Low-cost efficient solar cell electrode grid line structure
A technology for solar cells and electrode grid lines, applied in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of rising paste costs, increased grid line shielding area, high square resistance and low contact resistance, etc., and achieve silver paste consumption Reduce, improve conversion efficiency, reduce the effect of contact surface recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] For 156x156 size polysilicon cells, the design of electrode grid line structure is as follows (such as Figure 3-4 shown):
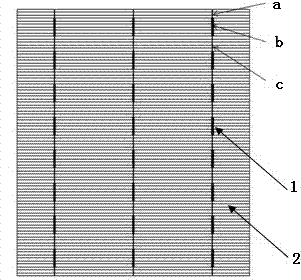
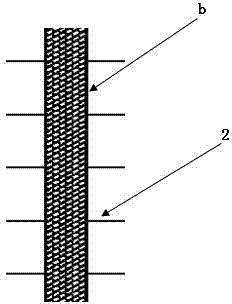
[0020] 1) The number of busbar lines is 3, which are distributed symmetrically around the center of the silicon wafer. The distance between the three busbar lines is 52mm; the busbar lines are divided into 8 sections, which are connected alternately with thin lines. The width of the busbar is 1.4mm and the length is 10mm; the width of the thin line part a at both ends of the busbar is 0.3mm and the length is 5mm; the width of the thin line part c connecting each segment in the middle of the busbar is 0.3mm and the length is 9mm; Segment b adopts a rectangular hollow design, distributed in an array, with a pitch of 0.1mm and an offset angle of 30°.
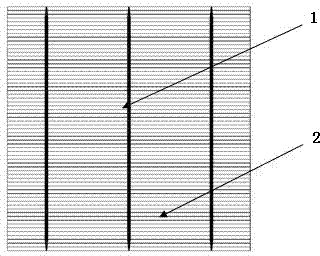
[0021] 2) Thin grid lines 2 are distributed in parallel with equal distances perpendicular to the main grid lines, the number of thin grid lines is 90, the width of the thin grid lines is 0.05mm, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] For a 125x125 size monocrystalline silicon cell, the electrode grid structure is designed as follows:
[0024] 1) The number of main grid lines is 2, which are distributed symmetrically around the center of the silicon wafer. The main grid lines are divided into 6 sections, which are connected alternately with thin lines. The length of the two main grid line segments on both sides is 13.4 mm, the length of the segmented part of the central busbar line is 8mm, the width of the segmented part of the busbar line is 1.4mm, the width of the thin lines at both ends of the busbar line is 0.3mm, and the length is 5mm, and the middle part of the busbar line connects each segment The width of the thin line part is 0.3mm, and the length is 10.8mm. The segmented part adopts a rectangular hollow design, distributed in an array, with a pitch of 0.1mm and an offset angle of 30°.
[0025] 2) The thin grid lines are distributed equidistantly perpendicular to the main grid, the number of...
Embodiment 3
[0027] For a 156x156 size monocrystalline silicon cell, the electrode grid structure is designed as follows:
[0028] 1) The number of busbar lines is 3, which are distributed symmetrically around the center of the silicon wafer. The distance between the three busbar lines is 52mm. The busbar lines are divided into 8 sections, which are alternately connected by thin lines. The width is 1.4mm and the length is 8mm; the width a of the thin lines at both ends of the busbar is 0.3mm and the length is 5mm; Adopt rectangular hollow design, array distribution, pitch 0.1mm, offset angle 30°.
[0029] 2) Thin grid lines 2 are distributed parallel to the vertical main grid lines at equal intervals, the number of thin grid lines is 90, the width of the thin grid lines is 0.05mm, and the distance between the grid lines is 1.54mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com