Method for detecting multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis, and related primer and liquid-phase chip thereof
A technology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and multi-drug resistance, applied in the field of medicine and biology, can solve the problems of ineffective high-throughput detection, unfavorable combination of PCR products and probes, and ineffective high-throughput detection. The effect of short time, strong sensitivity and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Embodiment 1 detects the liquid phase chip of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including
[0057] 1. Specific primers with tag sequences
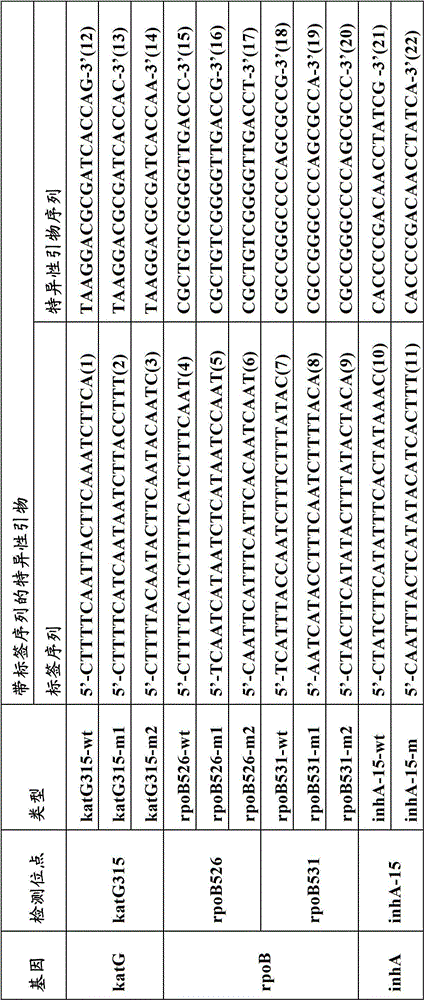
[0058] Specific primer sequences were designed for katG531, rpoB526, rpoB531, and inhA-15 associated with multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The specific primer with tag sequence consists of "tag sequence + specific primer sequence". The specific primer sequences with tag sequences are shown in the table below:
[0059] Table 1 Specific primer sequence with tag sequence (tag sequence + specific primer sequence)
[0060]
[0061] The numbers in brackets represent SEQ ID NO.; wt represents wild type; m represents mutant type; m1 represents mutant type I; m2 represents mutant type II.
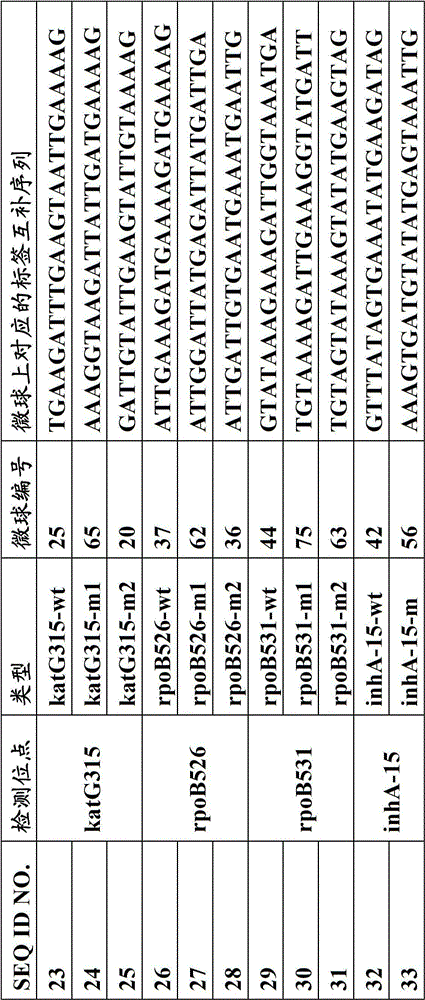
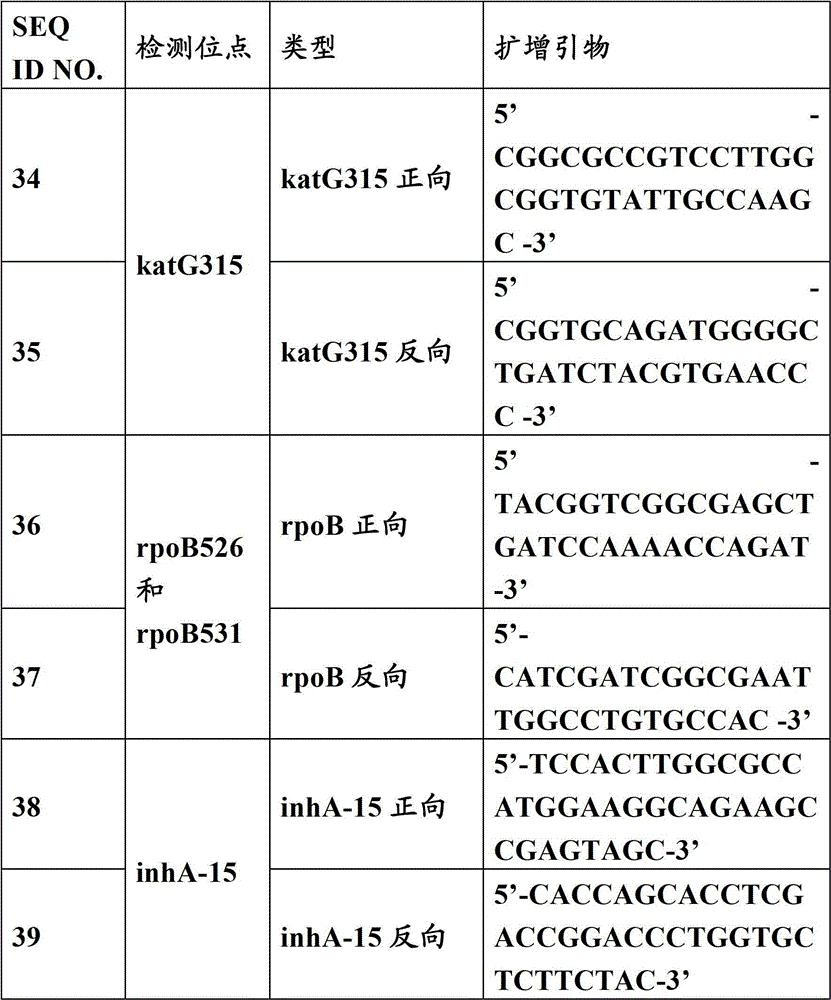
[0062] Each specific primer with a tag sequence includes two parts, the 5' end is a specific tag sequence for the complementary sequence of the tag on the relative microsphere, and the 3' end is a mutant or wild-type spe...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Embodiment 3: Simultaneous detection of said 4 sites and the comparison of detecting said 4 sites respectively
