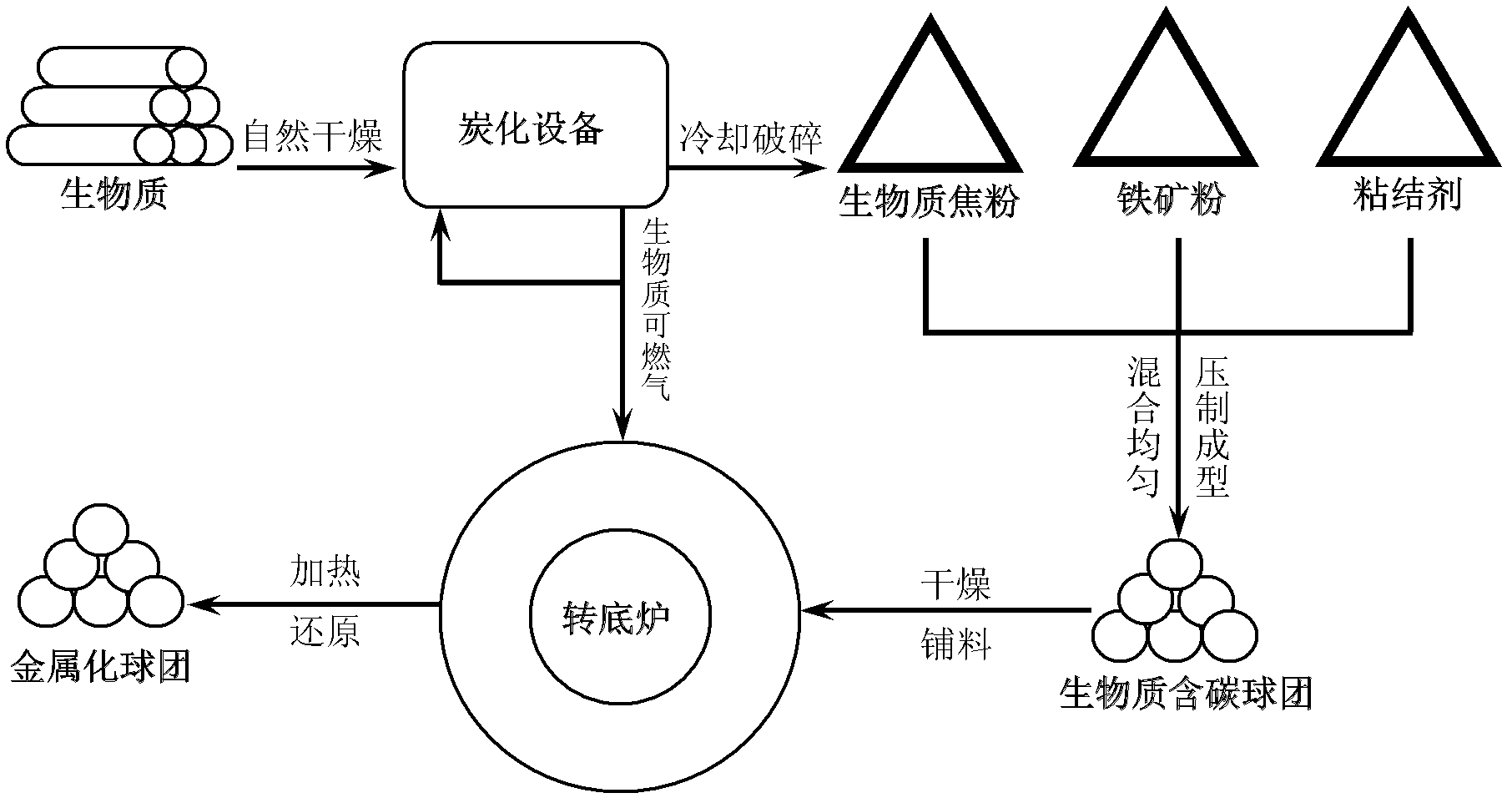
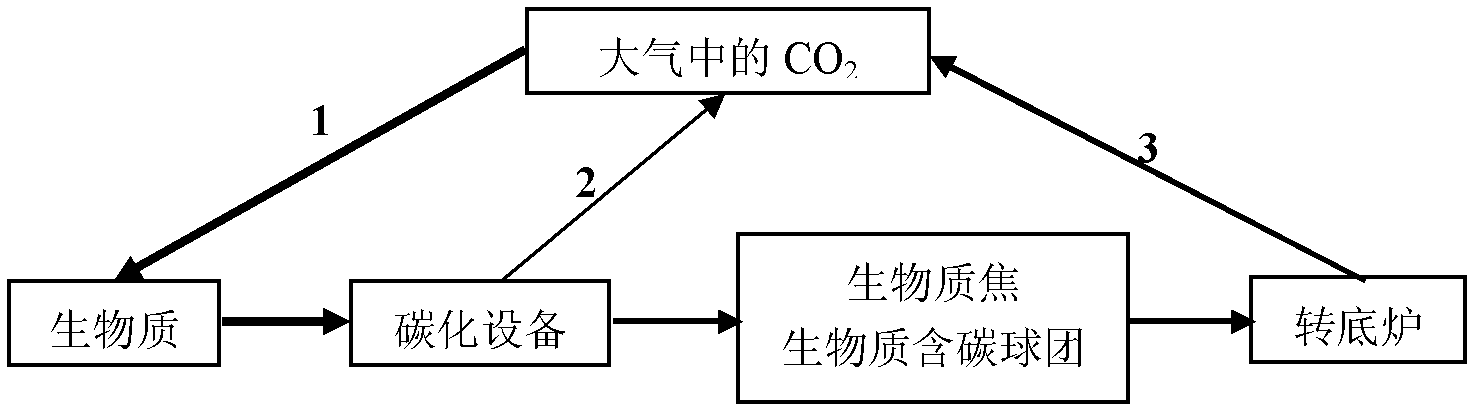
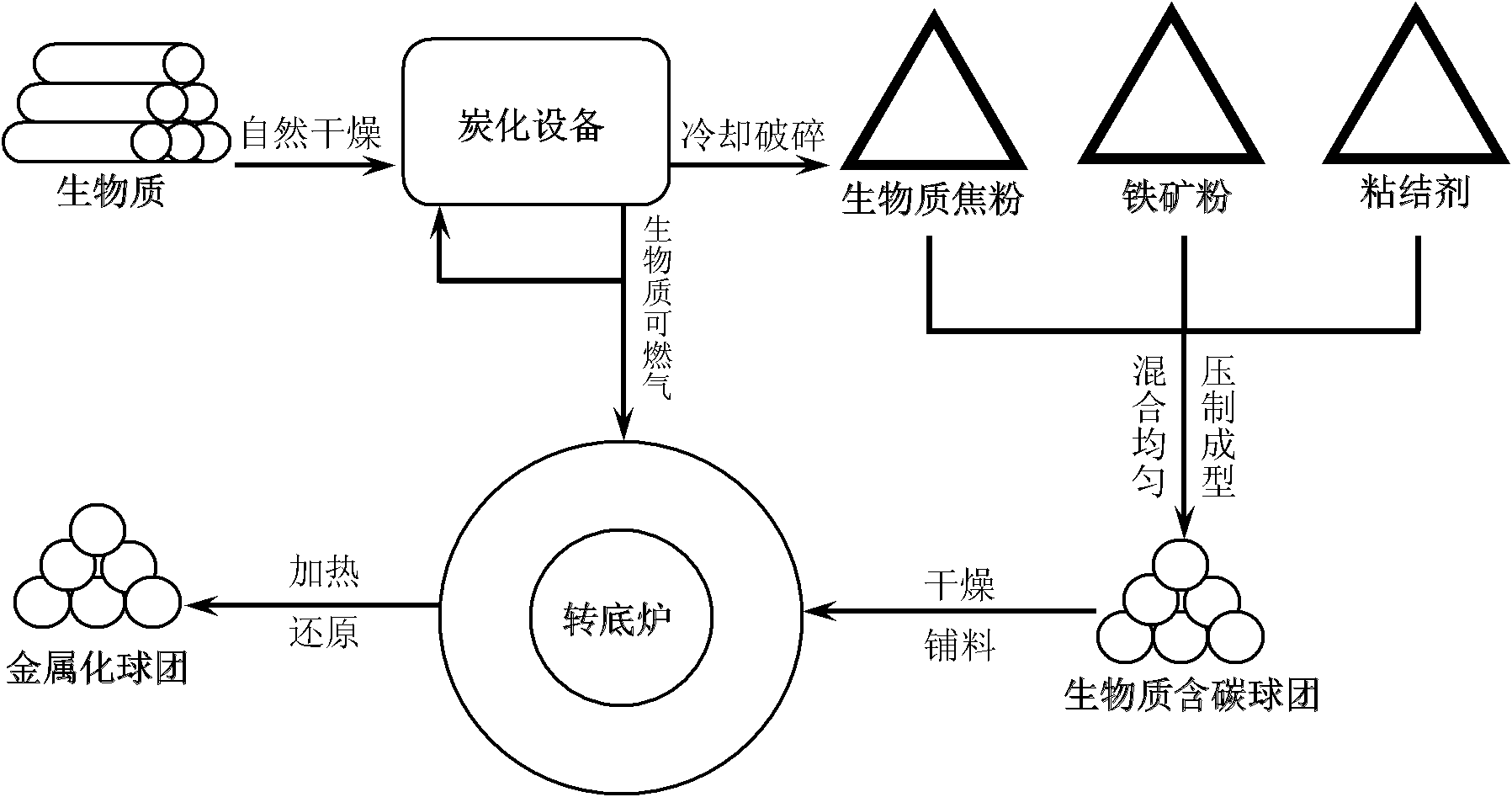
Rotary hearth furnace iron-making method utilizing biomass carbon-containing pellet to serve as raw material
A biomass raw material and biomass technology, applied in fluidized bed furnaces and other directions, can solve the problems of large consumption of fossil energy such as coal, low thermal efficiency and productivity of the process, and high sulfur content in products, so as to improve thermal efficiency, productivity, and thermal efficiency of the process. The effect of improvement and smelting efficiency improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The dried waste wood was carbonized in a carbonization furnace at 500°C for 40 minutes to obtain biomass coke (M=1.20%, A=0.75%, V=16.50%, FC=81.55%), which was crushed and sieved to less than 150 μm. According to C / O=1.15, mix a certain amount of