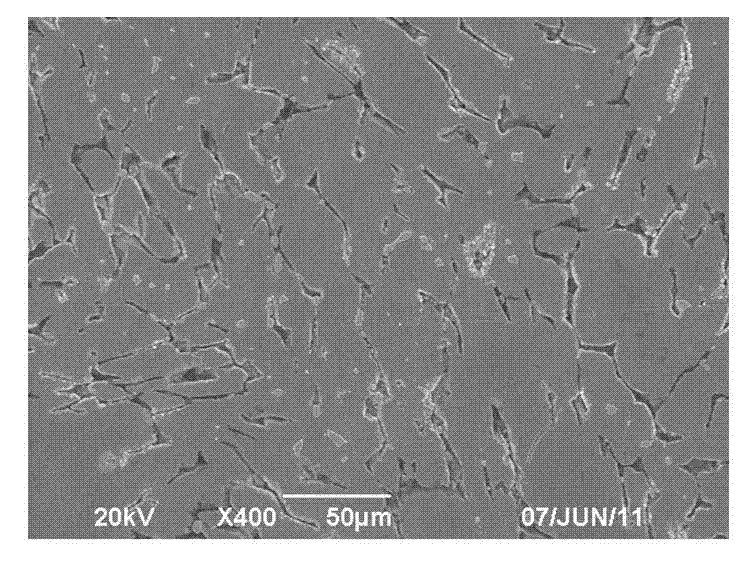
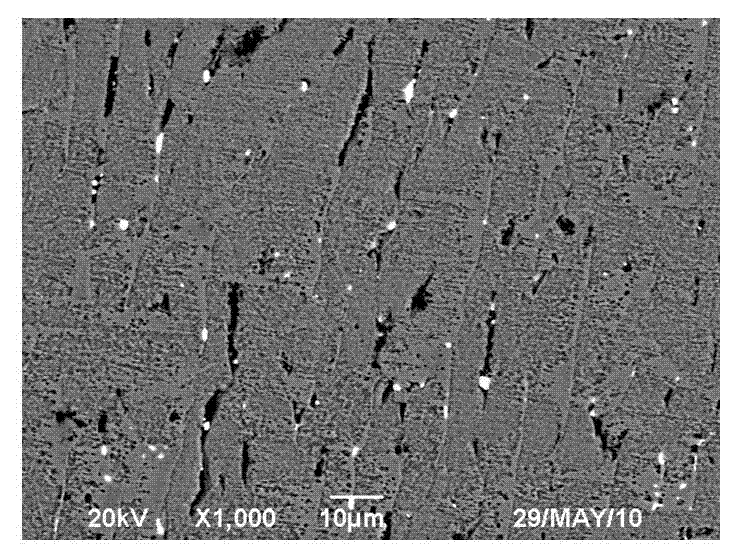
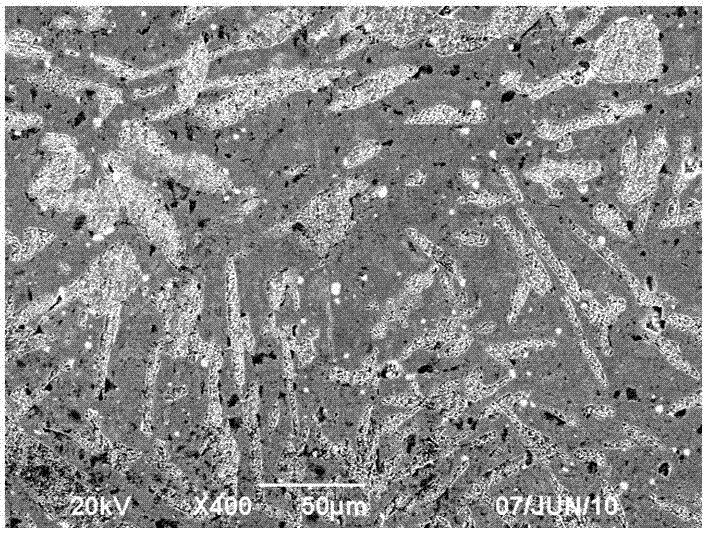
Lead-free free-cutting brass alloy and preparation method thereof
A brass alloy, free-cutting technology, applied in the field of lead-free free-cutting brass alloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of high cost and complicated production process, and achieve the effects of low cost, cost reduction and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Select Cu99.9% industrial pure copper and customized copper-zinc master alloy, copper-bismuth master alloy, copper-manganese master alloy, copper-lanthanum master alloy, and recycled nickel-plated tin copper plate scraps as raw materials, of which copper-zinc master alloy The zinc content in the alloy is 56.01%, the bismuth content in the copper-bismuth master alloy is 19.91%, the manganese content in the copper-manganese master alloy is 25.32%, the lanthanum content in the copper-lanthanum master alloy is 24.95%, and the tin content in the nickel-tin-plated copper plate is 14.10% , The nickel content is 9.20%. Calculate and weigh raw materials according to the weight percentage of the formula range: 25g Cu-Bi master alloy, 50g copper-manganese master alloy, 50g nickel-tin-plated copper plate, 5g Cu-RE master alloy, 600g Cu-Zn master alloy, 420g pure copper. Melt the weighed raw materials in a high-frequency induction heating furnace. First, put the copper-manganese int...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Choose Cu99.9% industrial pure copper and customized copper-zinc, copper-bismuth, copper-manganese, copper-lanthanum master alloys, as well as recycled nickel-plated tin copper plate scraps as raw materials, of which the zinc content in the copper-zinc master alloy 56.01%, the bismuth content in the copper-bismuth master alloy is 19.91%, the manganese content in the copper-manganese master alloy is 25.32%, the lanthanum content in the copper-lanthanum master alloy is 24.95%, the tin content in the nickel-plated tin copper plate is 14.10%, and the nickel content is 9.20%. Calculate and weigh raw materials according to the weight percentage of the formula range: 50g Cu-Bi master alloy, 75g Cu-Mn master alloy, 100g nickel-plated tin copper plate, 10g Cu-RE master alloy, 650g Cu-Zn master alloy, 265g pure copper. Melt the weighed raw materials in a high-frequency induction heating furnace. First, put the copper-manganese intermediate alloy and pure copper into ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 : Select Cu99.9% industrial pure copper and customized copper-zinc, copper-bismuth, copper-manganese, copper-lanthanum master alloys, as well as recycled nickel-plated tin-copper scraps as raw materials, of which the zinc in the copper-zinc master alloy content of 56.01%, the content of bismuth in copper-bismuth master alloy is 19.91%, the content of manganese in copper-manganese master alloy is 25.32%, the content of lanthanum in copper-lanthanum master alloy is 24.95%, the content of tin in nickel-plated tin copper plate is 14.10%, and the content of nickel 9.20%. Calculate and weigh the raw materials according to the weight percentage of the formula range: 75g Cu-Bi master alloy, 100g Cu-Mn master alloy, 150g nickel-tin-plated copper plate, 15g Cu-RE master alloy, 700g Cu-Zn master alloy, 110g pure copper. Melt the weighed raw materials in a high-frequency induction heating furnace. First, put the copper-manganese intermediate alloy and pure copper into t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com