Method for producing microcrystal glass ceramics composite board
A technology of glass-ceramic ceramics and production technology, which is applied in the field of inorganic material production, can solve the problem of pattern patterns without three-dimensional layering, etc., and achieves the effects of high quality product rate, simple and stable process, and continuous texture transition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] (1) Stamping to form adobe
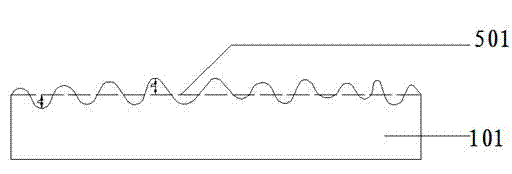
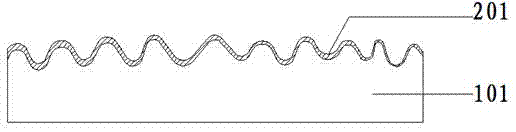
[0046] In this step, the conventional formula in the ceramic production technology can be selected. That is to say, feldspar, quartz, clay, talc and other conventional raw materials are used as raw materials. After ball milling, iron removal, and stale homogenization, they are spray-dried in a spray drying tower to make powder. The moisture content of the powder is 3-7%. ;Through the reverse punching distribution system (the reverse punching is the distribution method in which the upper surface of the adobe is under the punching), after the distribution, it is sent to the press for stamping to form the adobe. The mold cavity of the stamping die has a concave-convex pattern, and the distance d between the protrusions and depressions of the concave-convex pattern and the reference plane of the mold cavity is 0.22 to 1.1mm (the mold coefficient for ceramic production is about 1.1). After stamping, the upper surface of the adobe also has a conc...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0059] 1. The concave-convex pattern formed on the surface of the adobe in step (1) is similar to natural rosin jade with radial and needle-like crystal cleavage, and the distance d between the protrusions and depressions of the concave-convex pattern and the reference plane of the mold cavity is 0.55~1.1mm;
[0060] 2. The printing pattern in step (2) is similar to natural rosin jade corresponding to step 1, with radial and needle-like crystal cleavage patterns, and the color is mainly brown coffee;
[0061] 3. The primary firing temperature in step (3) is 1230°C, and the firing cycle is 100 minutes;
[0062] 4. The secondary firing temperature in step (5) is 1110°C, and the firing cycle is 110 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that before distributing the glass-ceramic frit in step (4), the frit particles containing the blue long-lasting fluorescent material are randomly scattered, which makes the frit particles after the second firing The products have as attached Figure 6 cross-sectional structure. Among them, 601 contains a luminous area formed by frit particles of blue-based long-lasting fluorescent materials.
[0065] In the above process, the particle size of the frit containing the blue long-lasting fluorescent material is 3-30 mesh, and the dosage is 20-50 g / piece.
[0066] When the product changes from bright to dark in the external environment, the long-lasting fluorescent material releases and absorbs photon energy, and some areas on the surface of the product have a light blue brilliance, which complements the pattern of the printing layer and complements each other, like a bright galaxy, with stars looming.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com