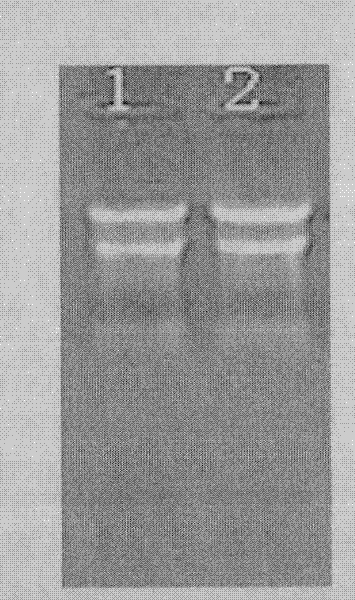Ultrafast detection method for nucleic acid
A detection method, ultra-fast technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of detection limitations of sudden infectious diseases, difficult to repeat results, complicated amplification process, etc., to achieve valuable treatment time and response The effect of shortening the time and improving the detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Ultra-rapid quantitative detection of hsa-miR-29a miRNA in human blood
[0016] 1. Total RNA extraction
[0017] (1) Sample treatment: Take 100 μL ~ 500 μL blood sample, add 1 mL TRIzol reagent, and mix repeatedly;
[0018] (2) RNA isolation: place the above sample solution at room temperature for 10 minutes, add 200 μL of chloroform, shake vigorously for about 1 minute, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 12,000 g at 4°C for 15 minutes, carefully take out the sample, and observe that the sample is divided into three layers. The top layer contains RNA components;
[0019] (3) RNA precipitation: Carefully pipette about 450 μL of the supernatant into a new centrifuge tube containing 600 μL of ice-cold isopropanol, mix well, and centrifuge at 12,000 g at 4°C for 10 minutes;
[0020] (4) RNA washing: remove the supernatant, add 500 μL of frozen 75% ethanol, bounce the precipitate, centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com