One kind of magnetic resonance imaging developers and two-photon imaging developers and preparation method thereof
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and two-photon imaging, which is applied in the preparation methods of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc., and can solve the problems of high preparation difficulty, difficult targeting, and low cellular uptake rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
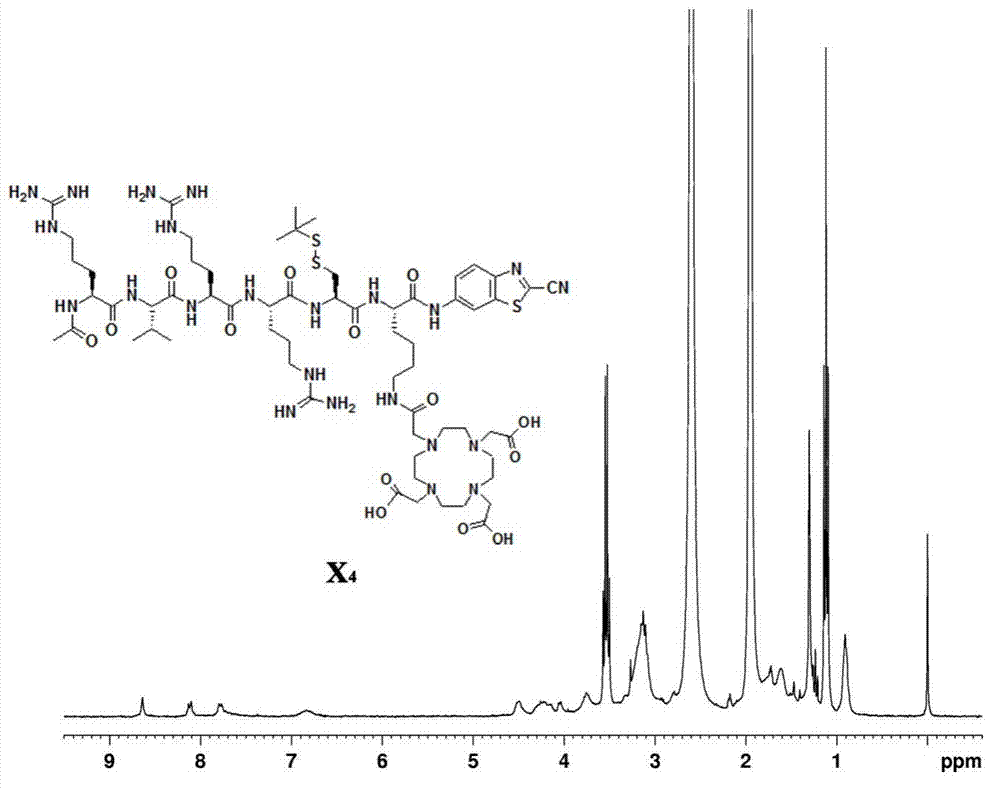
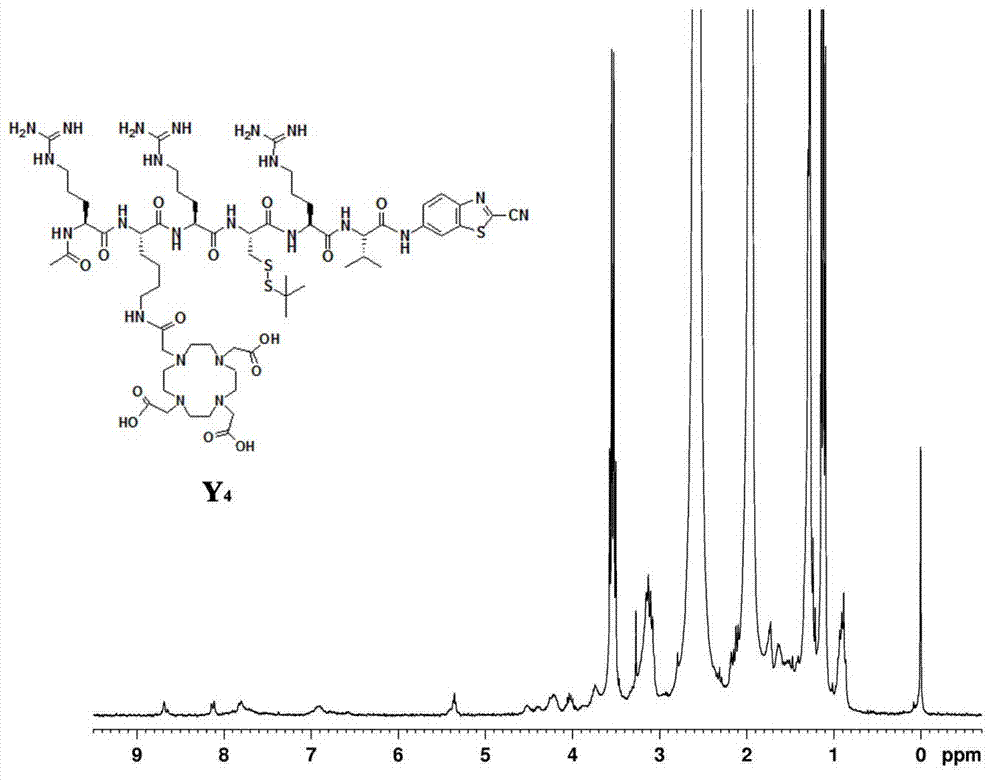
[0042] The final product A of the first compound in this embodiment 1 The synthetic route of is as follows:
[0043]
[0044] First, the lysine-cysteine-arginine-arginine-valine-arginine peptide is synthesized, and the specific steps are as follows: 0.33 mmol of 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin in 2 After eight minutes of swelling in mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, 0.66 mmol of the first amino acid N-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-N'-tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-lysine was added to the reactor Add 0.66 mmol N,N-diisopropylethylamine, react for two hours, react with 30 microliters of methanol for 20 minutes, cut off the first amino acid protecting group, Kaiser test shows blue, add activated 0.55 Millimoles of the second amino acid cysteine was reacted for two hours, and the Caesar test showed yellow, and the protective group was cut off, and the Caesar test was blue, and 0.55 mmol of activated third amino acid arginine was added to react for three hours, Caesar The test shows yellow, the ...
