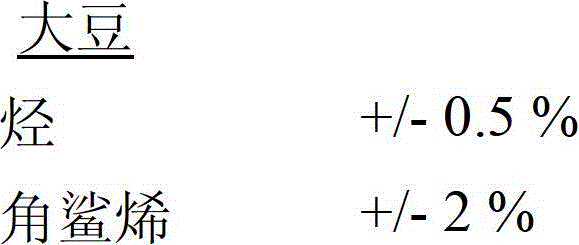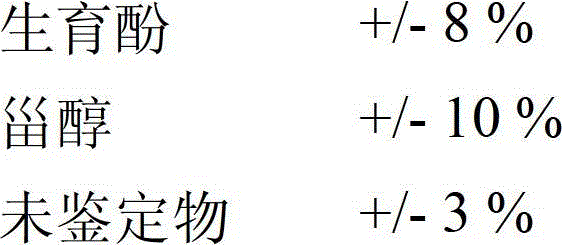Liquid/Liquid Extraction
An extraction, solvent technology, applied in some or all of the fields, that can solve problems such as unacceptable phase separation, negative environmental impact, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
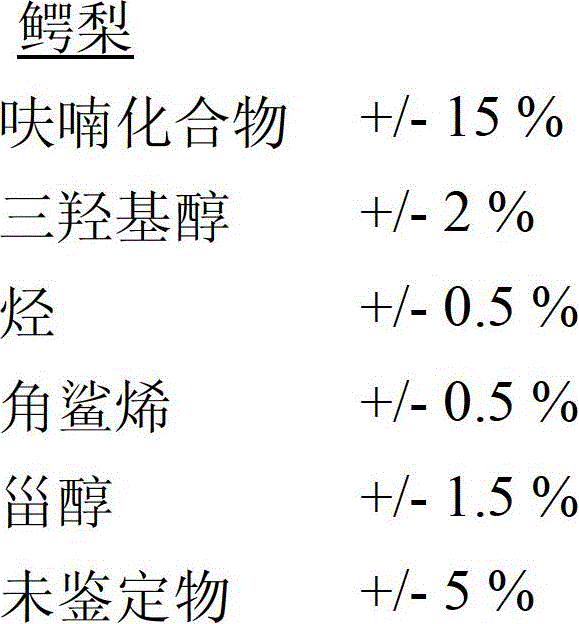
[0114] Example 1: Using DCE to extract avocado unsaponifiables (reference 1)
[0115] The first step consists of the saponification of the concentrate prepared by molecular distillation of avocado oil.
[0116] To this end, a given weight of avocado oil concentrate (45.6 g) was added successively to a 100 ml round bottom flask equipped with a condenser, followed by ethanol (36.6 g), 50% plant ash (5.2 g) and a few pumice stones particles.
[0117] The system was then refluxed for a total of 3.5 hours and, after cooling, diluted with demineralised water (60ml).
[0118] After saponification, a hydro-alcoholic solution is obtained which contains unsaponifiables (or unsaponifiable fractions). The unsaponifiables are then extracted using a first solvent system, specifically DCE.
[0119] Several consecutive extractions (5 x 70 ml) were performed; the collected organic phases were then combined and washed with tap water (5 x 70 ml) until neutral (phenolphthalein test).
[012...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Embodiment 2: Using HMDS to extract avocado unsaponifiables
[0123] Extraction was carried out according to the procedure of Example 1. After optimization to adapt it to the new solvent system, the extraction process consisted of an extraction step with 4 x 70 ml of HDMS (instead of DCE) and a step involving washing the organic phase with 3 x 70 ml of water. Measurements were carried out as in Example 1 and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3: Using HMDS-MeTHF mixture (90 / 10, by volume) to extract avocado unsaponifiables
[0125] Extraction was carried out according to the procedure of Example 1. After optimization to adapt it to the new solvent system, the extraction procedure consisted of extraction steps using 4 x 70 ml of HDMS-MeTHF mixture (90 / 10 by volume) (instead of DCE) and contained 2 x 70 ml The step composition of washing the organic phase with water. Measurements were carried out as in Example 1 and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com