Method of using plain soil to produce hydraulic engineering seepage-proofing brick in situ
A water conservancy project and plain soil technology, applied in sustainable waste treatment, solid waste management, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as compressive strength, poor shear resistance, increased handling costs, and large cement requirements , to achieve the effect of improving compressive strength and shear strength, high compactness and reducing gaps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
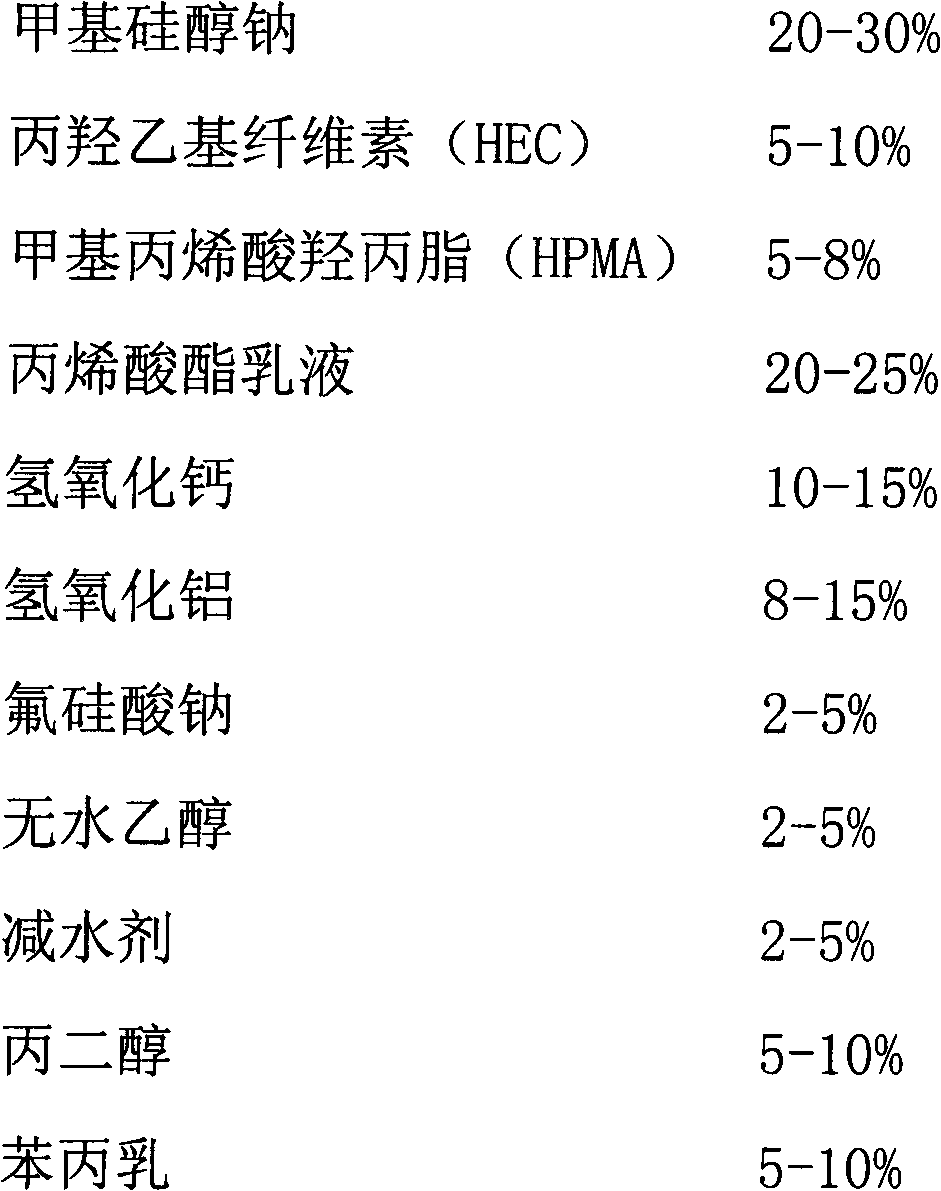
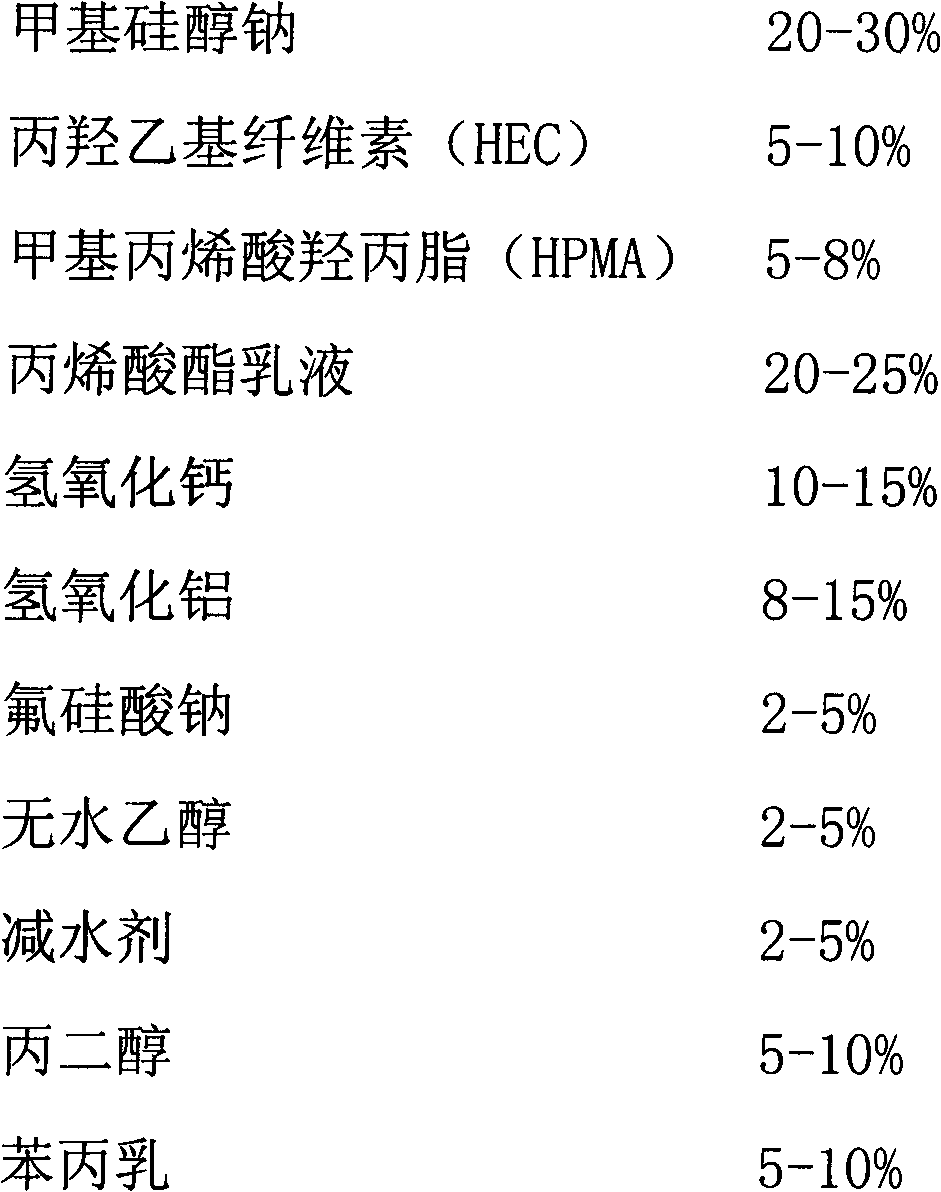
[0029] Take each material in proportion: 0.02 parts by weight of coagulant, 0.2 parts by weight of glass fiber chopped shreds (biological straw), 75 parts by weight of soil, 5 parts by weight of cement, 10 parts by weight of gravel (weathered soil), and 9 parts by weight of water ; Stirring: Stir the coagulant diluent in the mixture for 3-5 minutes, and then input it into the pressing mold after discharging; pressing and forming, the surface of the formed brick should be slightly wet; demoulding, and transport it to the health preservation area with a robot; curing: temperature 20°C , moisturizing for 10 days, maintaining humidity <75%, natural health preservation, and finished products. The strength test is above 10PMa, and the waterproof test is airtight.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com