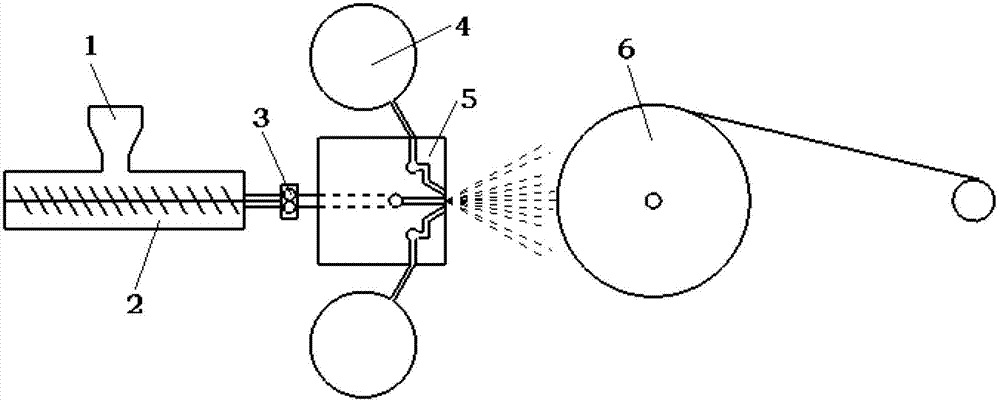
Meltblown mold head for preparing ultrafine fibers
A melt-blown die and ultra-fine fiber technology, which is applied in the field of melt-blown nonwovens, can solve the problems of difficult processing of the pointed die, increase the processing cost, and the tip end is easily damaged, so as to reduce the processing cost and reduce the processing cost. difficulty, and the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
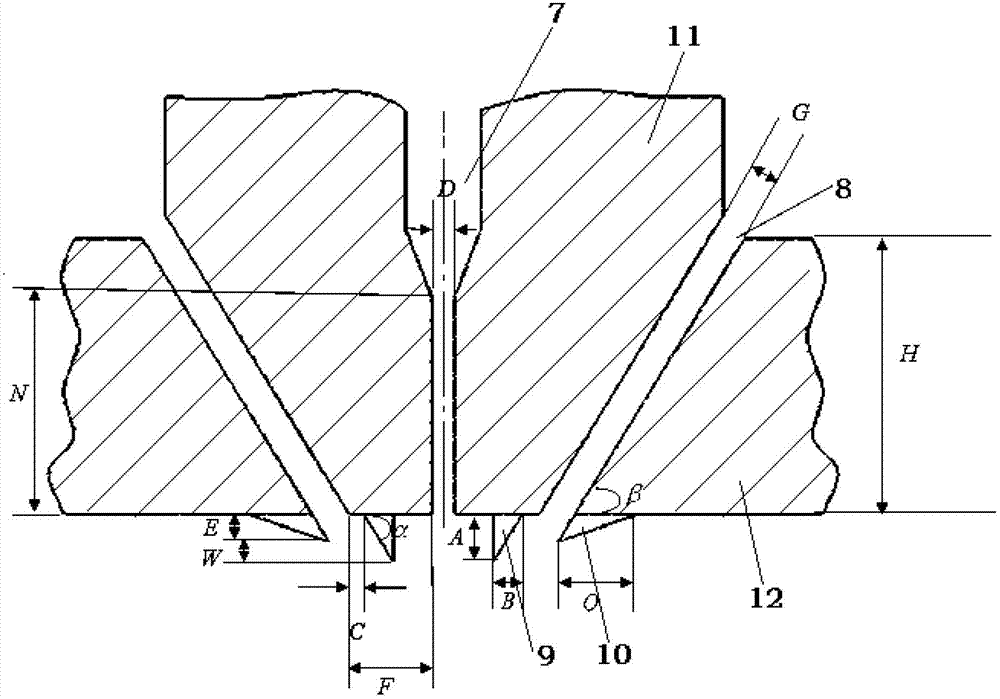
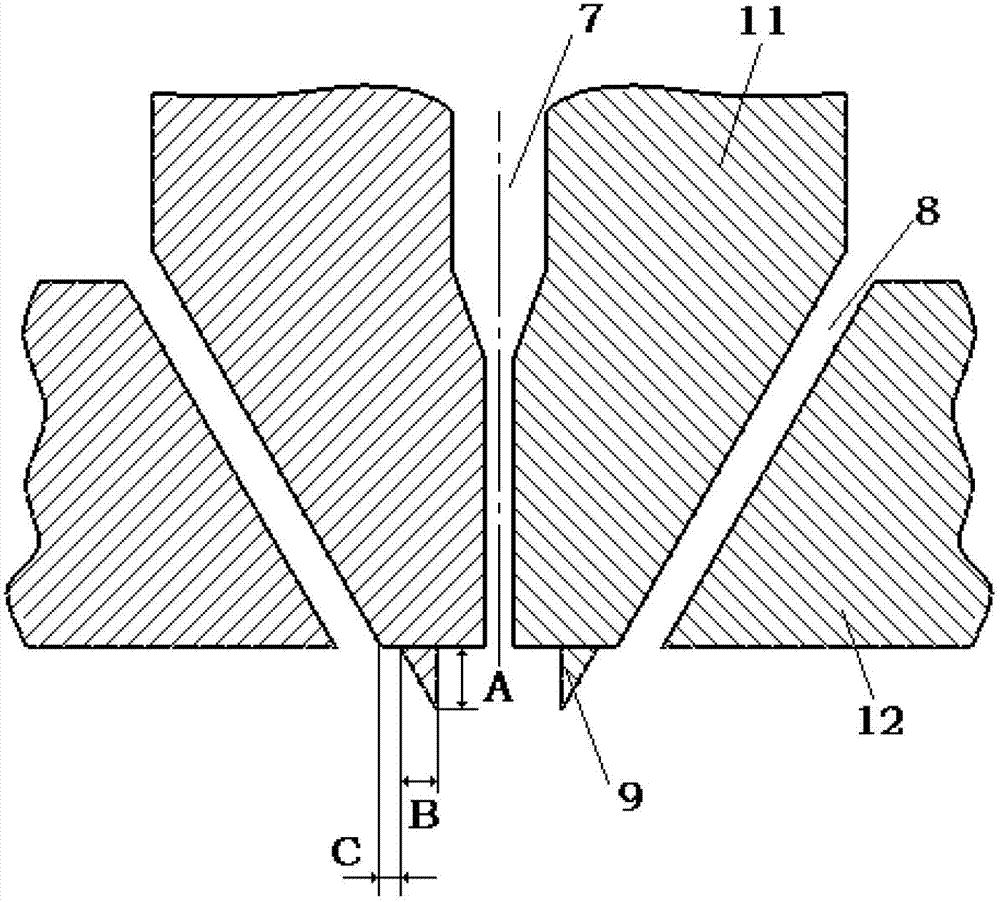
[0085] The new die head structure is attached image 3 Shown in: A=0.59mm, C=0mm, α=60°, β=60°, G=0.65mm, H=5mm, N=4mm, D=0.4mm, E=0mm and F=0 .65mm. The die head adopts continuous double-groove holes, and the length Q of the flow stabilizer is equal to the width P of the die head. The other dimensions of the double-groove blunt die used for comparison are the same. Spinning conditions: hot air temperature is 230°C, melt temperature is 270°C, air pressure at the inlet end of the air tank is 0.3atm; spinning raw material is polypropylene, melting temperature is about 170°C, and melt index is 1800. The specific experimental results are shown in Table 1.
[0086] Table 1 Experimental Results I
[0087]
[0088] Note: d-average diameter of fibers prepared by the new die; △d-diameter reduction, that is, the average diameter reduction of fibers prepared by the new die compared to the blunt die; △v-velocity increment, that is, the new die The maximum difference in spee...
Embodiment 2
