Preparation method of MgO-C castable
A castable and aggregate technology, applied in the field of refractory materials, can solve the problems of poor wettability, poor workability of castables, loose castable structure, etc., and achieve the effect of high strength, excellent thermal shock resistance and uniform structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Experiment number G1. Weigh the raw material components according to the following ratio:
[0027] Fused magnesia aggregate: 22 parts of 5~3mm aggregate, 17 parts of 3~1mm aggregate, 16 parts of 1~0.088mm aggregate; 32 parts of fused magnesia fine powder (<0.088mm); Granulated graphite with a carbon content of 30wt%: 10 parts; silica fume: 3 parts;
[0028] Additional additives: 1 part (of which Si: 0.5 part, SiC: 0.3 part, sodium hexametaphosphate: 0.1 part, sodium polyacrylate: 0.1 part).
[0029] After mixing the fused magnesia aggregate, fine powder, granulated graphite, silica fume and additives evenly, add water with a total weight of 4.7% of the raw materials and stir evenly to obtain a MgO-C castable with a carbon content of 3.0wt%. .
Embodiment 2
[0031] Experiment number G2. Weigh the raw material components according to the following ratio:
[0032] Fused magnesia aggregate: 14 parts of 5~3mm aggregate, 10 parts of 3~1mm aggregate, 13 parts of 1~0.088mm aggregate; 33 parts of fused magnesia fine powder (<0.088mm); Granulated graphite with a carbon content of 27.1wt%: 15 parts; silica fume: 5 parts;
[0033] Additional additives: 2 parts (of which Si: 1.2 parts, B4C: 0.5 parts, FS20: 0.1 parts, Tween-80: 0.1 parts, sodium polyacrylate: 0.1 parts).
[0034] After mixing the fused magnesia aggregate, fine powder, granulated graphite, silica fume and additives evenly, add water with a total weight of 4.9% of the raw materials and stir evenly to obtain a MgO-C castable with a carbon content of 4.0wt%. .
Embodiment 3
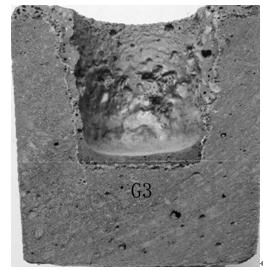
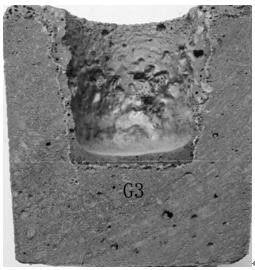
[0036] Experiment number G3. Weigh the raw material components according to the following ratio:
[0037] Fused magnesia aggregate: 19 parts of 5~3mm aggregate, 20 parts of 3~1mm aggregate, 12 parts of 1~0.088mm aggregate; 29 parts of fused magnesia fine powder (<0.088mm); Granulated graphite with a carbon content of 41.7wt%: 18 parts; silica fume: 2 parts;
[0038] Additional additives: 3 parts (of which SiC: 1 part, B4C: 1 part, FS20: 0.2 part, sodium tripolyphosphate: 0.1 part, N1055: 0.3 part, Tween-80: 0.4 part).
[0039] After mixing the fused magnesia aggregate, fine powder, granulated graphite, silica fume and additives evenly, add water with a total weight of 5.1% of the raw materials and stir evenly to obtain a MgO-C castable with a carbon content of 7.3wt%. .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com