Polyester woven fabric anti-slippage finishing agent and preparation method thereof
A finishing agent and weaving technology, which is applied in the field of anti-slip finishing agent and preparation of polyester woven fabrics, can solve the problems of fabric tear strength reduction, loss of use value, easy to generate static electricity, etc., and achieve the reduction of movable space , prevent the fabric from slopping, and increase the effect of washing durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1. Add 200 grams of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 2000), 10.5 grams of neopentyl glycol, 60.5 grams of isophorone diisocyanate, 60 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone, and 0.08 grams of zinc isooctanoate into a condenser equipped with and the reactor of the stirring device, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 5 hours to make a prepolymer;
[0026] 2. Cool the prepolymer to 25°C, add 15 grams of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, and stir and react at 25°C for 50 minutes;
[0027] 3. Put the product obtained in step 2 into an emulsification device, add 600 grams of deionized water, and emulsify at 10°C to obtain a nonionic polyurethane resin emulsion;
[0028] 4. Add 94.6 grams of epoxy-modified silicone emulsion to the polyurethane resin emulsion obtained in step 3 and stir evenly to obtain the anti-slip finishing agent.
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1. Add 260 grams of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 2000), 14 grams of neopentyl glycol, 77 grams of isophorone diisocyanate, 50 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone, and 0.05 grams of zinc isooctanoate into a condenser equipped with And the reactor of the stirring device, stirred and reacted at 85°C for 5 hours to make a prepolymer;
[0031] 2. Cool the prepolymer to 30°C, add 18 grams of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, and stir and react at 30°C for 40 minutes;
[0032] 3. Put the product obtained in step 2 into an emulsification device, add 810 grams of deionized water, and emulsify it at 20°C to make a nonionic polyurethane resin emulsion;
[0033] 4. Add 184 grams of epoxy-modified silicone emulsion to the polyurethane resin emulsion obtained in step 3 and stir evenly to obtain the anti-slip finishing agent.
Embodiment 3
[0035] 1. Add 160 grams of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 2000), 5.6 grams of neopentyl glycol, 41.4 grams of isophorone diisocyanate, 30 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone, and 0.03 grams of zinc isooctanoate into a condenser equipped with And the reactor of the stirring device, stirred and reacted at 90°C for 5 hours to make a prepolymer;
[0036] 2. Cool the prepolymer to 30°C, add 8.5 grams of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, and stir and react at 30°C for 35 minutes;
[0037] 3. Put the product obtained in step 2 into an emulsification device, add 455 grams of deionized water, and emulsify it at 15°C to make a nonionic polyurethane resin emulsion;
[0038] 4. Add 50 grams of epoxy-modified silicone emulsion to the polyurethane resin emulsion obtained in step 3 and stir evenly to obtain the anti-slip finishing agent.
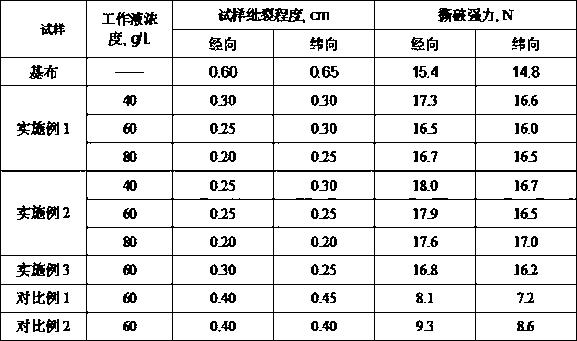
[0039] Product performance test:
[0040] The examples and comparative examples were formulated as working liquids as shown in the table below to pad the 19...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com