Vegetable antiseptic treatment method
A technology for anti-corrosion treatment and vegetables, which is applied in the direction of preservation of fruits and vegetables, preservation of fruits/vegetables with acid, preservation of fruits/vegetables by dehydration, etc., and can solve the problems of vegetable rot, inactivation, and taste deterioration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
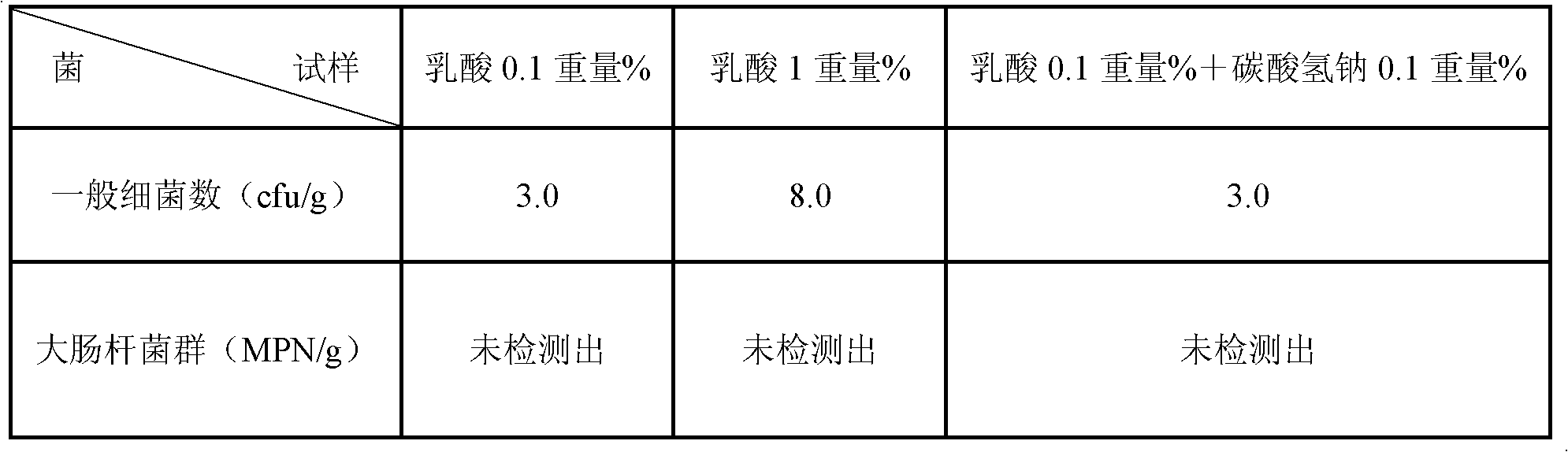
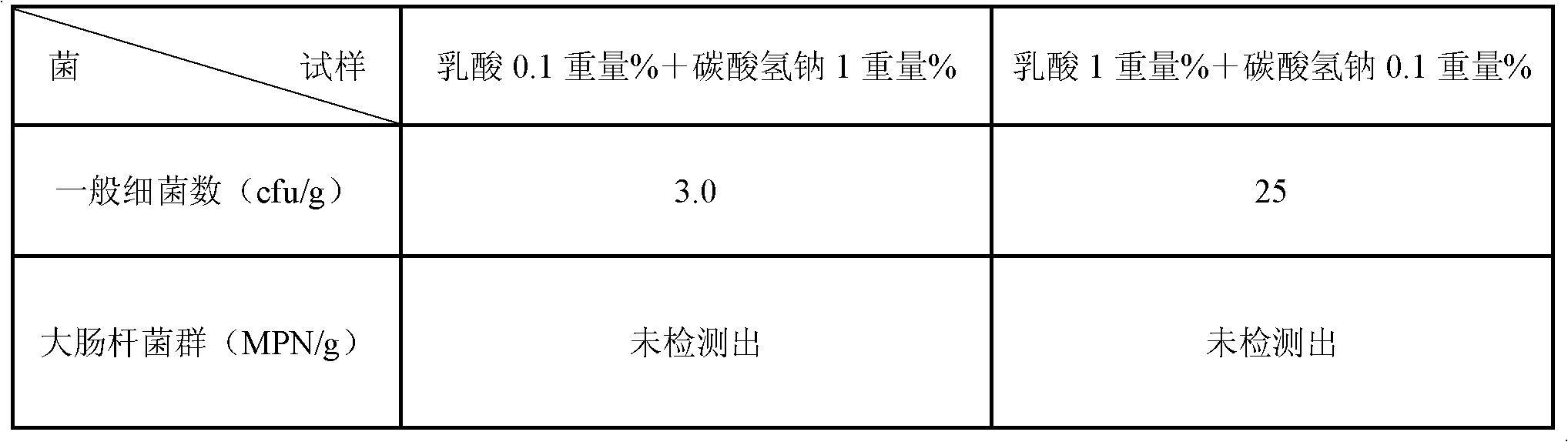
[0036] Here, the vegetable was chosen garlic. After buying raw garlic from Akita prefecture and selling it on the market, if it is left as it is, the surface of the garlic is usually 10 3 The spoilage bacteria adhered to about 1 / g immediately multiplies, and usually rots inside.
[0037] As the anticorrosion treatment process of the present invention, three kinds of aqueous solutions of 0.1% by weight lactic acid aqueous solution, 1% by weight lactic acid aqueous solution and 0.1% by weight lactic acid+0.1% by weight sodium bicarbonate (sodium bicarbonate) aqueous solution were prepared, for each 10 kg of each aqueous solution, 5 kg of raw garlic were respectively immersed therein.
[0038] The temperature of the immersion liquid was 25 degreeC, and the immersion process was performed for 15 minutes. In the present invention, it is preferable that the temperature of the immersion liquid is in the range of 20° C. to 35° C., and the immersion time is in the range of 10 minutes...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Prepare the same dipping solution as above, and dip each 5 kg of onions, carrots, taro, kidney bean pods (sheath ingen beans), komatsuna, broccoli, and shiitake mushrooms into 10 kg of each aqueous solution.
[0049] The temperature of the immersion solution was set at 25° C., and the immersion treatment was performed for 15 minutes.
[0050] The temperature of this immersion liquid is made into the range of 20 degreeC - 35 degreeC, and the immersion time is made into the range of 10 minutes - 20 minutes. However, for komatsuna, bean pods, broccoli, and shiitake mushrooms, the temperature of the dipping solution is below 30°C.
[0051] After the immersion treatment, samples were taken out from each immersion liquid, and dehydration treatment was performed for 5 minutes with a centrifugal separator.
[0052] Thereafter, the anticorrosion-treated sample was dried in a drying room kept at room temperature at 30° C., and dried by blowing air at room temperature until the sur...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A test was conducted on garlic that had been deodorized according to the deodorization treatment described in JP-A-6-311857.
[0056] The odorless garlic treatment of the samples generally went through the following procedures.
[0057] Water was put into the autoclave to boil the water, raw garlic was put therein and covered, and steaming was performed for 2 minutes after confirming that the temperature reached 120° C. at 1 atmosphere. The garlic is taken out from the autoclave, and dried by blasting at a low temperature below 35°C. This is not so much the deodorization of garlic, but rather steaming the garlic, and the processed garlic does not have a bad smell or a sharp taste even if you eat it.
[0058] The known deodorized garlic has decomposed components having a bactericidal effect contained in the garlic, so the bactericidal ability is reduced, and if it is stored or left as it is, a large amount of spoilage bacteria will adhere. When the moisture and tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com