Magnetic suspension planar motor with superconductor excitation structure
A planar motor and superconductor technology, applied in superconducting magnets/coils, magnetic circuits, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization efficiency of windings, large plane movement range, low system efficiency, etc., and achieve small thermal deformation and large suspension height , good dynamic characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
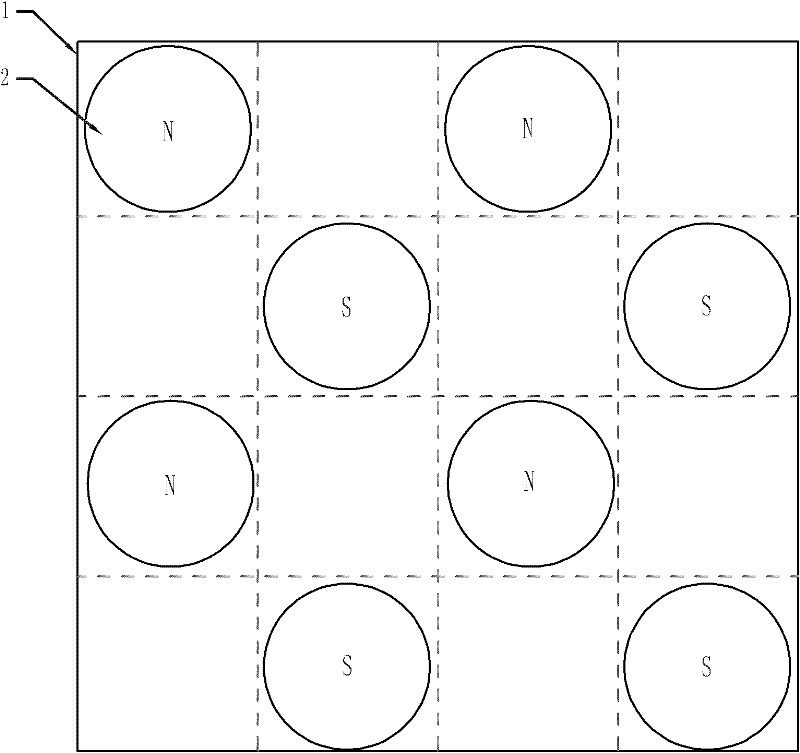
[0019] Embodiment 1: The magnetic levitation planar motor with superconductor excitation structure described in this embodiment includes a primary and a secondary, an air gap exists between the primary and the secondary, the primary includes a primary substrate and an armature winding, and the primary substrate is flat , the armature winding is fixed on the air-gap side of the primary substrate; the secondary consists of the secondary substrate 1, cooling container and 2h 2 A superconducting magnet 2, the secondary substrate 1 is evenly divided into 2h×2h magnet cells, where h is a natural number, and the side length of the magnet cell is the magnet array pole pitch τ p , the 2h 2 Two superconducting magnets 2 are respectively fixed in the diagonally adjacent superconducting magnet 2 unit cells on the secondary substrate 1, and the superconducting magnets 2 are not adjacent to each other in parallel and vertically, and the superconducting magnets 2 are parallel Magnetization,...
Embodiment approach 2
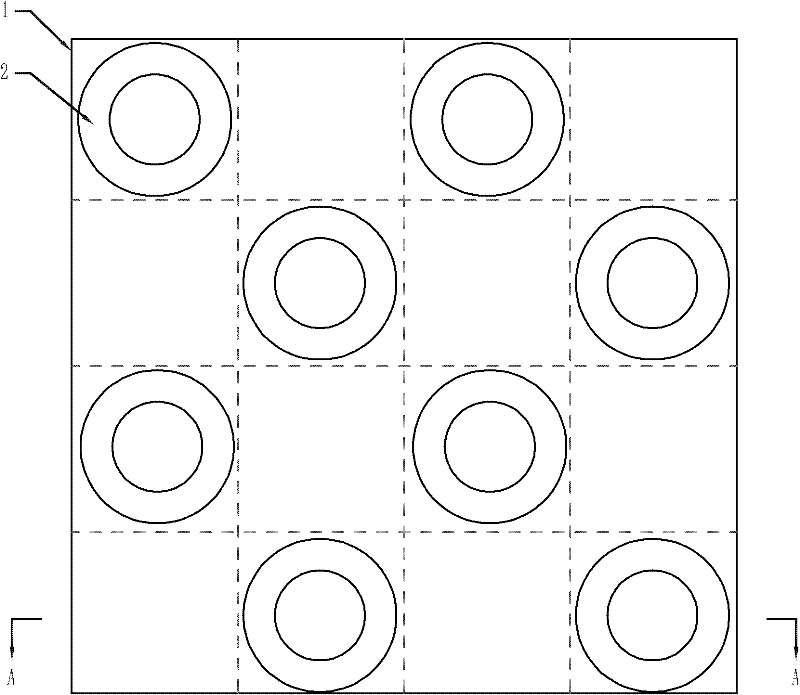
[0021] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the maglev planar motor with superconducting excitation structure described in Embodiment 1 is that the superconducting magnet 2 is realized by a superconducting block, and the superconducting block is disc-shaped or ring-shaped.
[0022] see figure 1 Shown is the structure of a magnetic levitation planar motor with a superconducting excitation structure described in this embodiment. In this structure, h=2, the secondary substrate is divided into 4×4 cells, and there are 8 superconducting magnets in the secondary 2 , the distribution of the 8 supermagnets 2 see figure 1 shown.
[0023] figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of the above structure when the superconducting block is in the form of a ring.
Embodiment approach 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the magnetic levitation planar motor with superconducting excitation structure described in Embodiment 1 is that the superconducting magnet 2 is realized by superconducting blocks, and the superconducting blocks are in the shape of a truncated cone, and the diameter of the circular truss is relatively small. The large base is fixedly connected to the secondary substrate.
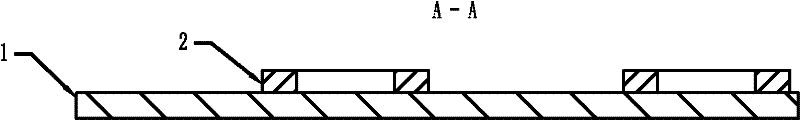
[0025] see figure 2 and 4 Shown is the structure of a magnetic levitation planar motor with a superconducting excitation structure described in this embodiment. In this structure, h=2, the secondary substrate 1 is divided into 4×4 cells, and there are 8 superconducting magnets in the secondary 2. For the distribution of the 8 super-body magnets 2, see figure 1 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com