Electroluminescence device
A technology of electroluminescent devices and light-emitting layers, which is applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing device life, increasing device temperature, and restricting blue light emission, so as to improve energy utilization and luminescence Efficiency enhancement, the effect of improving luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
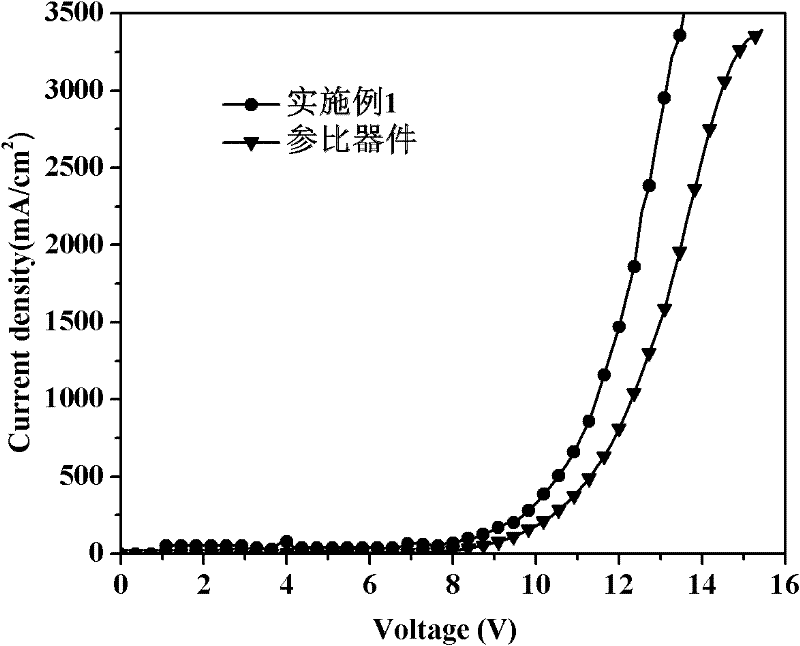
Embodiment 1
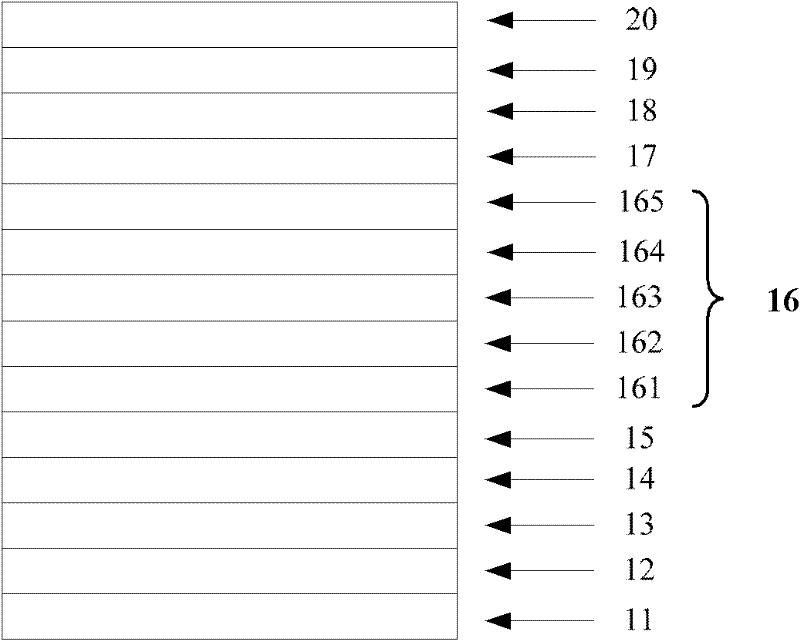
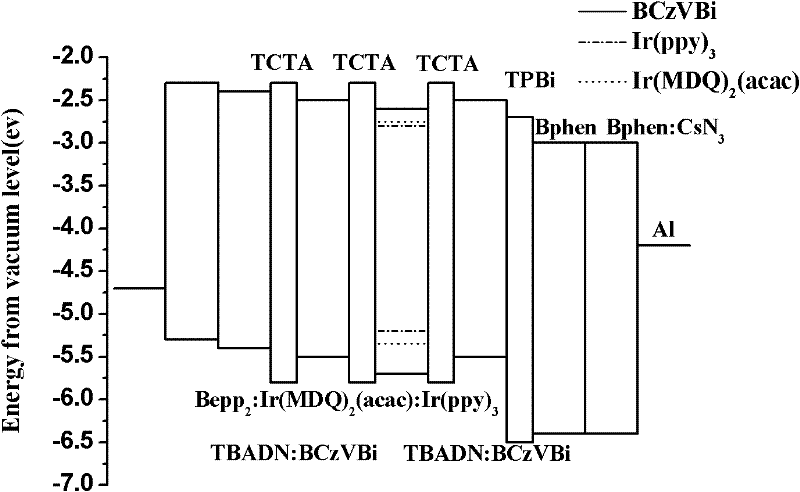
[0035] An electroluminescent device, its structure is: glass / ITO / MoO 3 / NPB / TCTA / TBADN:BCzVBi / TCTA / Bepp 2 :Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac):Ir(ppy) 3 / TCTA / TBADN:BCzVBi / TPBi / Bphen / Bphen:CsN 3 / Al.
[0036] Regarding the electroluminescent device in this example, according to its structure, and using evaporation technology, each organic functional layer is prepared by evaporation in turn; wherein, in the composite structure of the light-emitting layer: the blue light of the first and second blue light-emitting layers The material is BCzVBi, the host material, that is, the hole transport material is TBADN, the doping ratio of the blue light material is 10%, and the thickness is 10nm; the first quantum well material is TCTA, and the thickness is 2nm; in the red-green phosphorescent emitting layer, The red light material is Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac), the doping ratio of the red light material is 1%, and the green light material is Ir(ppy) 3 , the doping ratio of the green light material is 7%, the t...
Embodiment 2
[0044] An electroluminescent device, its structure is: glass / ITO / WO 3 / TPD / TCTA / TPD:BCzVB / TPD / BeBq 2 :Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac):Ir(ppy) 3 / TPD / TPD:BCzVB / TAZ / TPBI / Cs 2 CO 3 / Al.
