Method for labeling escherichia coli proteome by using SILAC (Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Cultures) and special culture medium
A technology of Escherichia coli and culture medium, applied in the fields of peptide preparation methods, microorganism-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of hindering the progress of Escherichia coli quantitative proteomics, lack of labeling methods, etc., and achieve the elimination of genetic conditions. The effect of limiting, eliminating tedious steps, and efficient marking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
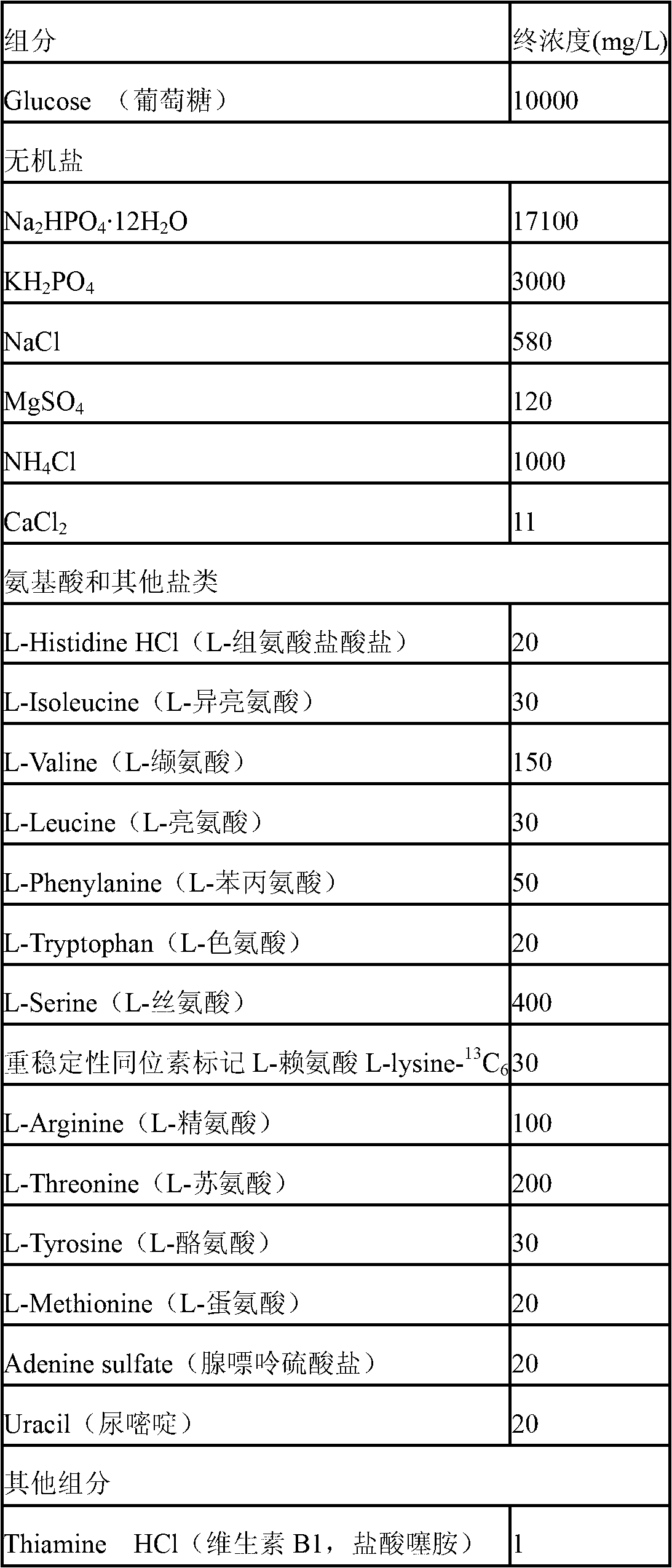
[0049] Embodiment 1, SILAC marker Escherichia coli special culture medium
[0050] Table 1 is the composition of the special medium for SILAC-labeled Escherichia coli
[0051]
[0052] Remarks: Inorganic reagents are ordinary analytical pure domestic reagents, light-labeled amino acids were purchased from Amresco Company in the United States, L-lysine- 13 C 6 Purchased from American CIL Company, article number: CNLM-291-0.25.
