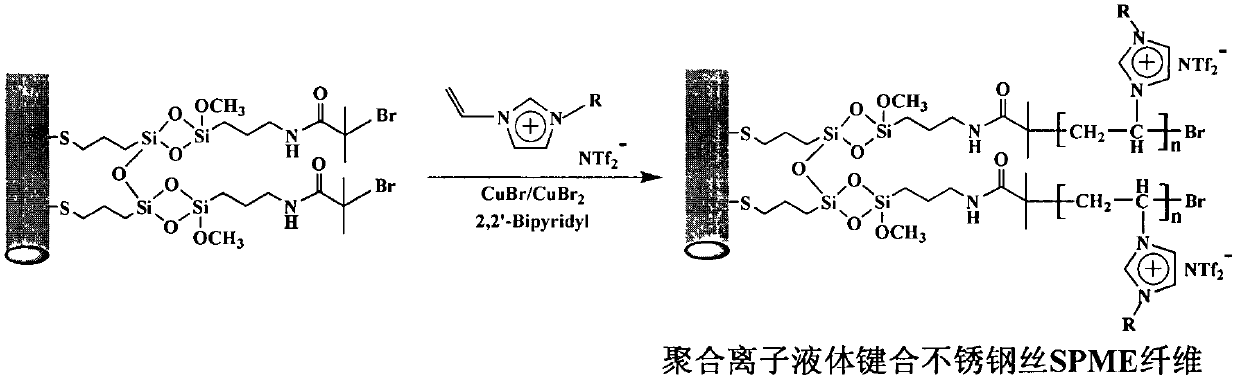
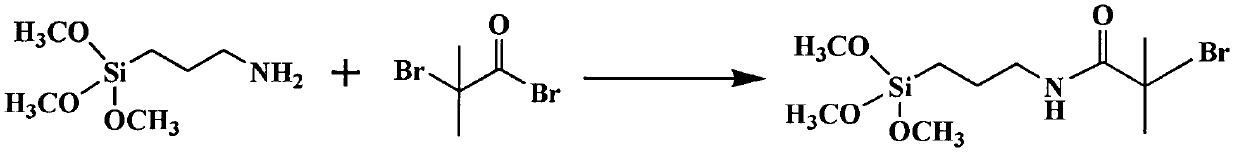Preparation method of solid-phase microextraction fibers by bonding metal wire with polyion liquid
A polyionic liquid and metal-bonding technology, applied in the field of solid-phase micro-extraction fibers, can solve the problems of easily broken quartz carrier, no chemical bonding, low sensitivity, etc., to control the repeatability of preparation, expand the scope of application, and improve the mechanical strength. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Preparation of polyionic liquid-bonded stainless steel wire solid-phase microextraction fibers
[0028] It includes the following three steps A, B, and C in turn:
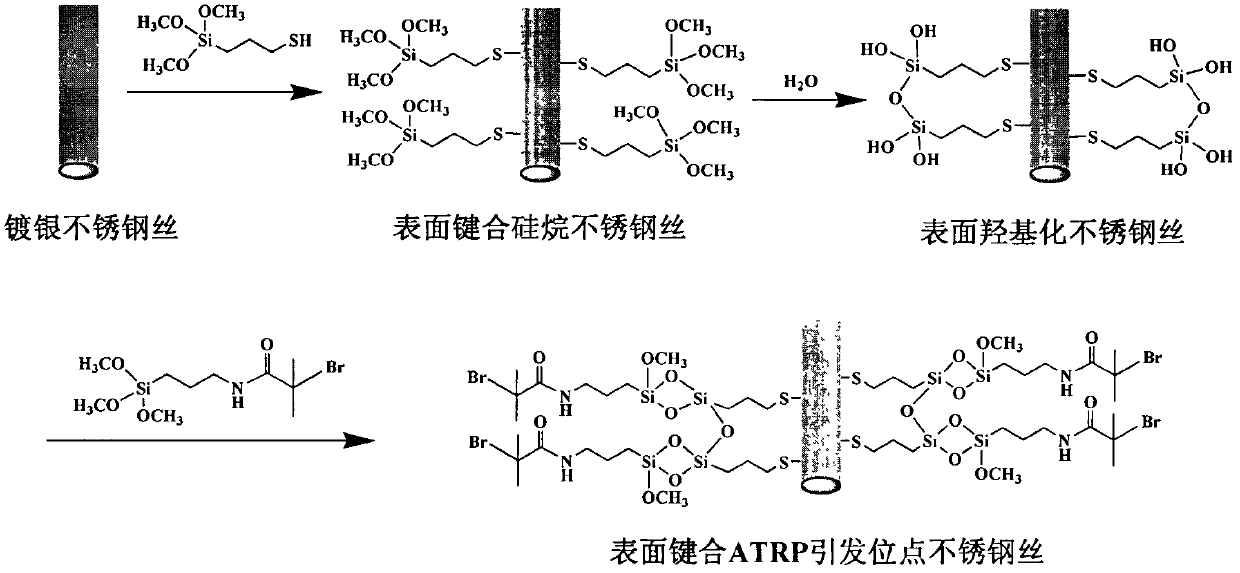
[0029] A. Electroless silver plating on the surface of stainless steel wire
[0030] After polishing the surface of the stainless steel wire with fine sandpaper, wash it with water and ethanol in turn to remove impurities on the surface and increase the surface area. The treated stainless steel wire is put into a mixed solution of silver ammonia solution and glucose solution, the molar ratio of silver ammonia ion and glucose is 1:0.5, the mass concentration of glucose is 30%, and the reaction is carried out at room temperature for 2 hours.
[0031] B. Bonding of Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Initiation Sites
[0032] Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane and 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide with a ratio of 1:1 were reacted at 0 ° C for 2 hours to obtain an atom transfer radical polymerization initiator (s...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Preparation of polyionic liquid-bonded titanium silk solid-phase microextraction fibers
[0036] It includes the following three steps A, B, and C in turn:
[0037] A. Electroless silver plating on the surface of titanium wire
[0038] After polishing the surface of the titanium wire with fine sandpaper, wash it with water and ethanol in turn to remove impurities on the surface and increase the surface area. The treated titanium wire is put into a mixed solution of silver ammonia solution and glucose solution, the molar ratio of silver ammonia ion and glucose is 1:3, the mass concentration of glucose is 5%, and the reaction is carried out at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0039] B. Bonding of Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Initiation Sites
[0040]Atom transfer radical polymerization initiator was prepared by reacting aminopropyltrimethoxysilane and 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide in a ratio of 1:1 at 0°C for 12 hours. The silver-plated stainless steel wir...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Preparation of polyionic liquid-bonded nickel wire solid-phase microextraction fibers
[0044] It includes the following three steps A, B, and C in turn:
[0045] A. Electroless silver plating on the surface of nickel wire
[0046] After polishing the surface of the nickel wire with fine sandpaper, wash it with water and ethanol in turn to remove impurities on the surface and increase the surface area. The treated nickel wire is put into a mixed solution of silver ammonia solution and glucose solution, the molar ratio of silver ammonia ion and glucose is 1:2, the mass concentration of glucose is 15%, and the reaction is carried out at room temperature for 0.5 hour.
[0047] B. Bonding of Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Initiation Sites
[0048] Atom transfer radical polymerization initiator was prepared by reacting aminopropyltrimethoxysilane with 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide in a ratio of 1:1 at 0°C for 6 hours. The silver-plated stainless steel wire wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com