[0045] Regarding the electroluminescent device in this example, according to its structure, and using evaporation technology, each organic functional layer is prepared by evaporation in turn; wherein, in the composite structure of the light-emitting layer: the blue light of the first and second blue light-emitting layers The material is BCzVB, the host material, that is, the hole transport material is TPD, the doping ratio of the blue light material is 5%, and the thickness is 10nm; the first quantum well material is TPD, and the thickness is 2nm; in the red-green phosphorescence emitting layer, The red light material is Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac), the doping ratio of the red light material is 0.5%, and the green light material is Ir(ppy) 3 , the doping ratio of the green light material is 7%, the thickness of th...
Embodiment 3
[0047] An electroluminescent device, its structure is: glass / ITO / VO x / TDAPB / NPB / TCTA:TBPe / NPB / BeMQ 2 :Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac):Ir(ppy) 3 / TDAPB / TCTA:TBPe / BND / TPQ / LiF / Al.
[0048] Regarding the electroluminescent device in this example, according to its structure, and using evaporation technology, each organic functional layer is prepared by evaporation in turn; wherein, in the composite structure of the light-emitting layer: the blue light of the first and second blue light-emitting layers The material is TBPe, the host material, that is, the hole transport material is TCTA, the doping ratio of the blue light material is 20%, and the thickness is 10nm; the first quantum well material is NPB, and the thickness is 2nm; in the red-green phosphorescence emitting layer, The red light material is Ir(MDQ) 2 (acac), the doping ratio of the red light material is 5%, and the green light material is Ir(ppy) 3 , the doping ratio of the green light material is 10%, the thickness of the red...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com