Embodiment 2
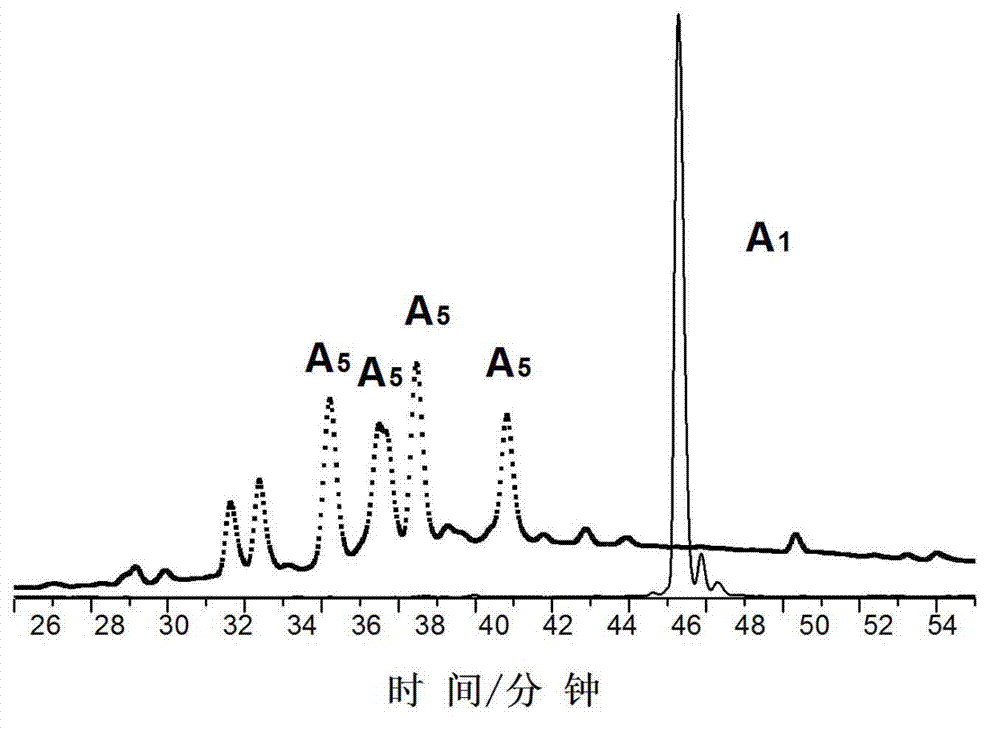
[0083] Example 2: Final product A of the first compound 1 In vitro verification experiment of condensation reaction
[0084] What adopted in this embodiment in vitro experiment is the final product A of the first compound 1 At a concentration of 100 μmol / L, in a total volume of 100 mmol / L 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid buffer, 1 mmol / L trichloroethyl phosphate, 1 mmol / L calcium chloride, and 5 μL of furin Incubate 100 μL of solution at 30°C for 17 hours to condense into dimers and self-assemble into nanoparticles.
[0085] Figure 5 The final product A of the first compound in this example is given 1 Transmission electron microscopy characterization of in vitro condensation-formed nanoparticles; Image 6 Be the final product A of the first compound in embodiment 2 1 UV absorption at 500-700nm before and after in vitro digestion.
[0086] in Figure 5 It is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) characterization of the nanoparticles prepared by the method ...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: Verifying the occurrence of condensation reactions at the cellular level
[0088] Firstly, human malignant breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468 was cultured, and the specific operation was as follows: the malignant breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468 was cultured in DMEM high-glucose medium containing 10% bovine serum albumin by volume, and the cells were cultured in The concentration is 5% CO 2 Cultured in a 37°C incubator in an air environment, and the medium was changed once a day.
[0089] Observe the slices of cells and compounds cultured by transmission electron microscope photos, the specific operation is as follows: the malignant breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468 cells are planted in two 6 cm culture dishes, about 6 million cells, on the top The stated volume concentration is 5% CO 2 After culturing in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C in an air environment for 12 hours, add the final product A of the first compound to the two plates of cells r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com