[0053] According to the above-mentioned components and their final concentrations, prepare with ultrapure water to obtain a special medium for SILAC-labeled Escherichia coli. Inorganic salts and glucose are sterilized by autoclaving, and amino acids and vitamins are sterilized by filtration.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2, the application of SILAC marker Escherichia coli special medium
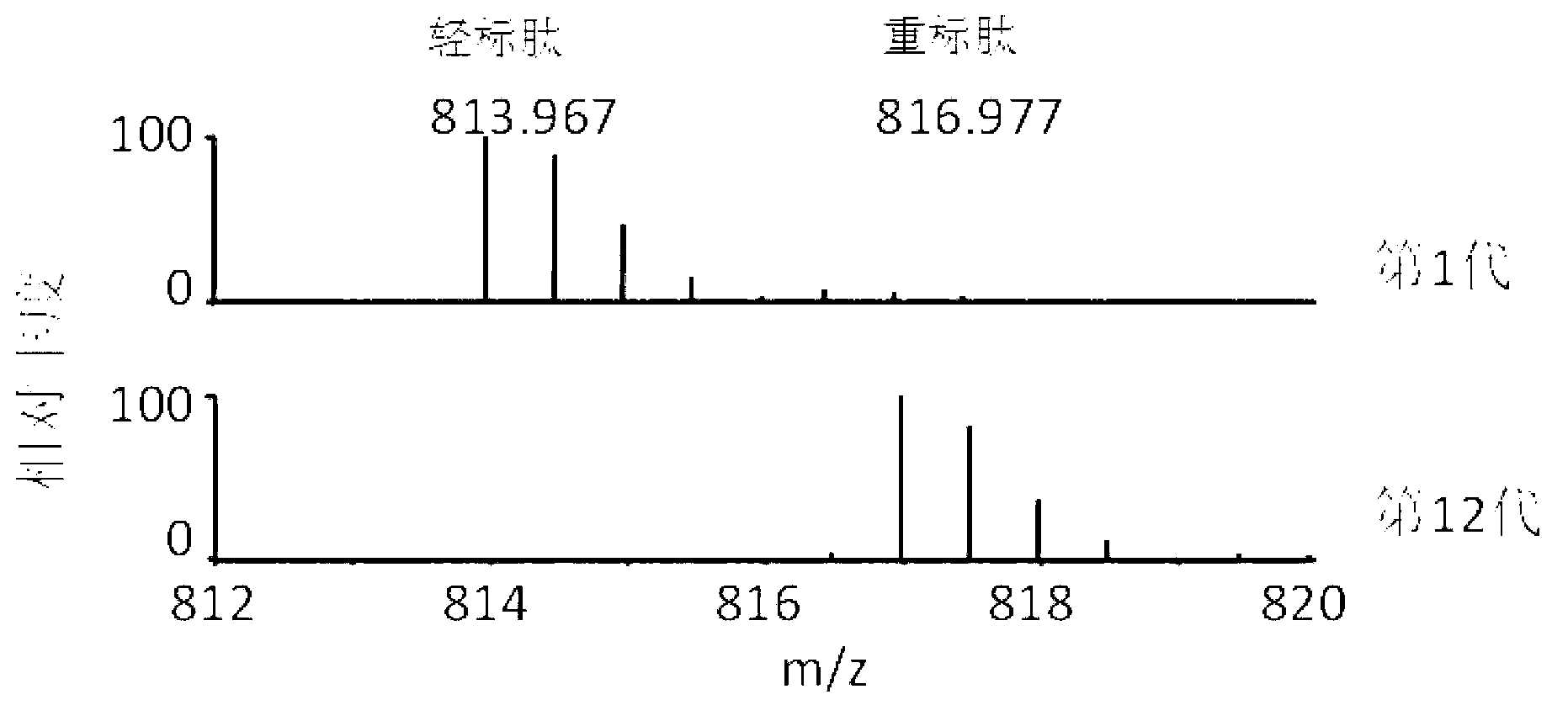
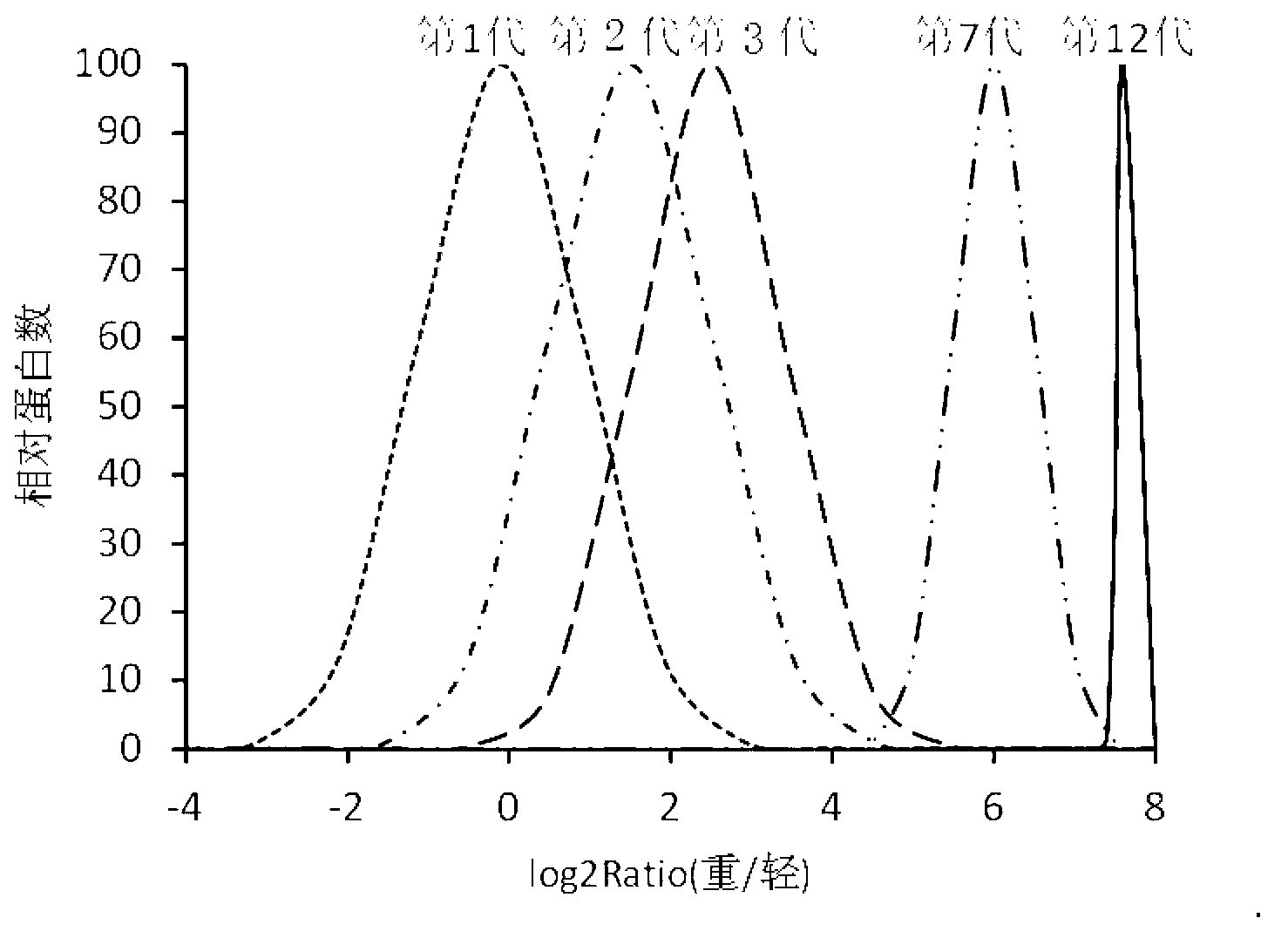
[0055] 1. SILAC-labeled E. coli special medium to mark E. coli
[0056] 1. SILAC mark
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com