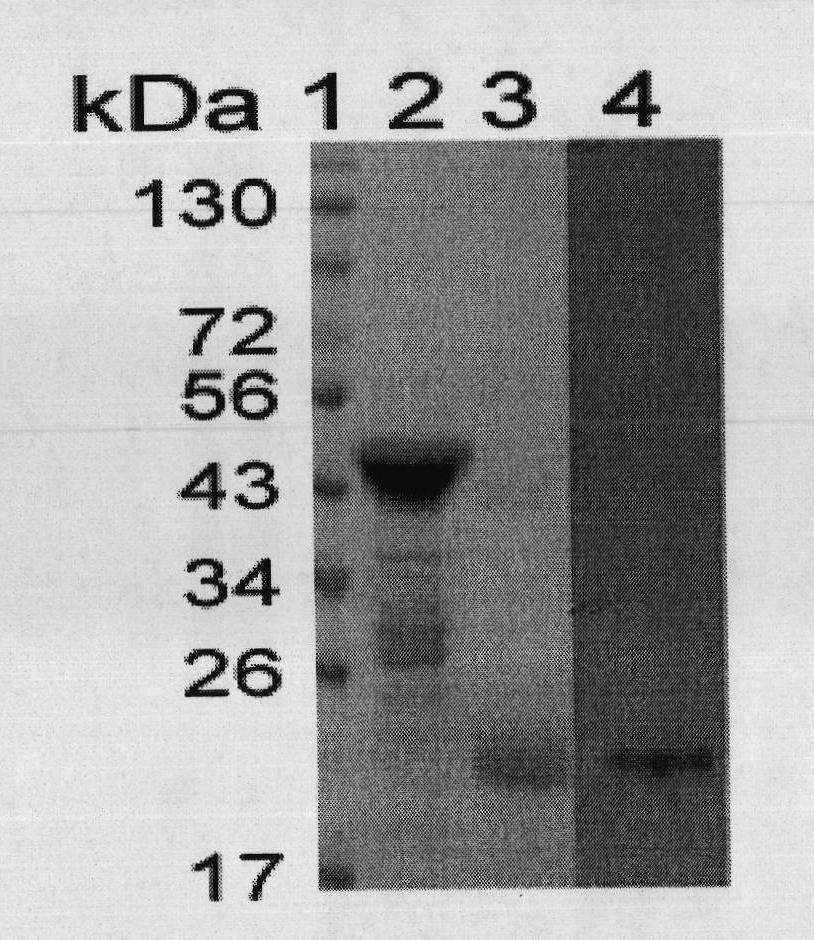
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 2, HBcAg
[0042] 1. Prepare the DNA shown in sequence 4 and insert it between the BamH1 and Xho1 restriction sites of the prokaryotic expression vector pGEX (purchased from GE, product number 28-9546-48, with a GST tag) to obtain a recombinant plasmid pGEX-HBcAg.
[0043] 2. The recombinant plasmid pGEX-HBcAg was introduced into Escherichia coli DH5α (purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology Company, product number CB101-03) to obtain recombinant bacteria.
[0044] 3. Inoculate the recombinant bacteria in LB medium, cultivate to OD ≈ 0.6, add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.5 mM, and continue to cultivate at 37°C for 4 hours.
[0045] 4. The collected cells were sonicated in an ice bath (200W, broken for 4s and stopped for 6s, 3 cycles of 99 times), and centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 20min at 4°C. Collect the supernatant.
[0046] 5. The supernatant was subjected to affinity chromatography at 4°C. The carrier was Glutathione-Sepha...
Embodiment 3
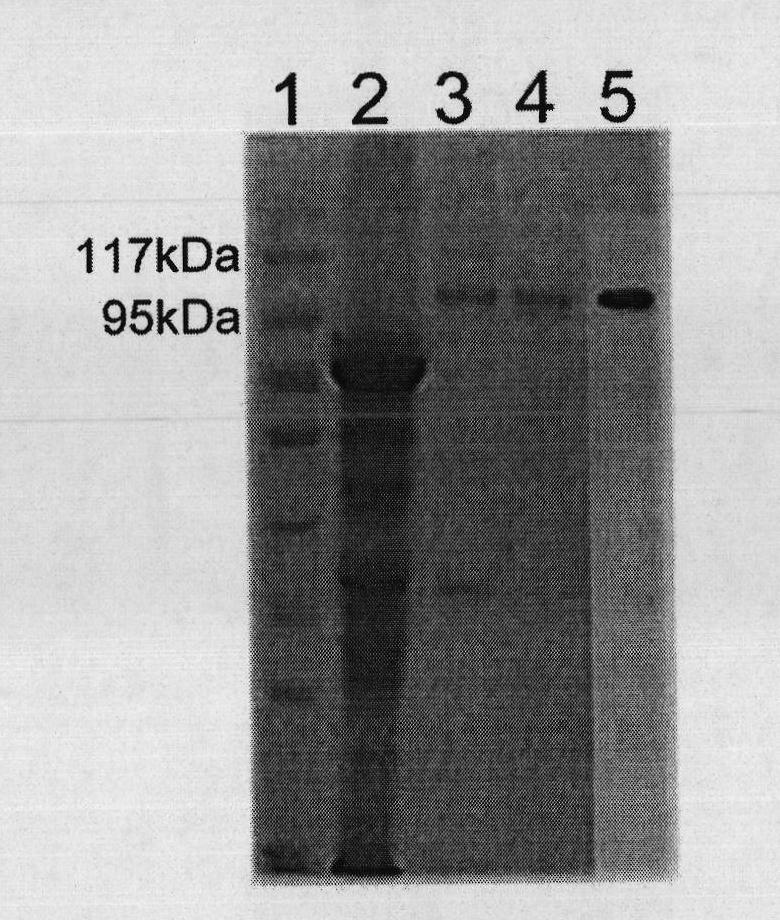
[0053] Embodiment 3, the preparation of recombinant gp96 protein (rgp96)
[0054] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmid pHFMDZ-R1L2GAmy-gp96
[0055] 1. Extract the mRNA of human liver cancer cell HepG2, reverse transcribe and synthesize cDNA.
[0056] 2. Perform PCR amplification using the cDNA in step 1 as a template to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0057] Upstream primer: 5'-CCGgaattcATGGACGATGAAGTTGATG-3';
[0058] Downstream primer: 5'-CCGctcgagCTATTAGAATTCATCTTTTTCAGCTGTAG-3'.
[0059] 3. Double-digest the PCR amplification product with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and XhoI, and recover the digested product.
[0060] 4. The plasmid pHFMDZ-R1A (purchased from Invitrogen, product number V20520) was double digested with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and XhoI, and the vector backbone was recovered.
[0061] 5. Ligate the digested product of step 3 with the vector backbone of step 4 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pHFMDZ-R1-gp96.
[0062] Sequencing resul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com