Method for preparing fluorescence labeling polyactic acid nanometer microsphere
A nano-microsphere and fluorescent labeling technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of complicated synthesis process, low product yield and high cost, and achieve the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Preparation of polylactic acid nanoparticles with fluorescent labeling properties:
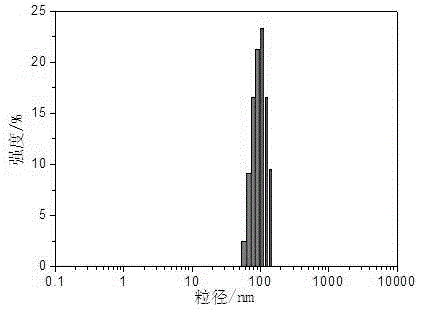
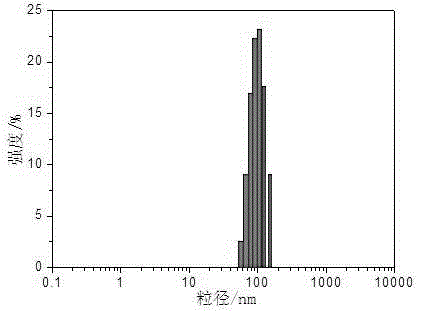
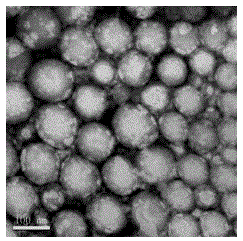
[0031] (1) Disperse 100 mg of polylactic acid microspheres with an average particle size of 120 nm in 50 ml of distilled water to form a mixture A.
[0032] (2) 1 mg fluorescent dye rhodamine B was dissolved in 1 g glycidyl methacrylate to form a mixed solution B.
[0033] (3) Under magnetic stirring, take 50 mg of mixed solution B and add it to mixed solution A.
[0034] (4) Heat up to 60 °C, add 0.25 mg of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate oxidation-reduction initiator (the mixing mass ratio of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate is 2:3), stop stirring after 6 h, and obtain fluorescently labeled poly Suspension of lactic acid microspheres.
[0035] (5) Put the above suspension in a dialysis bag, and dialyze with redistilled water for 48 hours to remove ungrafted Rhodamine B.
[0036] (6) Freeze-dry the suspension permeated from the dialysis bag to obtain fluorescentl...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1. Preparation of fluorescently labeled polylactic acid nanospheres loaded with felodipine (an antihypertensive drug):
[0042] (1) Suspend and disperse 50 mg of felodipine-loaded polylactic acid microspheres with an average particle size of 500 nm in 50 ml of distilled water to form a mixture C.
[0043] (2) 1 mg of fluorescent dye rhodamine B was dissolved in 1 g of glycidyl methacrylate to form a mixture D.
[0044] (3) Under magnetic stirring, take 50 mg of mixed solution D and add it to mixed solution C.
[0045] (4) Heat up to 60 °C, add 0.25 mg of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate oxidation-reduction initiator (the mixing mass ratio of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate is 2:3), stop stirring after 6 h, and obtain the drug-loaded fluorescent label Polylactic acid microsphere suspension.
[0046] (5) Take the above suspension and place it in a dialysis bag, and dialyze it with double-distilled water for 48 hours to remove ungrafted rhodamine B.
[...
Embodiment example 3
[0050] 1. Preparation of fluorescently labeled cyclosporin A-loaded polylactic acid nanospheres:
[0051] (1) Disperse 100 mg of cyclosporin A-loaded polylactic acid microspheres with an average particle size of 200 nm in 50 ml of distilled water to form a mixture E.
[0052] (2) 1 mg of the fluorescent dye rhodamine B was dissolved in 1 g of glycidyl methacrylate to form a mixed solution F.
[0053] (3) Under magnetic stirring, take 50 mg of the mixed solution F solution and add it to the mixed solution E.
[0054] (4) Heat up to 60 °C, add 0.25 mg of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate oxidation-reduction initiator (the mixing mass ratio of ammonium persulfate and sodium ascorbate is 2:3), stop stirring after 6 h, and obtain the drug-loaded fluorescent label Suspension of polylactic acid microspheres.
[0055] (5) Put the above suspension in a dialysis bag, and dialyze with distilled water for 48 hours to remove ungrafted Rhodamine B.
[0056] (6) Freeze-dry the susp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com