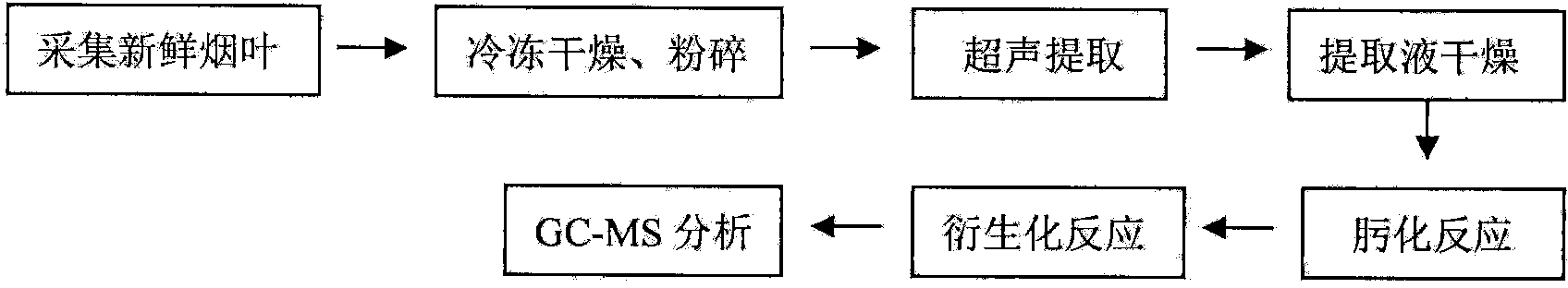
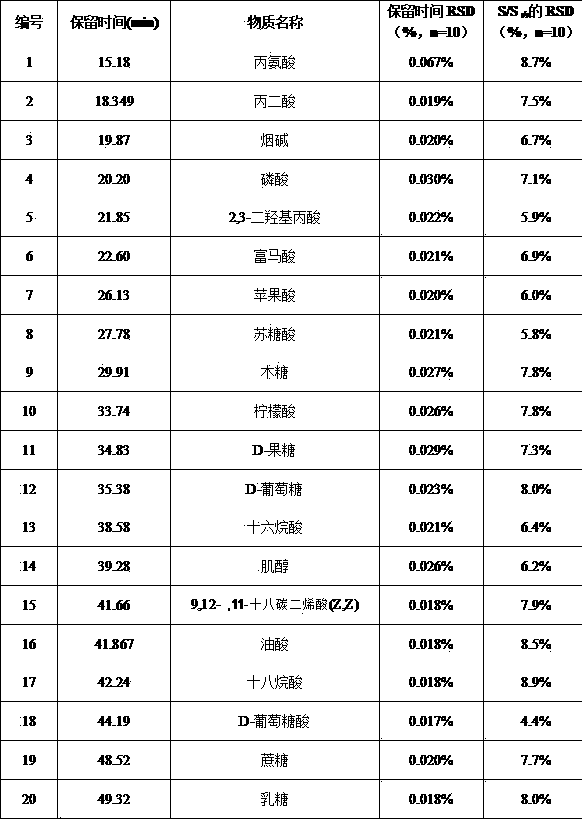
Method for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves by using derivatization GC-MS
A secondary metabolite, GC-MS technology, applied in the field of derivatized GC-MS for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Collect 6 fresh tobacco leaves (safflower Dajinyuan variety) from the laboratory in the long-lived tobacco plant, quickly remove the main stem and wrap it with tin foil, and freeze it with liquid nitrogen. Take out the tin foil package from the liquid nitrogen, pat it lightly, and immediately freeze it in a freeze dryer for 24 hours to remove the water, and grind it to 40-60 mesh. Weigh 10mg of tobacco powder into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add 200μl deuterated hexadecanoic acid internal standard solution, 1.0ml of 5:2:2 methanol-water-chloroform solution, ultrasonic extraction for 30min, centrifuge at 10000r / min for 10min, Take 200μl of supernatant and place it in another 1.5ml centrifuge tube and blow dry with a nitrogen blower at 40°C. Add 30μl of methoxyamine hydrochloride solution (in pyridine) with a concentration of 20mg / ml, rotate and shake for 1min and keep in a 37℃ water bath for 90min, then add 30μl of TFMSA, rotate and shake for 1min, then place in a 37℃ water ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Method recovery evaluation: Three mature tobacco leaves of nc297 were collected in Zunyi, Guizhou, the main stems were quickly removed, wrapped in tin foil, and quickly frozen with liquid nitrogen. Take the tin foil package out of liquid nitrogen, bury it in dry ice, air express it to the laboratory, and place it in a -80 degree refrigerator. Take out the tin foil package from the refrigerator, pat it lightly, and immediately freeze it in a freeze dryer for 24 hours to remove the water, and grind it to 40-60 mesh. Weigh 20mg of tobacco powder into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add 200μl of deuterated hexadecanoic acid internal standard solution, 1.0ml of 5:2:2 methanol-water-chloroform solution, 100μl of mixed standard solution (addition to each standard Concentrations are 20μg / ml, 100μg / ml, 200μg / ml in three levels, see Table 2), ultrasonic extraction for 30min, centrifugation at 10000r / min for 10min, transfer 0.4ml of supernatant to a 5ml centrifuge tube, at 40℃ Blow dry w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com