Phyllostachys edulis violaxanthin deepoxidase (PeVDE) protein, and coding gene and applications thereof
A technology of cyclooxygenase and violaxanthin, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems that there is no bamboo violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene, and the molecular basis of bamboo xanthophyll cycle metabolism pathway is unclear, so as to reduce the Cost, effect of high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Acquisition of Phylloxanthin Decycloxygenase Gene PeVDE Sequence in Phyllostachys pubescens
[0028] RNA was extracted from young fresh leaves of Phyllostachys edulis, and reverse-transcribed into cDNA using Promega’s reverse transcription kit (Cat#A3500) as a template. Degenerate primers were designed based on the conserved sequence of the VDE family of enzyme genes, and the coding sequence was amplified by PCR.
[0029] Upstream primer: 5′-CC(A / T)GA(T / C)GA(A / G)AC(T / C / G)GA(A / G)TG(C / T)CA-3′(SEQ ID No.5),
[0030] Downstream primer: 5′-C(C / A)(A / G)CC(A / T)CCATA(T / G)CCATCCCA-3′(SEQ ID No.6)
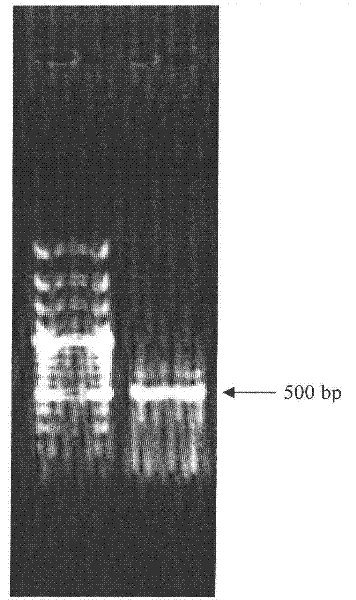
[0031] PCR amplification products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis, such as figure 1 shown. Cut out the target band for purification and recovery, connect the recovered DNA fragments to the pGEM-T easy vector, transform Escherichia coli (Esherichia coli) DH5α competent cells, and screen the positive clones with blue and white spots, extract positive clone plas...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Construction of a recombinant expression vector carrying the violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene of Phyllostachys pubescens
[0042] Using the cDNA of Phyllostachys pubescens as a template, primers were designed according to SEQ ID No.1, and the deoxyribonucleotide sequence of the mature protein encoded by the violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene of Phyllostachys pubescens was amplified by PCR. Nco I and Xho I restriction sites were introduced at both ends of the primers respectively, and the primer sequences are as follows:
[0043] Upstream: 5′-CATG CCATGG CCACCGATGCTCTCCAAGAC-3', introducing Nco I restriction site (SEQ ID No.11);
[0044] Downstream: 5′-CCG CTCGAG CCTTAGCTTCCTTATTGGC-3', introducing the Xho I restriction site (SEQ ID No. 12).
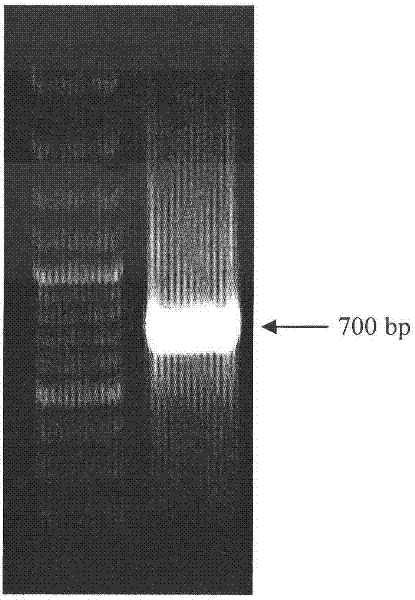
[0045] Perform agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the PCR amplification product, cut out the target band, purify and recover, connect the recovered DNA fragment to the pGEM-T easy vector, transform Escherichia ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Prokaryotic expression and protein purification of embodiment 3PeVDE gene
[0048] The recombinant expression vector pET-32b-PeVDE constructed in Example 2 was transformed into Escherichia coli Rosetta-gami B(DE3) competent cells, and a single colony grown on the Amp-resistant plate was picked for enzyme digestion identification and sequencing. Sequencing results showed that the monoclonal colony contained the target gene fragment, which could be used for the induced expression experiment of the protein.
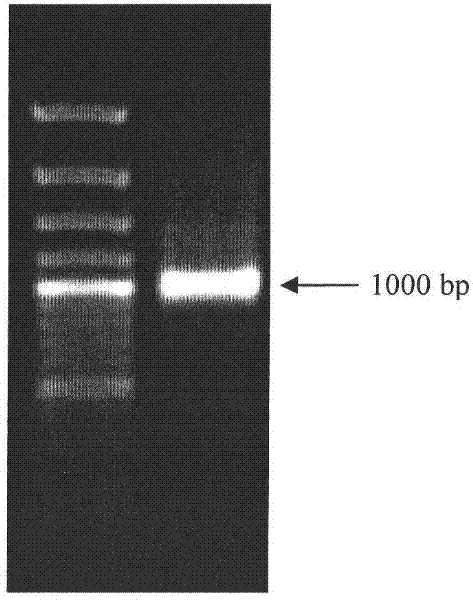
[0049] Correctly identified clones were cultured overnight, and the overnight cultured bacterial solution was added to ampicillin-containing (100 mg L) at a ratio of 1:100. -1 ) cultured in LB medium until OD 600 When the temperature is 0.6-0.8, add IPTG (final concentration 0.4mM), and culture at 20°C and 30°C respectively. Take 50ml of the induced bacterial solution, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10min, and collect the cells; add 3ml of Tris-EDTA solution and 10μL of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com