[0090] The new die head structure is attached image 3 Shown in: A=0.76mm, C=0mm, α=60°, β=60°, G=0.65mm, H=5mm, N=4mm, D=0.2mm, E=0mm and F= 0.65mm; the style of the stabilizer inside the air groove is as Figure 5 As shown, the length Q of the stabilizer is equal to the width P of the die head. The other dimensions of the double-groove blunt die are the same. Spinning conditions: hot air temperature is 150 °C, melt heating temperature and spinning assembly temperature are both 210 °C, air pressure at the inlet end of the air tank is 0.2 atm; spinning raw material is low melting point multi-component copolyamide, melting temperature is about 120°C, the melt index is 35. The experimental results are shown in Table 2.
[0091] Table 2 Experimental Results II
[0092]
Embodiment 3
[0094] New die structure such as figure 2 Shown: A=0.76mm, C=0mm, α=60°, β=60°, G=0.65mm, H=5mm, N=4mm, D=0.2mm, E=0.76mm, O =2mm and F=0.6mm; Figure 5 As shown, the length Q of the stabilizer is equal to the width P of the die head. The other dimensions of the double-groove blunt die are the same. Spinning conditions: hot air temperature is 190°C, melt heating temperature and spinning assembly temperature are both 230°C, air pressure at the inlet end of the air tank is 0.5atm; spinning raw material is polyurethane, and the melting temperature is about 160°C °C, the melt index is 1200. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.
[0095] Table 3 Experimental Results III
[0096]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com