[0145] As in the above experimental procedure, 10 drug-resistant samples were tested for 4 sites, and compared with the results of simultaneous detection of the 4 sites in a reaction system in Example 2. The test results are compared in Table 8 below. The results in Table 8 show that there is no significant difference in the experimental results whether the four sites are detected in a single reaction or in a reaction system.
[0146] Table 8: The results of simultaneous detection of 4 loci in 10 drug-resistant samples (sample numbers 1-10) and the results of detection of 4 loci separately (sample numbers 1A-10A).
[0147]
Embodiment 4
[0148] Example 4: Comparison of the results of simultaneous detection of 5 sites and simultaneous detection of 4 sites
[0149] In order to verify the impact of adding sites on the sensitivity of detection and whether adding sites is necessary, add sites inhA-8, wild-type T, and mutant G. For samples 1-20, the results of simultaneous detection of 5 sites and simultaneous detection of 4 sites were compared.
[0150] The experimental procedure is as above, but adding inhA-8 wild-type (inhA-8-wt) microsphere code No.42; inhA-8 mutant (inhA-8-m) microsphere code No.63. inhA-8-wt primers: tag sequence: CACTACACATTTATCATAACAAAT; specific primer sequence: TGGCAGTCACCCCGACAA. inhA-8-m primer: tag sequence: CTAAATCACATACTTAACAACAAA; specific primer sequence: TGGCAGTCACCCCGACAC. The results are shown in Table 9 below. From the comparison of the two sets of data in Table 9, it can be seen that when a new detection site is added, it will interfere with the detection of other sites, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com