magnetite powder with a grade of 65% and biomass coke powder, add 3% of bentonite binder and 6% of the total mass of water, and mix well to make carbon-containing spheres The pellets were dried and placed in a rotary hearth furnace for reduction. The reduction temperature was 1280°C and the reduction time was 25 minutes. Metallized pellets with a metallization rate of 80% and a sulfur content of 0.007% were obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0028] The dried waste wood was carbonized in a carbonization furnace at 600°C for 50 minutes to obtain biomass coke (M=0.80%, A=0.85%, V=12.50%, FC=85.85%), which was crushed and sieved to a size below 150 μm. Mix a certain amount of hematite powder with a grade of 60% and biomass coke powder according to C / O=1.25, add 2.5% of bentonite binder and 7% of the total mass of water, and mix well to make carbon-containing spheres The pellets were dried and placed in a rotary hearth furnace for reduction. The reduction temperature was 1350°C and the reduction time was 35 minutes. Metallized pellets with a metallization rate of 85% and a sulfur content of 0.009% were obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0030] The dried waste wood was carbonized in a carbonization furnace at 700°C for 30 minutes to obtain biomass coke (M=0.75%, A=0.95%, V=12.30%, FC=86.00%), which was crushed and sieved to a size below 150 μm. Mix a certain amount of 55% iron-containing powder with biomass coke powder according to C / O=1.20, add 3.5% bentonite binder and 6.5% water in total mass, and mix well to make carbon-containing spheres The pellets were dried and placed in a rotary hearth furnace for reduction. The reduction temperature was 1300°C and the reduction time was 30 minutes. Metallized pellets with a metallization rate of 82% and a sulfur content of 0.008% were obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com